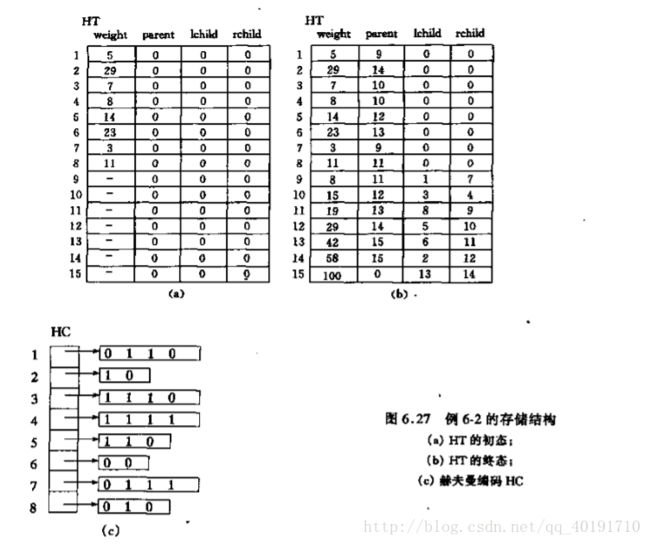
第六章-树(6)赫夫曼树
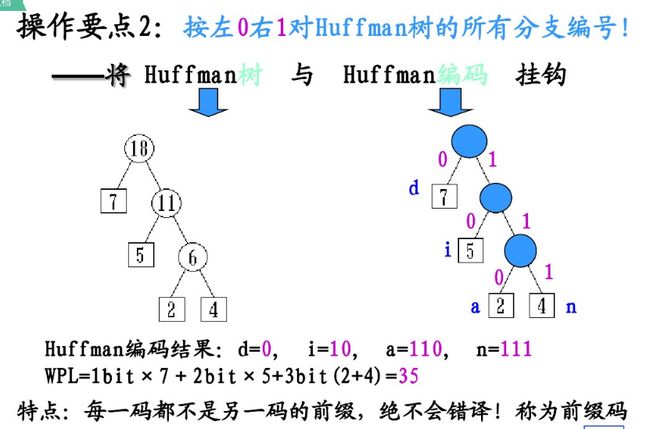
赫夫曼编码的基本思想是:概率大的字符用短码,概率小的用长码。
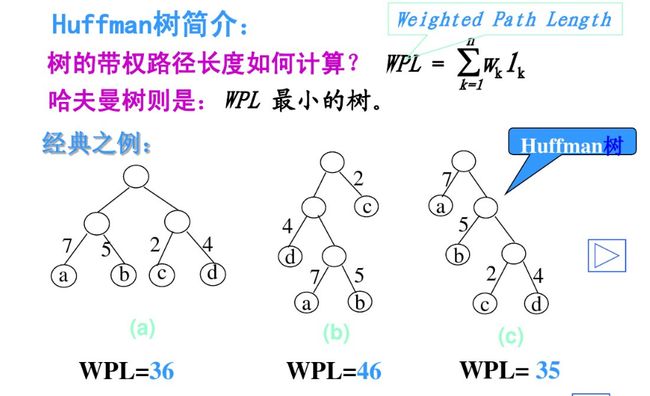
由于赫夫曼树的WPL最小,说明编码所需的比特数最小。
这种编码已经广泛应用于网络通信中。
构建赫夫曼树和赫夫曼编码:
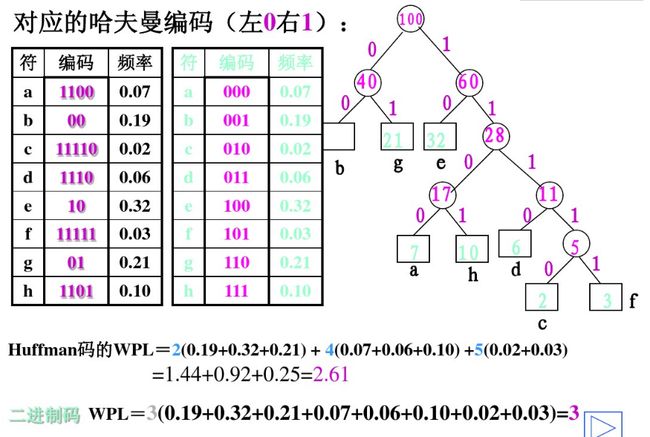
出现的字符:
',','a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','g','k','l','m','n','o','p','q','4','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z'
字符出现的概率:
187,64,13,22,32,103,21,15,47,57,1,5,32,20,57,63,15,1,48,51,80,23,8,13,1,16,1
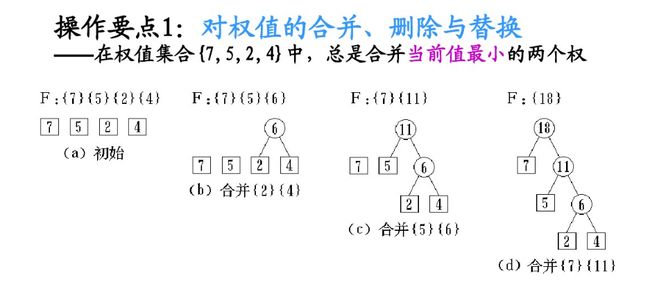
构建赫夫曼树和赫夫曼编码的方法:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//设字符集为26个英文字符,其出现频度如下表所示,要求编程实现
#include
#include
#define MaxValue 10000
#define MaxBit 10
#define MaxN 100
typedef struct{ //赫夫曼树的结点结构
int weight;
int flag;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
}HTNode,*HuffmanTree;
typedef struct{
unsigned int bit[MaxN];
int strat;
int weight;
}Code;
//构造赫夫曼树的算法
void HuffmanCoding(int weight[],int n,HTNode HT[]){
int i,j,m1,m2,x1,x2;
if(n<=1) return;
for(i=0;i<2*n-1;i++){ //初始化每一个结点的值
if(istrat=n-1;
cd->weight=HT[i].parent;
child=i;
parent=HT[child].parent;
while(parent!=-1){
if(HT[parent].lchild==child)
cd->bit[cd->strat]=0;
else
cd->bit[cd->strat]=1;
cd->strat--;
child=parent;
parent=HT[child].parent;
}
for(j=cd->strat+1;jbit[j];
HTCode[i].strat=cd->strat+1;
HTCode[i].weight=cd->weight;
}
}
void main(){
int i,j,k,n=27;
char s[]={',','a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','g','k','l','m','n','o','p','q','4','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z'};
int weight[]={187,64,13,22,32,103,21,15,47,57,1,5,32,20,57,63,15,1,48,51,80,23,8,13,1,16,1};
HTNode *myHaffTree=(HTNode *)malloc(sizeof(HTNode)*(2*n+1));
Code *myHaffCode=(Code *)malloc(sizeof(Code)*n);
if(n>MaxN)
{
printf("给出 n 越界,修改McxN");
exit(0);
}
HuffmanCoding(weight,n,myHaffTree);
HaffCode(myHaffTree,n,myHaffCode);
for(i=0;i 编码的方法有两种,一种是从叶子到根,一种是从根到叶。
与编码与之对应的就是译码了。
赫夫曼树编码的设计过程:
代码转自他人,只供交流学习。