深入学习java源码之Math.sin()与 Math.sqrt()
深入学习java源码之Math.sin()与 Math.sqrt()
native关键字
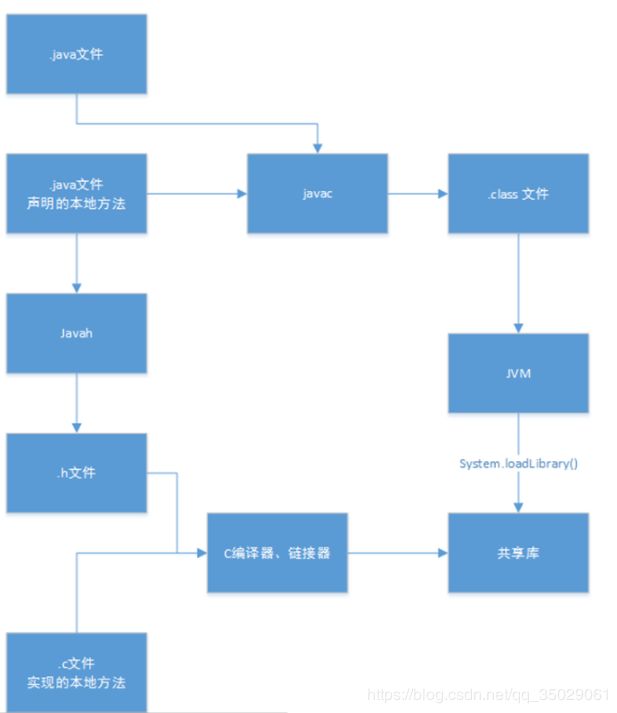
凡是一种语言,都希望是纯。比如解决某一个方案都喜欢就单单这个语言来写即可。Java平台有个用户和本地C代码进行互操作的API,称为JNI
native关键字告诉编译器(其实是JVM)调用的是该方法在外部定义,这里指的是C。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
static double |
acos(double a) 返回值的反余弦值; 返回的角度在0.0到pi的范围内。 |
static int |
addExact(int x, int y) 返回其参数的总和,如果结果溢出int,则抛出 |
static long |
addExact(long x, long y) 返回其参数的总和,如果结果溢出long,则抛出 |
static double |
asin(double a) 返回值的正弦值; 返回角度在pi / 2到pi / 2的范围内。 |
static double |
atan(double a) 返回值的反正切值; 返回角度在pi / 2到pi / 2的范围内。 |
static double |
atan2(double y, double x) 返回从直角坐标(转换角度 theta |
static double |
cbrt(double a) 返回 |
static double |
ceil(double a) 返回大于或等于参数的最小(最接近负无穷大) |
static double |
copySign(double magnitude, double sign) 使用第二个浮点参数的符号返回第一个浮点参数。 |
static float |
copySign(float magnitude, float sign) 使用第二个浮点参数的符号返回第一个浮点参数。 |
static double |
cos(double a) 返回角度的三角余弦。 |
static double |
cosh(double x) 返回的双曲余弦 |
static double |
exp(double a) 返回欧拉的数字 e提高到一个 |
static double |
expm1(double x) 返回 e x -1。 |
static double |
hypot(double x, double y) 返回sqrt( x 2 + y 2 ),没有中间溢出或下溢。 |
static double |
log(double a) 返回的自然对数(以 e为底) |
static double |
log10(double a) 返回一个 |
static double |
log1p(double x) 返回参数和1的和的自然对数。 |
static double |
pow(double a, double b) 将第一个参数的值返回到第二个参数的幂。 |
static double |
random() 返回值为 |
static double |
rint(double a) 返回与参数最接近值的 |
static long |
round(double a) 返回参数中最接近的 |
static int |
round(float a) 返回参数中最接近的 |
static double |
sin(double a) 返回角度的三角正弦。 |
static double |
sinh(double x) 返回的双曲正弦 |
static double |
sqrt(double a) 返回的正确舍入正平方根 |
static double |
tan(double a) 返回角度的三角正切。 |
static double |
tanh(double x) 返回的双曲正切 |
static double |
ulp(double d) 返回参数的ulp的大小。 |
static float |
ulp(float f) 返回参数的ulp的大小。 |
java源码
public final class Math {
private Math() {}
public static final double E = 2.7182818284590452354;
public static final double PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
public static double sin(double a) {
return StrictMath.sin(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double cos(double a) {
return StrictMath.cos(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double tan(double a) {
return StrictMath.tan(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double asin(double a) {
return StrictMath.asin(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double acos(double a) {
return StrictMath.acos(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double atan(double a) {
return StrictMath.atan(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double exp(double a) {
return StrictMath.exp(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double log(double a) {
return StrictMath.log(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double log10(double a) {
return StrictMath.log10(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double sqrt(double a) {
return StrictMath.sqrt(a); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
// Note that hardware sqrt instructions
// frequently can be directly used by JITs
// and should be much faster than doing
// Math.sqrt in software.
}
public static double cbrt(double a) {
return StrictMath.cbrt(a);
}
public static double IEEEremainder(double f1, double f2) {
return StrictMath.IEEEremainder(f1, f2); // delegate to StrictMath
}
public static double atan2(double y, double x) {
return StrictMath.atan2(y, x); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double pow(double a, double b) {
return StrictMath.pow(a, b); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
}
public static double sinh(double x) {
return StrictMath.sinh(x);
}
public static double cosh(double x) {
return StrictMath.cosh(x);
}
public static double tanh(double x) {
return StrictMath.tanh(x);
}
public static double hypot(double x, double y) {
return StrictMath.hypot(x, y);
}
public static double expm1(double x) {
return StrictMath.expm1(x);
}
public static double log1p(double x) {
return StrictMath.log1p(x);
}
}
public final class StrictMath {
private StrictMath() {}
public static final double E = 2.7182818284590452354;
public static final double PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
public static native double sin(double a);
public static native double cos(double a);
public static native double tan(double a);
public static native double asin(double a);
public static native double acos(double a);
public static native double atan(double a);
public static strictfp double toRadians(double angdeg) {
// Do not delegate to Math.toRadians(angdeg) because
// this method has the strictfp modifier.
return angdeg / 180.0 * PI;
}
public static strictfp double toDegrees(double angrad) {
// Do not delegate to Math.toDegrees(angrad) because
// this method has the strictfp modifier.
return angrad * 180.0 / PI;
}
public static native double exp(double a);
public static native double log(double a);
public static native double log10(double a);
public static native double sqrt(double a);
public static native double cbrt(double a);
public static native double IEEEremainder(double f1, double f2);
public static native double atan2(double y, double x);
public static native double pow(double a, double b);
public static native double sinh(double x);
public static native double cosh(double x);
public static native double tanh(double x);
public static native double hypot(double x, double y);
public static native double expm1(double x);
public static native double log1p(double x);
}