Java实现自定义注解开发
一直都对注解开发挺好奇的,最近终于有时间自己实践了一把,记录一下 万一后期会用到呢 哈哈哈
首先我们了解一下自定义注解的标准示例,注解类使用 @interface 关键字修饰,且在注解类上方声明注解相关信息,包含以下四种信息
@Documented – 注解是否将包含在JavaDoc中
@Retention – 什么时候使用该注解
@Target – 注解用于什么地方
@Inherited – 是否允许子类继承该注解
1.)@Retention – 定义该注解的生命周期
● RetentionPolicy.SOURCE : 在编译阶段丢弃。这些注解在编译结束之后就不再有任何意义,所以它们不会写入字节码。@Override, @SuppressWarnings都属于这类注解。
● RetentionPolicy.CLASS : 在类加载的时候丢弃。在字节码文件的处理中有用。注解默认使用这种方式
● RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME : 始终不会丢弃,运行期也保留该注解,因此可以使用反射机制读取该注解的信息。我们自定义的注解通常使用这种方式。
2.)Target – 表示该注解用于什么地方。默认值为任何元素,表示该注解用于什么地方。可用的ElementType 参数包括
● ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR: 用于描述构造器
● ElementType.FIELD: 成员变量、对象、属性(包括enum实例)
● ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE: 用于描述局部变量
● ElementType.METHOD: 用于描述方法
● ElementType.PACKAGE: 用于描述包
● ElementType.PARAMETER: 用于描述参数
● ElementType.TYPE: 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
3.)@Documented – 一个简单的Annotations 标记注解,表示是否将注解信息添加在java 文档中。
4.)@Inherited – 定义该注释和子类的关系
@Inherited 元注解是一个标记注解,@Inherited 阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一个使用了@Inherited 修饰的annotation 类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation 将被用于该class 的子类。
>> 自定义注解类的声明
@Target(value= {ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.FIELD}) 用于声明当前注解类的作用范围分别为 类 方法 属性
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 运行时保留该注解,可以通过反射读取注解信息
package com.gaunyi.batteryonline.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Created by S0111 on 2019/8/20.
* 自定义注解类声明
*/
@Target(value= {ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotationDefinition {
/*定义注解里面的参数信息*/
String name();
String value();
String path();
}
>>使用自定义注解
分别在类、方法、属性上使用注解信息
package com.gaunyi.batteryonline.annotation;
/**
* Created by S0111 on 2019/8/20.
* 自定义注解类使用
*/
@MyAnnotationDefinition(name="类名称",value="类值",path="类路径")
public class MyAnnotationUse {
@MyAnnotationDefinition(name="属性名",value="属性值",path="属性路径")
private String name;
@MyAnnotationDefinition(name="年龄",value="18",path="/user2")
private String age;
@MyAnnotationDefinition(name="方法名",value="方法值",path="方法访问路径")
public String testAnno(){
return "successs!!!";
}
@MyAnnotationDefinition(name="方法名1",value="方法值1",path="方法访问路径1")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
>> 读取注解信息(测试注解类)
这里通过反射读取注解信息,注解内容与对应的类、方法、属性对应。
package com.gaunyi.batteryonline.annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Created by S0111 on 2019/8/20.
* 自定义注解类测试
*/
public class MyAnnotationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.gaunyi.batteryonline.annotation.MyAnnotationUse");
//获取类注解信息
MyAnnotationDefinition classAnno =(MyAnnotationDefinition) clazz.getAnnotation(MyAnnotationDefinition.class);
System.out.println( classAnno.name()+"---"+classAnno.value()+"---"+classAnno.path());
//获取所以方法注解信息 ps:这里需要使用 isAnnotationPresent 判断方法上是否使用了注解
Method[] allMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(int i=0;i
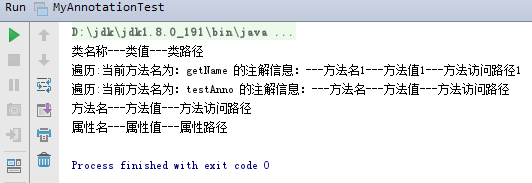
>>测试结果如下:
至此我们就实现了自定义注解啦.... 关于自定义注解的实际应用,待我使用时再来更新...