Android输入子系统浅析(一)
Linux输入子系统框架
1:Input输入子系统总体框架
Linux内核的输入子系统是对分散的,多种不同类别的输入设备(如键盘,鼠标,触摸屏)等字符设备进行统一处理的一层抽象,就是在字符设备驱动上抽象出的一层。但是这些输入设备都各有不同,那么输入子系统也就只能实现他们的共性,差异性则由设备驱动来实现,而差异性最直观的表现在这些设备功能上的不同。但是,为了更好的理解Linux的输入子系统,我们有必要仔细研究下它的框架。
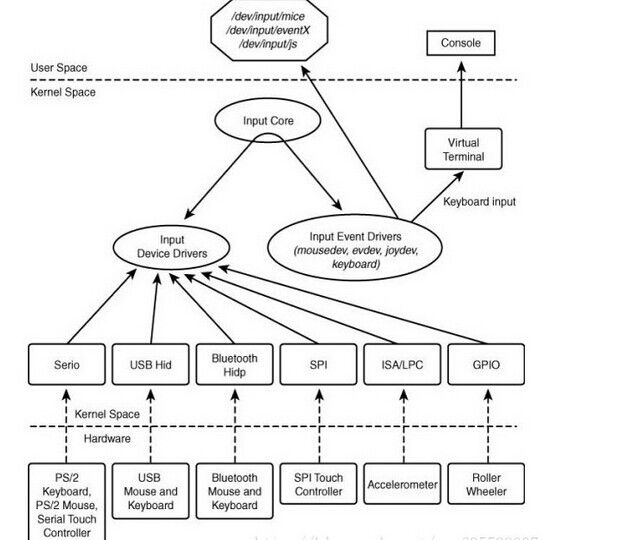
Linux输入子系统将输入驱动抽象为三层:设备驱动层、核心层、事件处理层,其内在联系如下图所示:
下面先对这三个部分做一个简要的概括,后面的分析也是基于这三个部分:
设备驱动层:主要实现对硬件设备的读写访问,中断设置,并把硬件产生的事件转换为核心层定义的规范提交给事件处理层
核心层:为设备驱动层提供了规范和接口。设备驱动层只关心如何驱动硬件并获得硬件数据,然后调用核心层提供的接口,核心层自动把数据提交给事件处理层
事件处理层:是用户编程的接口(设备节点),并处理驱动层提交的数据处理
本篇博文所述均是基于linux 3.4.5内核,android 4.2.2版本,硬件平台基于MT6589平台.
2:Input子系统分层分析
2.1:在分析这三部分之前,首先我们先看看input.h这个头文件,因为输入子系统的很多重要结构体都是在里面定义的。
路径:kernel/include/linux/input.h
重要结构体之input_dev:
struct input_dev {
const char *name; //设备名称
const char *phys; //设备在系统的物理路径
const char *uniq; //设备唯一识别符
struct input_id id; //设备ID,包含总线ID(PCI,USB)、厂商ID,与input_handler匹配时用到
unsigned long propbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(INPUT_PROP_CNT)]; //bitmap of device properties and quirks
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)]; //支持的所有 事件类型
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)]; //支持的键盘事件
unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)]; //支持的鼠标相对值事件
unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)]; //支持的鼠标绝对值事件
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)]; //支持的其他事件类型
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)]; //支持的led灯事件
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)]; //支持的声效事件
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)]; //支持的力反馈事件
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)]; //支持的开关事件
unsigned int hint_events_per_packet;
unsigned int keycodemax; //keycode表的大小
unsigned int keycodesize; //keycode表中的元素个数
void *keycode; //设备的键盘表
//配置keycode表
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_keymap_entry *ke,
unsigned int *old_keycode);
//获取keycode表
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
struct input_keymap_entry *ke);
struct ff_device *ff;
unsigned int repeat_key; //保存上一个键值
struct timer_list timer;//定时器
int rep[REP_CNT];
struct input_mt_slot *mt;
int mtsize;
int slot;
int trkid;
struct input_absinfo *absinfo;
unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
//操作接口
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
struct input_handle __rcu *grab; //当前使用的handle
spinlock_t event_lock;
struct mutex mutex;
unsigned int users;
bool going_away;
bool sync;
struct device dev;
struct list_head h_list; //h_list是一个链表头,用来把handle挂载在这个上
struct list_head node; //这个node是用来连到input_dev_list上的
};重要结构体之input_handler:
struct input_handler {
void *private; //私有数据
//操作接口
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);
const struct file_operations *fops;
int minor; //次设备号
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table;
struct list_head h_list; //h_list是一个链表头,用来把handle挂载在这个上
struct list_head node; //这个node是用来连到input_handler_list上的
};重要结构体之input_handle:
struct input_handle {
void *private; //私有数据
int open;
const char *name;
struct input_dev *dev; //指向input_dev
struct input_handler *handler; //指向input_handler
struct list_head d_node; //连到input_dev的h_list
struct list_head h_node; //连到input_handler的h_list
}; 重要结构体之evdev_client:
/*在进程打开event设备的时候调用evdev的open方法,在open中创建和初始化*/
struct evdev_client {
unsigned int head; //针对buffer数组的索引
unsigned int tail; //针对buffer数组的索引,当head和tail相等的时候,说明没事件
unsigned int packet_head; /* [future] position of the first element of next packet */
spinlock_t buffer_lock; /* protects access to buffer, head and tail */
struct wake_lock wake_lock;
bool use_wake_lock;
char name[28];
struct fasync_struct *fasync; //异步通知函数
