⑭HTML5 canvas的一系列使用方法(2)
Html5
- 使用图片&设置背景
- 渐变效果
- 绘制文本
- 例:canvas中 文本水平垂直居中
- 阴影(文本阴影&盒模型阴影)
- 像素操作
- 例:操作单个像素(行与列)
- 例:给图片加上马赛克
- 合成
- 其他用法
本人是个新手,写下博客用于自我复习、自我总结。
如有错误之处,请各位大佬指出。
学习资料来源于:尚硅谷
使用图片&设置背景
在canvas中插入图片(需要image对象):
1.canvas操作图片时,必须要等图片加载完才能操作
2.drawImage(image, x, y, width, height)
其中 image 是 image 或者 canvas 对象,x 和 y 是其在目标 canvas 里的起始坐标。width 和 height,这两个参数用来控制 当canvas画入时应该缩放的大小。
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
body {
background: pink;
}
#test {
background: gray;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="test" width="300" height="300">
<span>您的浏览器不支持画布元素span>
canvas>
body>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
var img = new Image();
// 指定图片路径
img.src = "tg.png";
img.onload = function () {
draw();
}
function draw() {
ctx.drawImage(img, 0, 0, img.width, img.height)
}
}
}
script>
html>
在canvas中设置背景(需要image对象):
createPattern(image, repetition)
image:图像源
epetition有以下几个选项:
“repeat”
“repeat-x”
“repeat-y”
“no-repeat”
一般情况下,我们都会将createPattern返回的对象作为fillstyle的值
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
var img = new Image();
img.src = "tg.png";
img.onload = function () {
draw();
}
function draw() {
var pattern = ctx.createPattern(img, "no-repeat")
ctx.fillStyle = pattern;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 300, 300);
}
}
}
渐变效果
canvas线性渐变
createLinearGradient(x1, y1, x2, y2)
表示渐变的起点 (x1,y1) 与终点 (x2,y2)
gradient.addColorStop(position, color)
gradient : createLinearGradient的返回值
addColorStop 方法接受 2 个参数,
position 参数必须是一个 0.0 与 1.0 之间的数值,表示渐变中颜色所在的相对位置。
例如,0.5 表示颜色会出现在正中间。
color 参数必须是一个有效的 CSS 颜色值(如 #FFF, rgba(0,0,0,1))
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
var gradient = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 200, 200);
gradient.addColorStop(0, "red");
gradient.addColorStop(0.5, "yellow");
gradient.addColorStop(0.7, "black");
gradient.addColorStop(1, "green");
ctx.fillStyle = gradient;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 300, 300);
}
}
canvas径向渐变
createRadialGradient(x1, y1, r1, x2, y2, r2)
前三个参数则定义另一个以(x1,y1) 为原点,半径为 r1 的圆,
后三个参数则定义另一个以 (x2,y2) 为原点,半径为 r2 的圆。
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
var gradient = ctx.createRadialGradient(150, 150, 50, 150, 150, 100)
gradient.addColorStop(0, "red");
gradient.addColorStop(0.5, "yellow");
gradient.addColorStop(0.7, "pink");
gradient.addColorStop(1, "green");
ctx.fillStyle = gradient;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 300, 300);
}
}
绘制文本
canvas 提供了两种方法来渲染文本:
fillText(text, x, y)
在指定的(x,y)位置填充指定的文本
strokeText(text, x, y)
在指定的(x,y)位置绘制文本边框
需要说明的是,文本样式 font 默认的字体是 10px sans-serif。
font属性在指定时,必须要有大小和字体 缺一不可。
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = "green"
ctx.font = "40px sans-serif"
ctx.fillText("csdn", 100, 100);
ctx.strokeText("csdn", 100, 100);
}
}
textAlign
文本对齐选项。可选的值包括:
left:文本左对齐。
right:文本右对齐。
center:文本居中对齐。
这里的textAlign="center"比较特殊。textAlign的值为center时候:
文本的居中是基于你在fillText的时候所给的x的值,也就是说文本一半在x的左边,一半在x的右边
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = "green";
ctx.font = "40px sans-serif";
ctx.textAlign = "center";
ctx.fillText("csdn", 50, 50);
}
}
textBaseline
描述绘制文本时,当前文本基线的属性。
top
文本基线在文本块的顶部。
middle
文本基线在文本块的中间。
bottom
文本基线在文本块的底部。
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = "green";
ctx.font = "40px sans-serif";
ctx.textBaseline = "middle";
ctx.fillText("csdn", 0, 0);
}
}

measureText
measureText() 方法返回一个 TextMetrics 对象,包含关于文本尺寸的信息(例如文本的宽度)
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = "green";
ctx.font = "60px sans-serif";
ctx.fillText("csdn", 50, 50);
var obj = ctx.measureText("csdn");
console.log(obj);
