MySQL基础系列(二)--DQL语句
目录
SELECT介绍
语法:
特点:
用法:
案例:
一、基础查询
二、条件查询
三、排序查询
自我测试:
SELECT介绍
-
语法:
-
SELECT column_name,column_name FROM table_name [WHERE Clause] [LIMIT N] [ OFFSET M] - 类似于:System.out.println()
-
-
特点:
- 查询列表可以是:表中的字段、常量值、表达式、函数
- 查询的结果是一个虚拟的表格
-
用法:
- 查询表中的单个字段
- select name from student;
- 查询表中的多个字段
- select id,name from student
- 查询表中的所有字段
- select id,name,age from student;
- select * from student;
- 查询常量值
- select 100;
- select 'john';
- 查询表达式
- select 100*98;
- 查询函数
- select version();
- 为字段或者常量等起别名
- 方式一:as
- select 100*98 as result;
- select name as 姓名,age as 年龄 from student;
- 方式二:空格
- select name 姓名,age 年龄 from student;
- 特例:如果别名有特殊符号,如空格,#等,需要将别名用双引号括起来------select name "姓 名" from student;
- 作用:
- 便于理解
- 如果要查询的字段有重名的情况,使用别名可以区分开来
- 方式一:as
- 去重
- select distinct name from student;
- +号的作用:
- MySQL的+号只有一个作用:运算符
- select 100+90; 两个操作数都为数值型,做加法运算
- select '123'+90; 其中一方为字符型,则试图将字符型转位数值型,转换成功就继续做加法运算
- select 'john'+90; 转换失败则将字符型转换为0
- select null+10; 只要其中一方为null,结果肯定为null
- 字符串拼接:concat(str1,str2,....);
- select concat(last_name,first_name) as name from employees;
- MySQL的+号只有一个作用:运算符
- 查询表中的单个字段
案例:
一、基础查询
显示出学生表中的全部id,且不重复
select distinct id from student;
二、条件查询
条件查询:根据条件过滤原始表的数据,查询到想要的数据 语法:
select 要查询的字段|表达式|常量值|函数 from 表 where 条件 ;
条件分类:
一、条件表达式
示例:
select * from employees where salary>12000;条件运算符: > < >= <= = != <>
二、逻辑表达式
示例:
select * from employees where salary>10000 && salary<=12000;
逻辑运算符:用于连接条件表达式
and(&&):两个条件如果同时成立,结果为true,否则为false
or(||):两个条件只要有一个成立,结果为true,否则为false
not(!):如果条件成立,则not后为false,否则为true
三、模糊查询
关键字:like、between and、in、is null、is not null
like:
特点:
-
一般和多个通配符搭配使用
- 通配符:
-
- %:任意多个字符,包含0个字符
- _:任意单个字符
-
- 通配符:
示例1:查询员工名中包含a的员工信息
select * from employees where last_name like '%a%';
示例2:查询员工名中第三个字符为e,第五个字符为a的员工名和工资
select concat(first_name,last_name) name,salary
from employees where concat(first_name,last_name) like '__e_a%';
示例3:查询员工名中第八个字符为_的员工名
解释:concat(first_name,last_name) like '_\_'(表明后面的下划线不做通配符)
在这里如果没有明确指定转义字符,默认的转义字符是反斜杠"\",也可以通过escape自己定义转义字符,例如: concat(first_name,last_name) like '_$_' escape '$'。
select concat(first_name,last_name) name from employees
where concat(first_name,last_name) like '_______\_%';
或select concat(first_name,last_name) name from employees
where concat(first_name,last_name) like '_______$_%' escape '$';
between and:
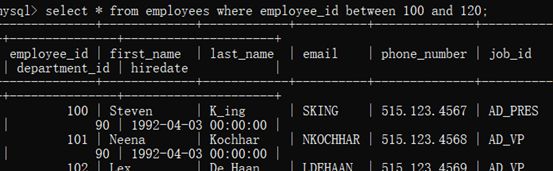
示例:查询id在100到120之间的员工信息
select * from employees where id between 100 and 120;
in:
解释:判断某字段的值是否是in列表中的一项,in列表的值类型必须一致或兼容。
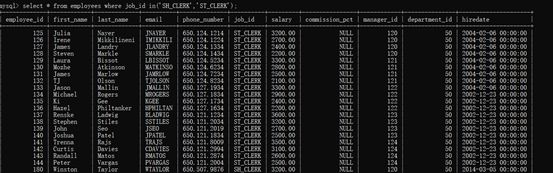
示例:查询表中职位id是SH_CLERK或ST_CLERK的员工信息
select * from employees where job_id in('SH_CLERK','ST_CLERK');
is (not) null:(=不能用于判断null值)
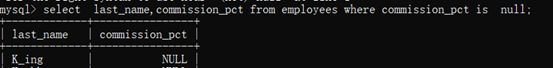