struct evdev *evdev; //evdev设备
struct list_head node; //evdev_client链表项
int clkid;
unsigned int bufsize;
struct input_event buffer[]; //一个input_event数据结构的数组,input_event代表一个事件
}; 重要结构体之evdev:
/*evdev结构体在配对成功的时候生成,由handler_connect生成*/
struct evdev {
int open; //打开引用计数
int minor; //次设备号
struct input_handle handle; //关联的input_handle
wait_queue_head_t wait; //等待队列
struct evdev_client __rcu *grab;
struct list_head client_list; //evdev_client链表,说明一个evdev设备可以处理多个evdev_client,可以有多个进程访问
spinlock_t client_lock; /* protects client_list */
struct mutex mutex;
struct device dev;
bool exist;
}; /*
* Event types
*/
#define EV_SYN 0x00 //同步时间
#define EV_KEY 0x01 //绝对二进制值,如键盘或者按钮
#define EV_REL 0x02 //绝对结果,如鼠标设备
#define EV_ABS 0x03 //绝对整数值,如TP,操纵杆
#define EV_MSC 0x04 //其他类
#define EV_SW 0x05 //开关事件
#define EV_LED 0x11 //led或其他指示设备
#define EV_SND 0x12 //声音输出,如蜂鸣器
#define EV_REP 0x14 //允许按键重复
#define EV_FF 0x15 //力反馈
#define EV_PWR 0x16 //电源管理
#define EV_FF_STATUS 0x17
#define EV_MAX 0x1f
#define EV_CNT (EV_MAX+1)2.2:input输入子系统的核心层input.c
路径:kernel/drivers/input/input.c
//先分析入口函数:input_init(void)
static int __init input_init(void)
{
int err;
//创建一个input_class类
err = class_register(&input_class);
if (err) {
pr_err("unable to register input_dev class\n");
return err;
}
//在/proc下创建入口项
err = input_proc_init();
if (err)
goto fail1;
//注册主设备号为INPUT_MAJOR(13)的设备,并与input_fops关联
err = register_chrdev(INPUT_MAJOR, "input", &input_fops);
if (err) {
pr_err("unable to register char major %d", INPUT_MAJOR);
goto fail2;
}
return 0;
fail2: input_proc_exit();
fail1: class_unregister(&input_class);
return err;
}static const struct file_operations input_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = input_open_file, //主要分析这个Open函数
.llseek = noop_llseek,
};static int input_open_file(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct input_handler *handler;
const struct file_operations *old_fops, *new_fops = NULL;
//......省略部分内容
//根据打开的文件次设备号来得到一个input_handler结构
handler = input_table[iminor(inode) >> 5];
//通过handler得到新的file_operations结构体
if (handler)
new_fops = fops_get(handler->fops);
//......省略部分内容
//保存文件之前的f_op
old_fops = file->f_op;
//将新的f_op赋值给当前文件的f_op
file->f_op = new_fops;
//调用open函数,当应用程序打开文件时会调用这个函数
err = new_fops->open(inode, file);
if (err) {
fops_put(file->f_op);
file->f_op = fops_get(old_fops);
}
fops_put(old_fops);
}static struct input_handler *input_table[8]; //定义
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
//......省略部分内容
if (handler->fops != NULL) {
if (input_table[handler->minor >> 5]) {
retval = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
input_table[handler->minor >> 5] = handler;
}
//......省略部分内容
}由上可知,input_table在input_register_handler()被赋值为handler。而input_register_handler()函数是在事件处理层中调用的,在2.3中我们会对其进行具体分析。当用户空间调用open时,实际上调用的就是handler fops中的open函数,而这个函数是在evdev.c中定义的,下面我们先看看这个open函数的实现(位于evdev.c中):
static int evdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct evdev *evdev;
struct evdev_client *client;
int i = iminor(inode) - EVDEV_MINOR_BASE;
unsigned int bufsize;
int error;
if (i >= EVDEV_MINORS) //判断是否超出了能处理的最大设备数
return -ENODEV;
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&evdev_table_mutex);
if (error)
return error;
evdev = evdev_table[i]; //得到evdev设备结构,每次调用evdev_connect配对成功后都会把分配的evdev结构体以minor为索引保存在evdev_table中
if (evdev)
get_device(&evdev->dev); //增加device引用计数
mutex_unlock(&evdev_table_mutex);
if (!evdev)
return -ENODEV;
bufsize = evdev_compute_buffer_size(evdev->handle.dev);
//分配用户端结构
client = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev_client) +
bufsize * sizeof(struct input_event),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_put_evdev;
