Spring源码解析之零 ------ 容器初始化过程(refresh()方法)概要
Spring的核心功能就是IOC和AOP。
IOC分两个过程:bean的解析注册 和 bean的实例化。
AOP是面向切面编程,但是它也离不开bean的解析注册。
本篇主要讲解,容器初始化时候的refresh()方法里的,几个重要方法的基本作用。
首先来看一下refresh()方法。spring容器的启动,创建bean,bean的初始化等一系列过程都在这个refresh方法里面,进行调用。接下来,对每个方法的作用做一个简要的说明。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();//bean的解析注册
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);//初始化非懒加载的bean
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}1.prepareRefresh()方法
设置spring上下文的刷新时间,并将active设为true,初始化一些容器启动必要的资源。我们可以看到,这个方法里面是打了日志的,在我debug的时候,我的日志打印如下:
[INFO][main][2017-07-03 11:56:40][org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext] - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7fac631b: startup date [Mon Jul 03 11:56:40 CST 2017]; root of context hierarchy
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refreshing " + this);
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet();
} beanFactoryPostprocessor的作用是在beanFactory初始化之后提供一个修改的机会。spring已经提供了不少实现,我们自己也可以写一些实现配置在xml中 或者手动调用。
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
}对于它的讲解,另外的两个博客,我觉得很好
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0e7f65afa156
http://blog.csdn.net/lsm135/article/details/53300912
3.obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法
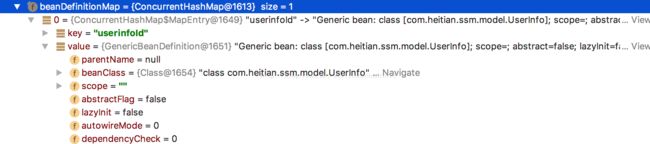
obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,是进行bean的解析注册的地方。所谓bean的解析注册就是指 将xml中配置的bean,转化为Java对象的BeanDefinition,并将它们保存在容器的map里。返回的beanFactory里面,就携带着存放beanName和BeanDefinition的map。
在这个方法执行完毕后,BeanDefinitionMap里面就存放着beanName和beanDefinition的对应信息。而这个时候,存放beanName和实例化bean对象的singletonObjections仍然为空。
这个方法对应着1,2
4.finishBeanInitialization(beanFactory)
这个方法里面,用来初始化非懒加载的bean。并非所有bean都在容器启动的时候实例化。在xml中配置bean的时候,有个lazy-ini属性,默认为false。所以默认情况下,单例的非懒加载的bean在容器启动的时候会实例化。如果是懒加载的,那么在getBean的时候,再实例化。
具体来说:
Spring什么时候实例化bean,首先要分2种情况第一:如果你使用BeanFactory作为Spring Bean的工厂类,则所有的bean都是在第一次使用该Bean的时候实例化
第二:如果你使用ApplicationContext作为Spring Bean的工厂类,则又分为以下几种情况:
(1):如果bean的scope是singleton的,并且lazy-init为false(默认是false,所以可以不用设置),则ApplicationContext启动的时候就实例化该Bean,并且将实例化的Bean放在一个map结构的缓存中,下次再使用该Bean的时候,直接从这个缓存中取
(2):如果bean的scope是singleton的,并且lazy-init为true,则该Bean的实例化是在第一次使用该Bean的时候进行实例化
(3):如果bean的scope是prototype的,则该Bean的实例化是在第一次使用该Bean的时候进行实例化
在我工程的Demo里,是通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext获取xml的。所以属于通过ApplicationContext获取bean,它的默认BeanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
最后通过这个图,可以大概了解整个流程: