01.python基础知识快速入门
代码格式
强制缩进
- Python开发者有意让违反了缩进规则的程序不能通过编译,以此来强制程序员养成良好的编程习惯。并且Python语言利用缩进表示语句块的开始和退出(Off-side规则),而非使用花括号或者某种关键字。增加缩进表示语句块的开始,而减少缩进则表示语句块的退出。缩进成为了语法的一部分。
- 根据PEP的规定,必须使用4个空格来表示每级缩进。
基本语法
- 弱类型
- 变量必须先赋值再使用
- 小心引用
- 2和3的常见差异
- xrange
- 数据类型统一,取消unicode和long
- utf8: 3.x代码默认utf-8
# 变量必须先赋值再使用
a = 1234
print(a)
a = 'abcd'
print(a)
try:
print(b)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
#传值使用的是引用
a = [1, 2, 3 , 4]
def func(a):
a[0] = 2
func(a)
print(a)关键字
常量
True False None对象与容器
class import from del逻辑操作
and or not函数
def return判断与循环控制
if elif else is in assert for while continue break异常
raise try except finally with as作用域
global nonlocal匿名函数与协程
yield lambda
循环判断
- 注意加“:”
- 没有do-while循环
- 没有switch
- break是中断整个循环
- continue是结束本次迭代进入下一个
score = 80
if score > 90:
print('A')
elif score > 70:
print('B')
elif score >= 60:
print('C')
else:
print('D')
total = 0
i = 1
while i <= 100:
total += i
i += 1 # 没有++i或者--i
print(total)
'''
for循环只作用于容器!!!
没有这种写法:
for (i = 0; i < 100; ++i):
# TODO
上面这种循环只能用while实现
'''
i = 0
while i < 3:
j = 0
while j <= 3:
if j == 2:
j += 1
continue # 又去了while j <= 3
print(i, j)
j += 1
i += 1
函数
- def定义函数
- 默认参数
- 名字参数
- 函数也是对象
- 函数式编程简介:map/reduce/lambda
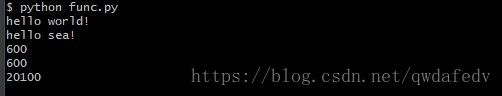
def hello(who = 'world'):
print('hello %s!' % (who))
hello()
hello('sea')
# f(x) = x * 5 + 100
# g(x) = x * 5; f(x) = x + 100
# => f(g(x)) = x * 5 + 100
def g(x):
return x * 5
def f(gf, x):
return gf(x) + 100
print(f(g, 100))
print(f(lambda x: x * 5, 100))
def f(gf, x, y):
return gf(x, y) + 100
print(f(lambda x, y: x * y, 100, 200))
容器
list:数组
# list就是数组
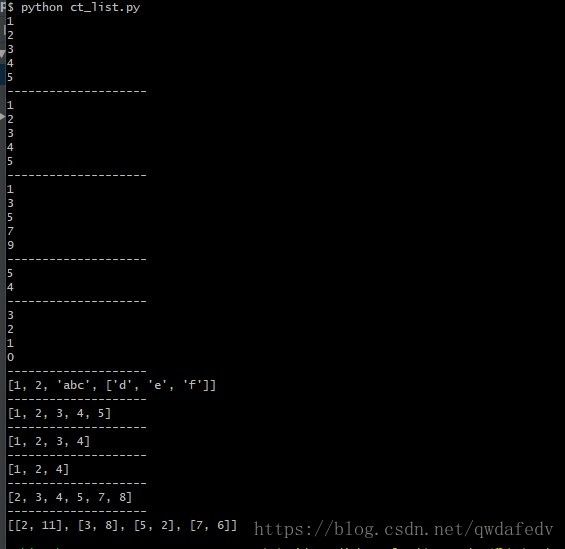
li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# 遍历
for i in li:
print(i)
print("--------------------")
# 用range模拟for (i = 0; i < x; ++i)
# range(x) => [0, x - 1]
# range(x, y) => [x, y - 1]
# range(x, y, z) => [x, x + z,..., < y]
for i in range(len(li)):
print(li[i])
print("--------------------")
for i in range(1, 10, 2):
print(i)
print("--------------------")
# 负数索引
print(li[-1])
print(li[-2])
print("--------------------")
# 负数step的range => [x, x - z, ..., > z]
for i in range(3, -1, -1):
print(i)
print("--------------------")
# 添加元素
li = []
li.append(1)
li.append(2)
li.append('abc')
li.append(['d', 'e', 'f'])
print(li)
print("--------------------")
# 按元素添加数组
li = [1, 2]
li_2 = [3, 4, 5]
# 我们想要[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# li.append(li_2) => [1, 2, [3, 4, 5]]
li.extend(li_2)
print(li)
print("--------------------")
# 删除元素
li.pop() # => [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(li)
print("--------------------")
li.pop(2) # => [1, 2, 4]
print(li)
print("--------------------")
li = [5, 8, 7, 4, 2, 3]
li.sort()
print(li)
print("--------------------")
# lambda帮助排序
li = [[5, 2], [3, 8], [2, 11], [7, 6]]
# li.sort(key = lambda x: x[0]) # 参数名字
# 与lamda等价写法
def item_key(x):
return x[0]
li.sort(key = item_key)
print(li)
tuple:只读数组
# 只读数组
tp = (1, 2, 3)
try:
tp[0] = 100
except Exception as e:
print(e)set:没有重复元素的数组