}
client->bufsize = bufsize;
spin_lock_init(&client->buffer_lock);
snprintf(client->name, sizeof(client->name), "%s-%d",
dev_name(&evdev->dev), task_tgid_vnr(current));
client->evdev = evdev; //使用户端与evdev设备结构关联起来
evdev_attach_client(evdev, client); //把client链接到evdev的client链表上
error = evdev_open_device(evdev); //打开设备
if (error)
goto err_free_client;
file->private_data = client;
nonseekable_open(inode, file);
return 0;
err_free_client:
evdev_detach_client(evdev, client);
kfree(client);
err_put_evdev:
put_device(&evdev->dev);
return error;
}static int evdev_open_device(struct evdev *evdev)
{
int retval;
retval = mutex_lock_interruptible(&evdev->mutex);
if (retval)
return retval;
if (!evdev->exist) //判断evdev结构体是否存在,在evdev_conect中初始化成员为1
retval = -ENODEV;
else if (!evdev->open++) {
retval = input_open_device(&evdev->handle); //打开设备
if (retval)
evdev->open--;
}
mutex_unlock(&evdev->mutex);
return retval;
}
int input_open_device(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev;
int retval;
retval = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (retval)
return retval;
//判断设备是否在open期间被注销
if (dev->going_away) {
retval = -ENODEV;
goto out;
}
handle->open++; //handle的打开计数加一
if (!dev->users++ && dev->open) //如果输入设备没有进程引用,并定义了打开方法,就调用open方法
retval = dev->open(dev);
if (retval) { //如果没打开成功
dev->users--;
if (!--handle->open) { //说明有进程打开了这个handle
/*
* Make sure we are not delivering any more events
* through this handle
*/
synchronize_rcu();
}
}
out:
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
return retval;
}到这里,如果input_dev有定义open方法,打开函数最终会调用到input_dev下面的open函数,否者只是简单的增加打开引用计数。
2.3:input输入子系统的事件处理层
这里我们以触摸屏的事件处理层代码进行分析,即:evdev.c
代码路径:kernel/drivers/input/evdev.c
//先分析入口函数
static int __init evdev_init(void)
{
return input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);//此处调用input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);
}int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
struct input_dev *dev;
int retval;
retval = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (retval)
return retval;
//初始化handler的h_list
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list);
//根据handler的minor将handler放到相应的input_table位置中
if (handler->fops != NULL) {
if (input_table[handler->minor >> 5]) {
retval = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
input_table[handler->minor >> 5] = handler;
}
//将handler通过node链接到input_handler_list链表中
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list);
//遍历input_dev_list链表,找出与这个handler匹配的input_dev,并和它connect,
//匹配和connect的操作就是input_attach_handler所做的事情
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
//唤醒input_devices_poll_wait的等待队列
input_wakeup_procfs_readers();
out:
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
return retval;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_handler);在具体看下上面的input_attach_handler函数(位于 input.c中):
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
int error;
//这个是主要的配对函数,主要比较id的各项
id = input_match_device(handler, dev);
if (!id)
return -ENODEV;
//配对成功调用handler的connect函数,这个函数在事件处理层
//主要生成一个input_handle结构体,并初始化,还生成一个事件处理器相关的设备结构
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);
if (error && error != -ENODEV)
pr_err("failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %d\n",
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error);
return error;
}input_match_device函数(位于input.c里面):
static const struct input_device_id *input_match_device(struct input_handler *handler,
struct input_dev *dev)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
int i;
//遍历handler的id_table与device进行匹配
