Spring源码:@AliasFor JDK动态代理源码分析
目录
0. 源码参见
1. isSynthesizable判断是否需要被代理
2. SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler创建和执行逻辑
2.1 DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor
2.1.1 AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor构造函数
2.1.2 接口方法getAttributeValue
2.2 SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler执行逻辑
3. 创建JDK动态代理
我们在使用注解或者自定义注解时,有时经常看到在注解方法上标注注解@AliasFor,见名知义,这是一种为注解属性定义别名的注解实现方式,这样在不同的场合赋值不同的属性,但获取两个属性值时是一样的,这里的实现原理实际上也是JDK动态代理的过程,下面对该代理过程进行分析;
0. 源码参见
@AliasFor 具体工作机制源码参见AnnotationUtils.synthesizeAnnotation(A annotation, Object annotatedElement) 方法:
/**
* Synthesize an annotation from the supplied {@code annotation}
* by wrapping it in a dynamic proxy that transparently enforces
* attribute alias semantics for annotation attributes that are
* annotated with {@link AliasFor @AliasFor}.
* @param annotation the annotation to synthesize
* @param annotatedElement the element that is annotated with the supplied
* annotation; may be {@code null} if unknown
* @return the synthesized annotation if the supplied annotation is
* synthesizable; {@code null} if the supplied annotation is
* {@code null}; otherwise the supplied annotation unmodified
* @throws AnnotationConfigurationException if invalid configuration of
* {@code @AliasFor} is detected
* @since 4.2
* @see #synthesizeAnnotation(Map, Class, AnnotatedElement)
* @see #synthesizeAnnotation(Class)
*/
public static A synthesizeAnnotation(A annotation, AnnotatedElement annotatedElement) {
return synthesizeAnnotation(annotation, (Object) annotatedElement);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static A synthesizeAnnotation(A annotation, Object annotatedElement) {
if (annotation == null) {
return null;
}
if (annotation instanceof SynthesizedAnnotation) {
return annotation;
}
Class annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (!isSynthesizable(annotationType)) {
return annotation;
}
DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor attributeExtractor =
new DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor(annotation, annotatedElement);
InvocationHandler handler = new SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler(attributeExtractor);
// Can always expose Spring's SynthesizedAnnotation marker since we explicitly check for a
// synthesizable annotation before (which needs to declare @AliasFor from the same package)
Class[] exposedInterfaces = new Class[] {annotationType, SynthesizedAnnotation.class};
return (A) Proxy.newProxyInstance(annotation.getClass().getClassLoader(), exposedInterfaces, handler);
}这里的处理过程包含如下几步:
- 如果已经是SynthesizedAnnotation实现类,即已经是代理类,直接返回;
- isSynthesizable判断该注解是不是标注了@AliasFor注解,是否需要被代理;
- 创建SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler,这是一个InvocationHandler类,用于构造JDK动态代理
- 创建JDK动态代理
下面主要分析下2~4步;
1. isSynthesizable判断是否需要被代理
具体代码如下:
/**
* Determine if annotations of the supplied {@code annotationType} are
* synthesizable (i.e., in need of being wrapped in a dynamic
* proxy that provides functionality above that of a standard JDK
* annotation).
* Specifically, an annotation is synthesizable if it declares
* any attributes that are configured as aliased pairs via
* {@link AliasFor @AliasFor} or if any nested annotations used by the
* annotation declare such aliased pairs.
* @since 4.2
* @see SynthesizedAnnotation
* @see SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static boolean isSynthesizable(Class annotationType) {
Boolean synthesizable = synthesizableCache.get(annotationType);
if (synthesizable != null) {
return synthesizable;
}
synthesizable = Boolean.FALSE;
for (Method attribute : getAttributeMethods(annotationType)) {
if (!getAttributeAliasNames(attribute).isEmpty()) {
synthesizable = Boolean.TRUE;
break;
}
Class returnType = attribute.getReturnType();
if (Annotation[].class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
Class nestedAnnotationType =
(Class) returnType.getComponentType();
if (isSynthesizable(nestedAnnotationType)) {
synthesizable = Boolean.TRUE;
break;
}
}
else if (Annotation.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
Class nestedAnnotationType = (Class) returnType;
if (isSynthesizable(nestedAnnotationType)) {
synthesizable = Boolean.TRUE;
break;
}
}
}
synthesizableCache.put(annotationType, synthesizable);
return synthesizable;
}
这里主要判断依据分为两点:
- 该注解属性上直接标注了AliasFor注解;
- 属性返回值为注解类型且标注了AliasFor注解,该部分的解析是通过递归来解析的;
2. SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler创建和执行逻辑
在SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler构造时,首先创建了一个DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor,下面首先看一下该类的功能实现,然后再分析SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler的执行过程;
2.1 DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor
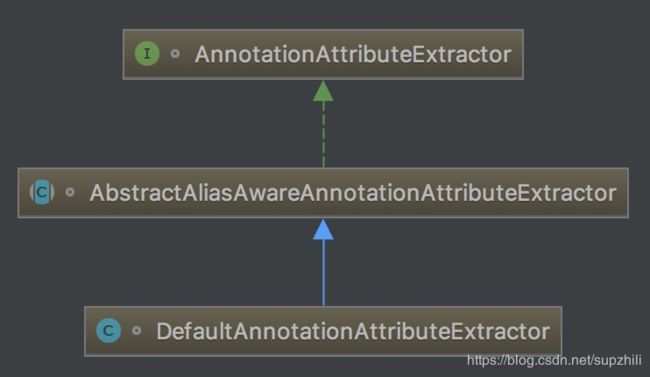
其继承结构类图如下:
接口AnnotationAttributeExtractor是一个注解属性提取器,主要用来获取注解的属性;
AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor实现了该接口,主要用于获取标注AliasFor注解的属性值;
DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor提供了实际获取属性值的反射调用方法;
在AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor抽象类中,核心逻辑都在构造函数以及getAttributeValue接口方法中,下面分别看下这两个方法的实现:
2.1.1 AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor构造函数
构造函数实现如下:
/**
* Construct a new {@code AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor}.
* @param annotationType the annotation type to synthesize; never {@code null}
* @param annotatedElement the element that is annotated with the annotation
* of the supplied type; may be {@code null} if unknown
* @param source the underlying source of annotation attributes; never {@code null}
*/
AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor(
Class annotationType, Object annotatedElement, S source) {
Assert.notNull(annotationType, "annotationType must not be null");
Assert.notNull(source, "source must not be null");
this.annotationType = annotationType;
this.annotatedElement = annotatedElement;
this.source = source;
this.attributeAliasMap = AnnotationUtils.getAttributeAliasMap(annotationType);
}最后一行用来获取原属性名和别名属性名之间的对应关系,具体不再展开,实际获取别名主要包含两个:
- 注解类直接包含了两个互为别名的属性;
- 注解类中两个属性的别名同为该注解元注解的某个属性,这样两个属性互为间接别名;
2.1.2 接口方法getAttributeValue
该接口方法主要获取直接属性值与所有别名属性值,并排除默认属性值之后,返回注解属性值,具体实现如下:
@Override
public final Object getAttributeValue(Method attributeMethod) {
String attributeName = attributeMethod.getName();
Object attributeValue = getRawAttributeValue(attributeMethod);
List aliasNames = this.attributeAliasMap.get(attributeName);
if (aliasNames != null) {
Object defaultValue = AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(this.annotationType, attributeName);
for (String aliasName : aliasNames) {
Object aliasValue = getRawAttributeValue(aliasName);
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, aliasValue) &&
!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, defaultValue) &&
!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(aliasValue, defaultValue)) {
String elementName = (this.annotatedElement != null ? this.annotatedElement.toString() : "unknown element");
throw new AnnotationConfigurationException(String.format(
"In annotation [%s] declared on %s and synthesized from [%s], attribute '%s' and its " +
"alias '%s' are present with values of [%s] and [%s], but only one is permitted.",
this.annotationType.getName(), elementName, this.source, attributeName, aliasName,
ObjectUtils.nullSafeToString(attributeValue), ObjectUtils.nullSafeToString(aliasValue)));
}
// If the user didn't declare the annotation with an explicit value,
// use the value of the alias instead.
if (ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, defaultValue)) {
attributeValue = aliasValue;
}
}
}
return attributeValue;
} 2.2 SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler执行逻辑
在接口方法invoke中,代理原目标方法,通过DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor获取属性值,这样就综合考虑了原属性值和别名属性值的作用,如下:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (ReflectionUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
return annotationEquals(args[0]);
}
if (ReflectionUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
return annotationHashCode();
}
if (ReflectionUtils.isToStringMethod(method)) {
return annotationToString();
}
if (AnnotationUtils.isAnnotationTypeMethod(method)) {
return annotationType();
}
if (!AnnotationUtils.isAttributeMethod(method)) {
throw new AnnotationConfigurationException(String.format(
"Method [%s] is unsupported for synthesized annotation type [%s]", method, annotationType()));
}
return getAttributeValue(method);
}
private Object getAttributeValue(Method attributeMethod) {
String attributeName = attributeMethod.getName();
Object value = this.valueCache.get(attributeName);
if (value == null) {
value = this.attributeExtractor.getAttributeValue(attributeMethod);
if (value == null) {
String msg = String.format("%s returned null for attribute name [%s] from attribute source [%s]",
this.attributeExtractor.getClass().getName(), attributeName, this.attributeExtractor.getSource());
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
// Synthesize nested annotations before returning them.
if (value instanceof Annotation) {
value = AnnotationUtils.synthesizeAnnotation((Annotation) value, this.attributeExtractor.getAnnotatedElement());
}
else if (value instanceof Annotation[]) {
value = AnnotationUtils.synthesizeAnnotationArray((Annotation[]) value, this.attributeExtractor.getAnnotatedElement());
}
this.valueCache.put(attributeName, value);
}
// Clone arrays so that users cannot alter the contents of values in our cache.
if (value.getClass().isArray()) {
value = cloneArray(value);
}
return value;
}3. 创建JDK动态代理
创建JDK动态代理还是通过Proxy.newProxyInstance来实现的,在目标接口中加入了SynthesizedAnnotation接口,该接口是一个marker接口,表示是否已经解析为代理对象;
Class[] exposedInterfaces = new Class[] {annotationType, SynthesizedAnnotation.class}; (A) Proxy.newProxyInstance(annotation.getClass().getClassLoader(), exposedInterfaces, handler);