哈夫曼编码的C语言实现
代码来自于《小甲鱼C++快速入门》
主程序main.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include "huffman.h"
int main()
{
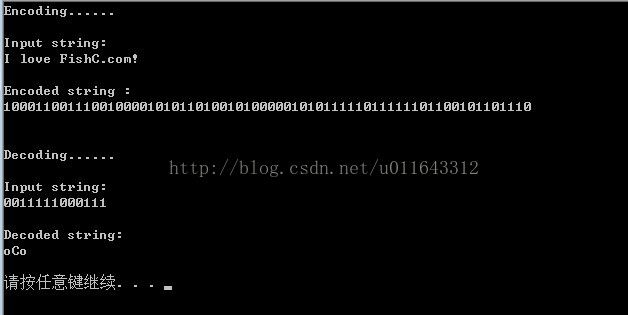
htTree *codeTree = buildTree("I love wwwwwwwwwFishC.com!");//建立哈夫曼树
hlTable *codeTable = buildTable(codeTree);//建立编码表
encode(codeTable,"I love FishC.com!");//对输入的字符串进行编码
decode(codeTree,"0011111000111");//解码
system("pause");
return 0;
}
两个头文件:
huffman.h:定义了哈夫曼树和编码表的结构
#pragma once
#ifndef _HUFFMAN_H
#define _HUFFMAN_H
typedef struct _htNode{
char symbol;
struct _htNode *left,*right;
}htNode;
typedef struct _htTree{
htNode *root;
}htTree;
typedef struct _hlNode{
char symbol;
char *code;
struct _hlNode *next;
}hlNode;
typedef struct _hlTable{
hlNode *first;
hlNode *last;
}hlTable;
htTree *buildTree(char *str);
hlTable *buildTable(htTree *huffmanTree);
void encode(hlTable *table, char *stringToEncode);
void decode(htTree *tree, char *stringToDecode);
#endif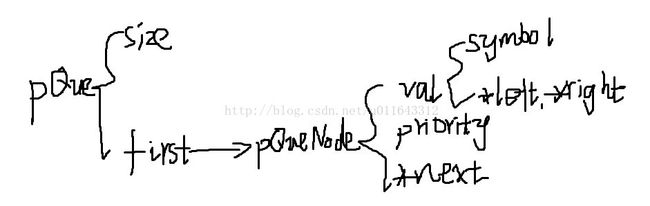
#pragma once
#ifndef _PQUEUE_H
#define _PQUEUE_H
#include "huffman.h"
#define MAX_SZ 256
#define TYPE htNode *
typedef struct _pQueueNode{
TYPE val;
unsigned int priority;
struct _pQueueNode *next;
}pQueueNode;
typedef struct _pQueue{
unsigned int size;
pQueueNode *first;
}pQueue;
void initPQueue(pQueue **queue);
void addPQueue(pQueue **queue, TYPE val, unsigned int priority);
TYPE getQueue(pQueue **queue);
#endif两个cpp文件实现两个头文件声明的函数:
huffman.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "queue.h"
#include "huffman.h"
#include
#include
#include
htTree *buildTree(char *str)
{
int *probability = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 256);
//初始化
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
probability[i] = 0;
}
//统计待编码的字符串各个字符出现的次数
for (int j = 0; str[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
probability[str[j]]++;
}
//定义队列的头指针
pQueue *huffmanQueue;
initPQueue(&huffmanQueue);
//填充队列
for (int k = 0; k < 256; k++)
{
if (probability[k] != 0)
{
htNode *aux = (htNode *)malloc(sizeof(htNode));
aux->left = NULL;
aux->right = NULL;
aux->symbol = (char)k;
addPQueue(&huffmanQueue, aux, probability[k]);
}
}
free(probability);
//生成哈夫曼树
while (huffmanQueue->size != 1)
{
unsigned int newPriority = huffmanQueue->first->priority + huffmanQueue->first->next->priority;
htNode *aux = (htNode *)malloc(sizeof(htNode));
aux->left = getQueue(&huffmanQueue);
aux->right = getQueue(&huffmanQueue);
addPQueue(&huffmanQueue, aux, newPriority);
}
htTree *tree = (htTree *)malloc(sizeof(htTree));
tree->root = getQueue(&huffmanQueue);
return tree;
}
void traverseTree(htNode *treeNode,hlTable **table,int k,char code[256])
{
if (treeNode->left == NULL&&treeNode->right == NULL)
{
code[k] = '\0';
hlNode *aux = (hlNode *)malloc(sizeof(hlNode));
aux->code = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(strlen(code) + 1));
strcpy(aux->code,code);
aux->symbol = treeNode->symbol;