for (id = handler->id_table; id->flags || id->driver_info; id++) {
//根据flags的标志位,按所需要匹配相应的字段
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS)
if (id->bustype != dev->id.bustype) //总线类型不匹配
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR)
if (id->vendor != dev->id.vendor) //生产厂商不匹配
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT)
if (id->product != dev->id.product) //产品不匹配
continue;
if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION) //版本不匹配
if (id->version != dev->id.version)
continue;
MATCH_BIT(evbit, EV_MAX); //匹配所有的事件
//下面匹配所有的子事件
MATCH_BIT(keybit, KEY_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(relbit, REL_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(absbit, ABS_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(mscbit, MSC_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(ledbit, LED_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(sndbit, SND_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(ffbit, FF_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(swbit, SW_MAX);
//如果有定义handler->match则调用它
//由于我们注册&evdev_handler时并没定义match函数,所以直接返回id
if (!handler->match || handler->match(handler, dev))
return id;
}evdev_handler定义(位于evdev.c中):
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event, //当有事件来的时候调用,把事件放入input_event数组,为用户空间读写事件做准备
.connect = evdev_connect,//在input_dev和input_handler注册过程最终都会调用这个函数,完成handle的注册
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect, //在nput_dev和input_handler注销过程最终会调用这个函数,完成handle的注销
.fops = &evdev_fops,//对事件的操作函数
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,//此设备号基数
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,//匹配项
};static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_device_id *id)
{
struct evdev *evdev;
int minor;
int error;
//EVDEV_MINOR为32,说明evdev这个handler可以同时有32个输入设备
//和它配对,evdev_table中以minor存放evdev结构体
for (minor = 0; minor < EVDEV_MINORS; minor++)
if (!evdev_table[minor])
break;
//判断32个位置是否被全部占用
if (minor == EVDEV_MINORS) {
pr_err("no more free evdev devices\n");
return -ENFILE;
}
//分配一个evdev结构体,这个结构体是evdev事件处理器持有的
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!evdev)
return -ENOMEM;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list);
spin_lock_init(&evdev->client_lock);
mutex_init(&evdev->mutex);
init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait);
//设置evdev中device的名字
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", minor);
evdev->exist = true;
evdev->minor = minor;
//初始化evdev中的handle,这样就连接了input_handler and input_dev
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev);
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev);
evdev->handle.handler = handler;
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + minor);
evdev->dev.class = &input_class;
//配对生成的device,父设备是与他相关联的 input_dev
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev;
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free;
device_initialize(&evdev->dev);
//注册handle结构体
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle);
if (error)
goto err_free_evdev;
//把evdev结构体保存在evdev_table中
error = evdev_install_chrdev(evdev);
if (error)
goto err_unregister_handle;
//注册到linux设备模型
error = device_add(&evdev->dev);
if (error)
goto err_cleanup_evdev;
return 0;
err_cleanup_evdev:
evdev_cleanup(evdev);
err_unregister_handle:
input_unregister_handle(&evdev->handle);
err_free_evdev:
put_device(&evdev->dev);
return error;
}int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler;
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev;
int error;
/*
* We take dev->mutex here to prevent race with
* input_release_device().
*/
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* Filters go to the head of the list, normal handlers
* to the tail.
*/
//将handle的d_node链接到其相关的input_dev的h_list链表中
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
/*
* Since we are supposed to be called from ->connect()
* which is mutually exclusive with ->disconnect()
* we can't be racing with input_unregister_handle()
* and so separate lock is not needed here.
*/
//将handle的h_node链接到其相关的input_handler的h_list链表中
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list);
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
return 0;
}这个函数基本没做什么事情,就是把一个handle结构体通过d_node链表项或h_node链表项,分别链接到input_dev的h_list,input_handler的h_list上。以后通过这个h_list就可以遍历相关的input_handle了。具体可参考下图:
2.4:input输入子系统的设备驱动层
其实上面两层基本都是系统做好了,我们要用linux的输入子系统的话,其实只要编写符合输入子系统框架的驱动程序即可。那么何为符合输入子系统框架呢?简单的可以概括如下:
①分配一个input_dev结构体;
②设置能够支持哪类事件及类下具体的事件类型
③注册input_dev结构体
④硬件相关的代码:如在中断中上报事件
在MTK 6589平台中,上面的前三步都是在mtk_tpd.c中完成,而第四步在中断中上报事件则是在具体的Touch Panel驱动中完成。下面先看mtk_tpd.c:
代码路径:alps/mediatek/custom/common/kernel/touchpanel/src/mtk_tpd.c
/* called when loaded into kernel */
//入口函数
static int __init tpd_device_init(void) {
printk("MediaTek touch panel driver init\n");
//注册到platform总线上,匹配成功调用探测函数
if(platform_driver_register(&tpd_driver)!=0) {
TPD_DMESG("unable to register touch panel driver.\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}static struct platform_driver tpd_driver = {
.remove = tpd_remove,
.shutdown = NULL,
.probe = tpd_probe, //探测函数
#ifndef CONFIG_HAS_EARLYSUSPEND
.suspend = NULL,
.resume = NULL,
#endif
.driver = {
.name = TPD_DEVICE,
},
};static int tpd_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//......省略部分内容
//这里注册了一个misc设备
if (misc_register(&tpd_misc_device))
{
printk("mtk_tpd: tpd_misc_device register failed\n");
}
//为tpd_device分配空间,是一个自定义的结构体,里面包括
//input_dev结构体
if((tpd=(struct tpd_device*)kmalloc(sizeof(struct tpd_device), GFP_KERNEL))==NULL) return -ENOMEM;
memset(tpd, 0, sizeof(struct tpd_device));
/* allocate input device */
//这里即是上面的第一步,分配了一个input_dev结构体
if((tpd->dev=input_allocate_device())==NULL) { kfree(tpd); return -ENOMEM; }
//......省略部分内容
/* struct input_dev dev initialization and registration */
//这里完成上面的第二步,设置支持哪些类事件及类下具体的事件类型
tpd->dev->name = TPD_DEVICE;
set_bit(EV_ABS, tpd->dev->evbit);
set_bit(EV_KEY, tpd->dev->evbit);
set_bit(ABS_X, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(ABS_Y, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(ABS_PRESSURE, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(BTN_TOUCH, tpd->dev->keybit);
set_bit(INPUT_PROP_DIRECT, tpd->dev->propbit);
//电容屏多点触控的一些设置
set_bit(ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(ABS_MT_TOUCH_MINOR, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_X, tpd->dev->absbit);
set_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_Y, tpd->dev->absbit);
//电容屏参数的一些设置
input_set_abs_params(tpd->dev, ABS_X, 0, TPD_RES_X, 0, 0);
input_set_abs_params(tpd->dev, ABS_Y, 0, TPD_RES_Y, 0, 0);
input_abs_set_res(tpd->dev, ABS_X, TPD_RES_X);
input_abs_set_res(tpd->dev, ABS_Y, TPD_RES_Y);
input_set_abs_params(tpd->dev, ABS_PRESSURE, 0, 255, 0, 0);
//注册input_dev结构体
if(input_register_device(tpd->dev))