}
}
例:canvas中 文本水平垂直居中
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
background: black;
}
#c1 {
background: white;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="c1" width="400" height="400">canvas>
body>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function () {
var oC = c1;
var oGC = oC.getContext('2d');
oGC.font = '60px impact';
oGC.textBaseline = 'middle';
var w = oGC.measureText('CSDN').width;
oGC.fillText('CSDN', (oC.width - w) / 2, (oC.height - 60) / 2);
};
script>
html>
阴影(文本阴影&盒模型阴影)
shadowOffsetX shadowOffsetY
shadowOffsetX 和 shadowOffsetY 用来设定阴影在 X 和 Y 轴的延伸距离,
它们默认都为 0。
shadowBlur
shadowBlur 用于设定阴影的模糊程度,其数值并不跟像素数量挂钩,也不受变换矩阵的影响,默认为 0。
shadowColor(必需项)
shadowColor 是标准的 CSS 颜色值,用于设定阴影颜色效果,默认是全透明的黑色。
window.onload = function () {
var oC = c1;
var oGC = oC.getContext('2d');
//文本阴影&盒阴影
oGC.shadowOffsetX = 20;
oGC.shadowOffsetY = 20;
oGC.shadowBlur = 30;
oGC.shadowColor = "yellow";
oGC.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
};
像素操作
在canvas中的像素操作:
到目前为止,我们尚未深入了解Canvas画布真实像素的原理,事实上,你可以直接通过ImageData对象操纵像素数据,直接读取或将数据数组写入该对象中
getImageData() 获得一个包含画布场景像素数据的ImageData对象,它代表了画布区域的对象数据。
ctx.getImageData(sx, sy, sw, sh)
sx:将要被提取的图像数据矩形区域的左上角 x 坐标。
sy:将要被提取的图像数据矩形区域的左上角 y 坐标。
sw:将要被提取的图像数据矩形区域的宽度。
sh:将要被提取的图像数据矩形区域的高度。
ImageData对象中存储着canvas对象真实的像素数据,它包含以下几个只读属性:
width:图片宽度,单位是像素
height:图片高度,单位是像素
data:Uint8ClampedArray类型的一维数组,
包含着RGBA格式的整型数据,范围在0至255之间(包括255)
R:0 --> 255(黑色到白色)
G:0 --> 255(黑色到白色)
B:0 --> 255(黑色到白色)
A:0 --> 255(透明到不透明)
putImageData()方法去对场景进行像素数据的写入。
putImageData(myImageData, dx, dy)
dx和dy参数表示你希望在场景内左上角绘制的像素数据所得到的设备坐标
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
/*imageData
width:横向上像素点的个数
height:纵向上像素点的个数
data:数组
每一个像素点的rgba信息
*/
// 100*100 10000个像素点
var imageData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, 100, 100);
for (var i = 0; i < imageData.data.length; i++) {
imageData.data[4 * i + 3] = 100;
}
ctx.putImageData(imageData, 0, 0)
}
}
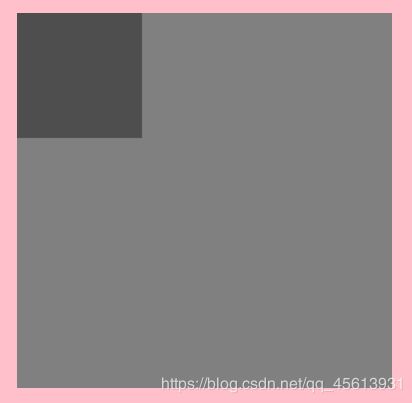
创建一个ImageData对象
ctx.createImageData(width, height);
width : ImageData 新对象的宽度。
height: ImageData 新对象的高度。
默认创建出来的是透明的
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
//默认创建出来 rgba(0,0,0,0)
var imageData = ctx.createImageData(100, 100);
for (var i = 0; i < imageData.data.length; i++) {
imageData.data[4 * i + 3] = 255;
}
ctx.putImageData(imageData, 100, 100)
}
}
例:操作单个像素(行与列)
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.save();
ctx.fillStyle = "pink";
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.fillRect(50, 50, 100, 100);
ctx.restore();
var imgdata = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
for (var i = 0; i < imgdata.width; i++) {
setPxInfo(imgdata, 30, i, [0, 0, 0, 255]);
}
ctx.putImageData(imgdata, 0, 0);
}
function getPxInfo(imgdata, x, y) {
var color = [];
var data = imgdata.data;
var w = imgdata.width;
var h = imgdata.height;
//r
color[0] = data[(y * w + x) * 4];
//g
color[1] = data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 1];
//b
color[2] = data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 2];
//a
color[3] = data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 3];
return color;
}
function setPxInfo(imgdata, x, y, color) {
var data = imgdata.data;
var w = imgdata.width;
var h = imgdata.height;
//(x,y) x:多少列 y:多少行
//r
data[(y * w + x) * 4] = color[0];
//g
data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 1] = color[1];
//b
data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 2] = color[2];
//a
data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 3] = color[3];
}
}
例:给图片加上马赛克
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