# 去重的数组
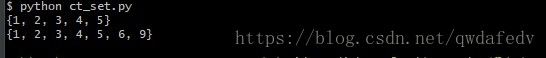
s = set([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5])
print(s)
s = set((2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2, 1, 9))
print(s)
dict:字典(哈希表)
# key<->value对应的hash表
di = {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'}
di['k3'] = 'v3'
di['k4'] = 'v4'
for k in di:
print(di[k])
for k, v in di.items():
print(k, v)
数组切片
# [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# => [1, 2, 3]
# => [3, 4]
li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
li_0_2 =li[0:3] # 0 <= ? < 3
# 等价li[:3]
print(li_0_2)
# [start, end, step] => [start, start + step, ..., < end]
# start默认是0,end默认-1,step默认1
li_last_3 = li[-1:-4:-1]
print(li_last_3)
# 直接用切片反转数组
print(li[::-1])
print(li[-2::-1])
# 切片是复制
li_0_2[-1] = 100
print(li)
字符串与数组的关系
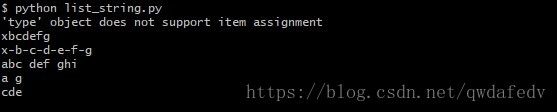
s = 'abcdefg'
try:
str[0] = 'x'
except Exception as e:
print(e)
# 修改字符串
li = list(s)
# print(li)
li[0] = 'x'
s = ''.join(li)
print(s)
s = '-'.join(li)
print(s)
# 切割
s = 'abc,def,ghi'
p1, p2, p3 = s.split(',')
print(p1, p2, p3)
# 下标访问和切片
s = 'abcdefg'
print(s[0], s[-1])
print(s[2:5])
面向对象
- 一切皆对象
- 获取对象信息:type和dir
- class声明对象
- 重要的self
- 继承与多态(什么是鸭子类型?)
# 用type查看对象类型
print(type([1, 2, 3, 4]))
print(type('abcd'))
print(type({1:2, 2:3}))
print("------------------")
# 用dir查看属性和方法
print(dir(list))
print("------------------")
class Clazz(object):
# self参考C++的this指针
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
# 声明成员函数的时候,第一个参数一定是self,不要忘记
def display(self):
print(self.x, self.y)
print(type(Clazz))
print("------------------")
clz = Clazz(100, 200)
clz.display() # => display(clz)
class Base:
def run(self):
print('Base::run')
class Tom(Base):
def run(self):
print('Tom::run')
t = Tom()
print(isinstance(t, Base))
print("------------------")
t.run()
# 鸭子类型
def run(runner):
runner.run()
class R1:
def run(self):
print('R1::run')
class R2:
def run(self):
print('R2::run')
run(R1())
run(R2())
文件读写
- 文本文件读写
with open('text.txt') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
print(line)with open('text.txt') as f:
while True:
line = f.readline()
if not line:
break
print(line)
- 二进制文件读写
with open('text.txt', 'rb') as f:
print(f.read())- string与bytes
s = 'abcdefg'
b = bytes(s)
print(b)- 文件和目录操作
import os
#遍历文件夹下的所有文件
for x in os.listdir("D:\\蚂蚁众包\\20180609"):
file_path = "%s\\%s"%("D:\\蚂蚁众包\\20180609",x)
#判断是否是文件夹
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
print(file_path,"is a dir.")
#判断是否是文件
elif os.path.isfile(file_path):
print(file_path,"is a file.")
else:
print(file_path,"is not a dir or file.")多线程
import threading
def thread_func(x):
# 自己加sleep和其它复杂操作看效果
print('%d\n' % (x * 100))
threads = []
for i in range(5):
threads.append(threading.Thread(target = thread_func, args = (100, )))
for thread in threads:
thread.start()
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
错误和异常处理
# 错误处理
import logging
try:
r = 10 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(type(e))
print(e)
finally:
# 主要防止资源泄露!
print('Always come here.')