TPD_DMESG("input_register_device failed.(tpd)\n");
}接下来第四步的上报事件在驱动文件文件ft5316_driver.c中进行:
代码路径:alps/mediatek/custom/common/kernel/touchpanel/ft5316/ft5316_driver.c
/* called when loaded into kernel */
//驱动入口函数
static int __init tpd_driver_init(void) {
//printk("MediaTek ft5316 touch panel driver init\n");
//i2c_register_board_info用于注册一个i2c client
i2c_register_board_info(0, &ft5316_i2c_tpd, 1);
//tpd_driver_add函数在mtk_tpd.c中实现
if(tpd_driver_add(&tpd_device_driver) < 0)
TPD_DMESG("add ft5316 driver failed\n");
return 0;
}/* Add driver: if find TPD_TYPE_CAPACITIVE driver sucessfully, loading it */
int tpd_driver_add(struct tpd_driver_t *tpd_drv)
{
//省略部分内容
for(i = 1; i < TP_DRV_MAX_COUNT; i++)
{
/* add tpd driver into list */
//将我们注册的TP驱动添加到tpd_driver_list链表中
if(tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_device_name == NULL)
{
tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_device_name = tpd_drv->tpd_device_name;
tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_local_init = tpd_drv->tpd_local_init;
tpd_driver_list[i].suspend = tpd_drv->suspend;
tpd_driver_list[i].resume = tpd_drv->resume;
tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_have_button = tpd_drv->tpd_have_button;
#if 0
if(tpd_drv->tpd_local_init()==0)
{
TPD_DMESG("load %s sucessfully\n", tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_device_name);
g_tpd_drv = &tpd_driver_list[i];
}
#endif
break;
}
if(strcmp(tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_device_name, tpd_drv->tpd_device_name) == 0)
{
return 1; // driver exist
}
}
return 0;
} for(i = 1; i < TP_DRV_MAX_COUNT; i++)
{
/* add tpd driver into list */
if(tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_device_name != NULL)
{
//此处调用我们注册的tpd_local_init函数
tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_local_init();
//msleep(1);
if(tpd_load_status ==1) {
TPD_DMESG("[mtk-tpd]tpd_probe, tpd_driver_name=%s\n", tpd_driver_list[i].tpd_device_name);
g_tpd_drv = &tpd_driver_list[i];
break;
}
}
} static struct tpd_driver_t tpd_device_driver = {
.tpd_device_name = "ft5316",
.tpd_local_init = tpd_local_init,
.suspend = tpd_suspend,
.resume = tpd_resume,
#ifdef TPD_HAVE_BUTTON
.tpd_have_button = 1,
#else
.tpd_have_button = 0,
#endif
};static int tpd_local_init(void)
{
TPD_DMESG("Focaltech ft5316 I2C Touchscreen Driver (Built %s @ %s)\n", __DATE__, __TIME__);
//注册i2c driver 这里会和i2c client匹配,然后进入i2c的probe函数
if(i2c_add_driver(&tpd_i2c_driver)!=0)
{
TPD_DMESG("ft5316 unable to add i2c driver.\n");
return -1;
}
if(tpd_load_status == 0)
{
TPD_DMESG("ft5316 add error touch panel driver.\n");
i2c_del_driver(&tpd_i2c_driver);
return -1;
}
#ifdef TPD_HAVE_BUTTON //虚拟按键的一些设置
tpd_button_setting(TPD_KEY_COUNT, tpd_keys_local, tpd_keys_dim_local);// initialize tpd button data
#endif
//表示电容TP
tpd_type_cap = 1;
return 0;
}
接下来看tp的i2c_probe()函数:
static struct i2c_driver tpd_i2c_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "ft5316",//.name = TPD_DEVICE,
// .owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = tpd_probe,
.remove = __devexit_p(tpd_remove),
.id_table = ft5316_tpd_id,
.detect = tpd_detect,
// .address_data = &addr_data,