aux->next = NULL;
if ((*table)->first == NULL)
{
(*table)->first = aux;
(*table)->last = aux;
}
else
{
(*table)->last->next = aux;
(*table)->last = aux;
}
}
if (treeNode->left != NULL)
{
code[k] = '0';
traverseTree(treeNode->left,table,k+1,code);
}
if (treeNode->right != NULL)
{
code[k] = '1';
traverseTree(treeNode->right, table, k + 1, code);
}
}
hlTable *buildTable(htTree *huffmanTree)
{
hlTable *table = (hlTable *)malloc(sizeof(hlTable));
table->first = NULL;
table->last = NULL;
char code[256];
int k = 0;
traverseTree(huffmanTree->root,&table,k,code);
return table;
}
void encode(hlTable *table, char *stringToEncode)
{
hlNode *traversal;
printf("Encoding......\n\nInput string:\n%s\n\nEncoded string :\n",stringToEncode);
for (int i = 0; stringToEncode[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
traversal = table->first;
while (traversal->symbol != stringToEncode[i])
traversal = traversal->next;
printf("%s", traversal->code);
}
printf("\n");
}
void decode(htTree *tree,char *stringToDecode)
{
htNode *traversal = tree->root;
printf("\n\nDecoding......\n\nInput string: \n%s\n\nDecoded string: \n",stringToDecode);
for (int i = 0; stringToDecode[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (traversal->left == NULL&&traversal->right == NULL)
{
printf("%c", traversal->symbol);
traversal = tree->root;
}
if (stringToDecode[i] == '0')
traversal = traversal->left;
else if (stringToDecode[i] == '1')
traversal = traversal->right;
else
{
printf("The input string is not coded correctly!\n");
return;
}
}
printf("\n\n");
return;
} queue.cpp:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include "queue.h"
void initPQueue(pQueue **queue)
{
*queue = (pQueue *)malloc(sizeof(pQueue));
(*queue)->first = NULL;
(*queue)->size = 0;
return;
}
void addPQueue(pQueue **queue, TYPE val, unsigned int priority)
{
if ((*queue)->size == MAX_SZ)
{
printf("\n Queue is full. \n");
return;
}
pQueueNode *aux = (pQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(pQueueNode));
aux->priority = priority;
aux->val = val;
if ((*queue)->size == 0||(*queue)->first==NULL)
{
aux->next = NULL;
(*queue)->first = aux;
(*queue)->size = 1;
return;
}
else
{
if (priority <= (*queue)->first->priority)
{
aux->next = (*queue)->first;
(*queue)->first = aux;
(*queue)->size++;
return;
}
else
{
pQueueNode *iterator = (*queue)->first;
while (iterator->next!=NULL)
{
if (priority <= iterator->next->priority)
{
aux->next = iterator->next;
iterator->next = aux;
(*queue)->size++;
return;
}
iterator = iterator->next;
}
if (iterator->next == NULL)
{
aux->next = NULL;
iterator->next = aux;
(*queue)->size++;
return;
}
}
}
}
TYPE getQueue(pQueue **queue)
{
TYPE returnValue;
if ((*queue)->size > 0)
{
returnValue = (*queue)->first->val;
(*queue)->first = (*queue)->first->next;
(*queue)->size--;
}
else
{
returnValue = NULL;
printf("\n Queue is empty \n");
}
return returnValue;
}