#msk {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate3d(-50%, -50%, 0);
}
style>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="msk">canvas>
body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var oc = msk;
if (oc.getContext) {
var ctx = oc.getContext("2d");
var img = new Image();
img.src = "left01.jpg";
img.onload = function () {
oc.width = img.width;
oc.height = img.height;
draw();
}
function draw() {
ctx.drawImage(img, 0, 0);
var oldImgdata = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, img.width, img.height);
var newImgdata = ctx.createImageData(img.width, img.height);
//马赛克
/*
1.选取一个马赛克矩形
2.从马赛克矩形中随机抽出一个像素点的信息(rgba)
3.将整个马赛克矩形中的像素点信息统一调成随机抽出的那个
*/
//选取一个马赛克矩形
var size = 5;
for (var i = 0; i < oldImgdata.width / size; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < oldImgdata.height / size; j++) {
//Math.random() [0,1)
//Math.random()*size [0,5)
//Math.floor(Math.random()*size) [0,4]
//从马赛克矩形中随机抽出一个像素点的信息(rgba)
var color = getPxInfo(oldImgdata, i * size + Math.floor(Math.random() * size), j * size + Math.floor(Math.random() * size));
//将整个马赛克矩形中的像素点信息统一调成随机抽出的那个
for (var a = 0; a < size; a++) {
for (var b = 0; b < size; b++) {
setPxInfo(newImgdata, i * size + a, j * size + b, color)
}
}
}
}
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, oc.width, oc.height);
ctx.putImageData(newImgdata, 0, 0);
}
function getPxInfo(imgdata, x, y) {
var color = [];
var data = imgdata.data;
var w = imgdata.width;
var h = imgdata.height;
color[0] = data[(y * w + x) * 4];
color[1] = data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 1];
color[2] = data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 2];
color[3] = data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 3];
return color;
}
function setPxInfo(imgdata, x, y, color) {
var data = imgdata.data;
var w = imgdata.width;
var h = imgdata.height;
data[(y * w + x) * 4] = color[0];
data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 1] = color[1];
data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 2] = color[2];
data[(y * w + x) * 4 + 3] = color[3];
}
}
script>
html>
合成
全局透明度的设置globalAlpha
这个属性影响到 canvas 里所有图形的透明度,
有效的值范围是 0.0 (完全透明)到 1.0(完全不透明)
默认是 1.0
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = "red";
ctx.globalAlpha = .5;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
ctx.fillRect(100, 100, 100, 100);
}
}
覆盖合成
globalCompositeOperation的参数:
source-over(默认值):源在上面,新的图像层级比较高
source-in :只留下源与目标的重叠部分(源的那一部分)
source-out :只留下源超过目标的部分
source-atop:砍掉源溢出的部分
destination-over:目标在上面,旧的图像层级比较高
destination-in:只留下源与目标的重叠部分(目标的那一部分)
destination-out:只留下目标超过源的部分
destination-atop:砍掉目标溢出的部分
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = "pink";
ctx.fillRect(50, 50, 100, 100);
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "destination-atop";
ctx.fillStyle = "green";
ctx.fillRect(100, 100, 100, 100);
}
}
其他用法
将画布导出为图像toDataURL(注意是canvas元素接口上的方法)
window.onload = function () {
//拿到画布
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 199, 199);
var result = canvas.toDataURL();
console.log(result);
}
}
事件操作ctx.isPointInPath(x, y)
判断在当前路径中是否包含检测点
x:检测点的X坐标
y:检测点的Y坐标
注意,此方法只作用于最新画出的canvas图像
window.onload = function () {
var canvas = test;
if (canvas.getContext) {
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(100, 100, 50, 0, 360 * Math.PI / 180);
ctx.fill();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(200, 200, 50, 0, 360 * Math.PI / 180);
ctx.fill();
canvas.onclick = function (ev) {
ev = ev || event;
var x = ev.clientX - canvas.offsetLeft;
var y = ev.clientY - canvas.offsetTop;
if (ctx.isPointInPath(x, y)) {
alert(123);
}
}
}
}