};static int __devinit tpd_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
//......省略部分内容
//reset管脚的配置
mt_set_gpio_mode(GPIO_CTP_RST_PIN, GPIO_CTP_RST_PIN_M_GPIO);
mt_set_gpio_dir(GPIO_CTP_RST_PIN, GPIO_DIR_OUT);
mt_set_gpio_out(GPIO_CTP_RST_PIN, GPIO_OUT_ONE);
msleep(10);
hwPowerOn(TPD_POWER_SOURCE,VOL_2800,"TP"); //TP在此处上电,TPD_POWER_SOURCE为电源脚
msleep(100);
//中断脚的配置
mt_set_gpio_mode(GPIO_CTP_EINT_PIN, GPIO_CTP_EINT_PIN_M_EINT);
mt_set_gpio_dir(GPIO_CTP_EINT_PIN, GPIO_DIR_IN);
mt_set_gpio_pull_enable(GPIO_CTP_EINT_PIN, GPIO_PULL_ENABLE);
mt_set_gpio_pull_select(GPIO_CTP_EINT_PIN, GPIO_PULL_UP);
//中断及处理函数的注册
mt65xx_eint_set_sens(CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_NUM, CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_SENSITIVE);
mt65xx_eint_set_hw_debounce(CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_NUM, CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_DEBOUNCE_CN);
mt65xx_eint_registration(CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_NUM, CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_DEBOUNCE_EN, CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_POLARITY, tpd_eint_interrupt_handler,0);
mt65xx_eint_unmask(CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_NUM);
//创建一个内核线程,这是TP工作的核心
thread = kthread_run(touch_event_handler, 0, TPD_DEVICE);
if (IS_ERR(thread))
{
retval = PTR_ERR(thread);
TPD_DMESG(TPD_DEVICE " failed to create kernel thread: %d\n", retval);
}
//自动创建字符设备节点,用于调试
#ifdef FTS_CTL_IIC
if (ft_rw_iic_drv_init(client) < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s:[FTS] create fts control iic driver failed\n",
__func__);
#endif
} static int touch_event_handler(void *unused)
{
//......省略部分内容
do
{
mt65xx_eint_unmask(CUST_EINT_TOUCH_PANEL_NUM);
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
//当TP无触摸动作时,线程在此处阻塞
//当TP有触摸动作时,线程往下运行,标志位实在前面probe的中断函数中改变和唤醒的,
//中断函数只进行标志位的改变和唤醒线程,比较简单,不在分析
wait_event_interruptible(waiter,tpd_flag!=0);
//标志位清零
tpd_flag = 0;
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
//tpd_touchinfo函数用于获取触摸信息,此处不在祥解
if (tpd_touchinfo(&cinfo, &pinfo))
{
//printk("point_num = %d\n",point_num);
TPD_DEBUG_SET_TIME;
//根据获取的触摸信息,进行相应的上报工作
if(point_num >0)
{
//printk("TPD Down!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!\n");
tpd_down(cinfo.x[0], cinfo.y[0], cinfo.p[0]);
if(point_num>1)
{
tpd_down(cinfo.x[1], cinfo.y[1], cinfo.p[1]);
if(point_num >2)
{
tpd_down(cinfo.x[2], cinfo.y[2], cinfo.p[2]);
if(point_num >3)
{
tpd_down(cinfo.x[3], cinfo.y[3], cinfo.p[3]);
if(point_num >4)
{
tpd_down(cinfo.x[4], cinfo.y[4], cinfo.p[4]);
}
}
}
}
input_sync(tpd->dev); //上报完所有点后,再上报一个sync事件用于表示上报完
//printk("press --->\n");
}
//当现在无触摸动作而上次有触摸,抬起上次触摸的所有点
else if(p_point_num>0)
{
int i;
for(i=0;idev);
}
/* else
{
tpd_up(cinfo.x[0], cinfo.y[0], 0);
//printk("Ghong_zguoqing_marked tpd point release --->\n");
//input_mt_sync(tpd->dev);
input_sync(tpd->dev);
}*/ //Ghong_zguoqing
}
}while(!kthread_should_stop());
} static void tpd_down(int x, int y, int p)
{
input_report_key(tpd->dev, BTN_TOUCH, 1);
input_report_abs(tpd->dev, ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR, 1);
//分别上报x,y轴坐标
input_report_abs(tpd->dev, ABS_MT_POSITION_X, x);