示例1:查询提成为null的员工的姓名和提成。
select last_name,commission_pct from employees where commission_pct is null;
示例2:查询提成不为null的员工和提成
select last_name,commission_pct from employees where commission_pct is not null;
安全等于<=>:既可以判断null值,又可以判断普通的数值
示例1: 查询表中员工提成为null的姓名和提成
select last_name,commission_pct from employees where commission_pct <=> null;
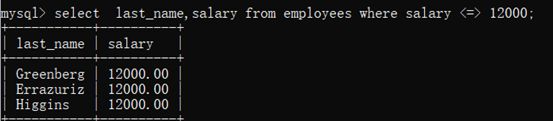
示例2: 查询表中员工提成为12000的姓名和提成
select last_name,salary from employees where salary <=> 12000;
三、排序查询
语法:
select
要查询的东西
from
表
where
条件
order by 排序的字段|表达式|函数|别名 【asc|desc】特点:
- ASC为升序,DESC为降序,如果不写,则默认为升序
- order by 子句中可以支持单个字段、多个字段、表达式、函数、别名
- order by 一般放在查询语句的最后面(limit子句放在其后面)
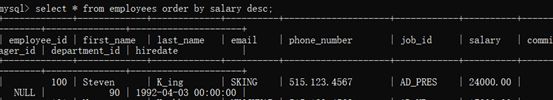
示例1:查询员工信息,要求工资从高到低排序【降序】
select * from employees order by salary desc; //从高到低
示例2:查询部门编号大于等于90的员工信息,按入职时间的先后进行排序【升序】
select * from employees where employee_id>=90
order by hiredate asc; 或select * from employees
where employee_id>=90 order by hiredate;
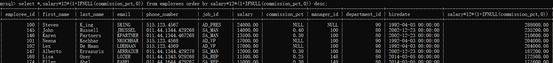
示例3:按年薪的高低显示员工的信息【按照表达式排序】
select *,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0))
from employees order by salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) desc;
示例4:按年薪的高低显示员工的信息【按照别名排序】
select *,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) yearsalary
from employees order by yearsalary desc;
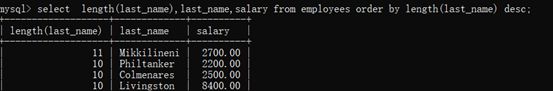
示例5:按姓名的长度显示员工的姓名和工资【按函数排序】
select length(last_name),last_name,salary from employees order by length(last_name) desc;
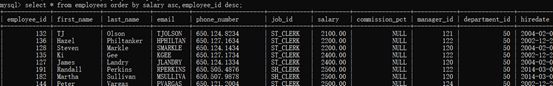
示例6:查询员工信息,要求先按工资升序,再按员工编号降序【按多个字段排序】
select * from employees order by salary asc,employee_id desc;
解释:总体是按照工资升序,当工资一样时,按照员工编号排序。(理解这里就可以容易理解3个或3个以上字段同时排序的结果)
自我测试:
1. 查询员工的姓名和部门号和年薪,按年薪降序 按姓名升序
2. 选择工资不在 8000 到 17000 的员工的姓名和工资,按工资降序
3. 查询邮箱中包含 e 的员工信息,并先按邮箱的字节数降序,再按部门号升序
答案:
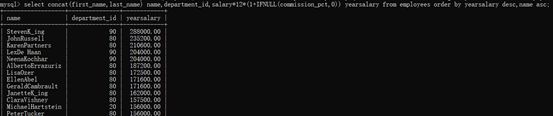
1、
select concat(first_name,last_name) name,department_id,
salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) yearsalary from
employees order by yearsalary desc,name asc;
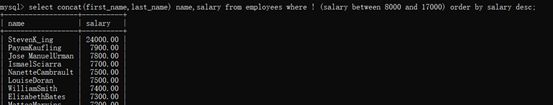
2、
select concat(first_name,last_name) name,salary from employees
where ! (salary between 8000 and 17000) order by salary desc;
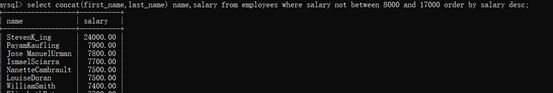
或select concat(first_name,last_name) name,salary from employees
where salary not between 8000 and 17000 order by salary desc;
3、
select *,length(email) from employees
where email like '%e%' order by length(email) desc,department_id asc;
注:本篇博客基于尚硅谷的视频所做,基本覆盖了DQL语句的所有用法,由于编译器问题,可能布局有些问题,可以通过看我的有道云笔记链接获得更好的体验,此外,本篇博客的SQL文件也在有道云笔记中
有道云笔记链接:http://note.youdao.com/noteshare?id=0d4ebce123d6baca0dafabf0b0f853ed&sub=2DCFDC450AC24D889713B9AE3DD4D7B0