input_report_abs(tpd->dev, ABS_MT_POSITION_Y, y);
input_mt_sync(tpd->dev);
}static inline void input_report_abs(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int code, int value)
{
input_event(dev, EV_ABS, code, value);
}
input_event()函数:
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
unsigned long flags;
//判断是否支持这种类型的事件
if (is_event_supported(type, dev->evbit, EV_MAX)) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->event_lock, flags);
add_input_randomness(type, code, value);
//对上报的事件进行处理
input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->event_lock, flags);
}
}static void input_handle_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
//......省略部分内容
switch (type)
{
//......省略部分内容
case EV_KEY:
if (is_event_supported(code, dev->keybit, KEY_MAX) &&
!!test_bit(code, dev->key) != value) {
if (value != 2) {
__change_bit(code, dev->key);
if (value)
input_start_autorepeat(dev, code);
else
input_stop_autorepeat(dev);
}
disposition = INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS;
}
break;
case EV_SW:
if (is_event_supported(code, dev->swbit, SW_MAX) &&
!!test_bit(code, dev->sw) != value) {
__change_bit(code, dev->sw);
disposition = INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS;
}
break;
//......省略部分内容
if (disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS)
input_pass_event(dev, type, code, value);
}
}static void input_pass_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
struct input_handler *handler;
struct input_handle *handle;
rcu_read_lock();
//判断是否是绑定的handle
handle = rcu_dereference(dev->grab);
if (handle)
handle->handler->event(handle, type, code, value);
else {
//没有则遍历dev_list列表寻找handle
bool filtered = false;
list_for_each_entry_rcu(handle, &dev->h_list, d_node) {
//如果打开则将消息传递到input子系统去
if (!handle->open)
continue;
handler = handle->handler;
if (!handler->filter) {
if (filtered)
break;
handler->event(handle, type, code, value);
} else if (handler->filter(handle, type, code, value))
filtered = true;
}
}
rcu_read_unlock();
}static void evdev_pass_event(struct evdev_client *client,
struct input_event *event,
ktime_t mono, ktime_t real)
{
event->time = ktime_to_timeval(client->clkid == CLOCK_MONOTONIC ?
mono : real);
/* Interrupts are disabled, just acquire the lock. */
spin_lock(&client->buffer_lock);
//传递消息
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event;
client->head &= client->bufsize - 1;
if (unlikely(client->head == client->tail)) {
/*
* This effectively "drops" all unconsumed events, leaving
* EV_SYN/SYN_DROPPED plus the newest event in the queue.
*/
client->tail = (client->head - 2) & (client->bufsize - 1);
client->buffer[client->tail].time = event->time;
client->buffer[client->tail].type = EV_SYN;
client->buffer[client->tail].code = SYN_DROPPED;
client->buffer[client->tail].value = 0;
client->packet_head = client->tail;
if (client->use_wake_lock)
wake_unlock(&client->wake_lock);
}
if (event->type == EV_SYN && event->code == SYN_REPORT) {
client->packet_head = client->head;
if (client->use_wake_lock)
wake_lock(&client->wake_lock);
kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
spin_unlock(&client->buffer_lock);
}至此,linux的输入子系统就先分析道此处.