一、一个Linux操作系统需具备的组件
在制作一个精简的Linux系统之前,首先了解一下制作一个系统所必备的组件。我们需要一个Linux内核文件、bash命令解释器、各种命令、grub引导程序、init程序等。知道了一个系统的启动流程后,我们就可以开始动手改装操作系统了。
二、制作精简版CentOS6.4
我们以一个CentOS6.4的系统为宿主机,在此系统的基础上,通过增加栽剪的方法,实现一个精简版的Linux操作系统。
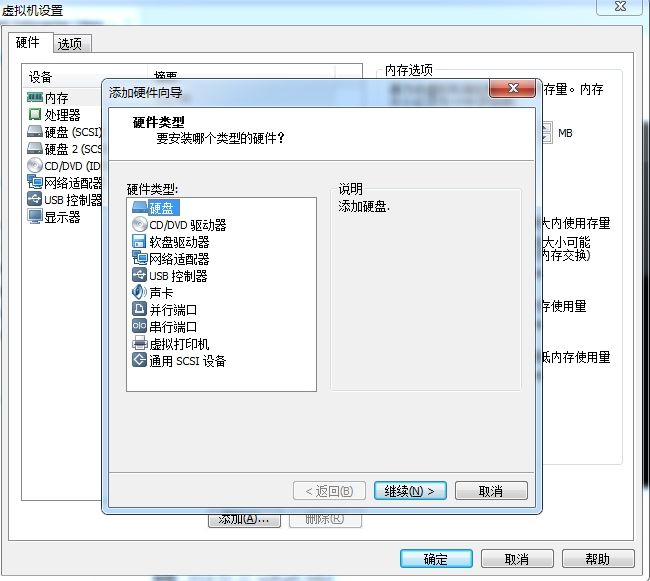
1、给当前CentOS6.4系统新加一块硬盘
使用单个文件,大小20G够用了。
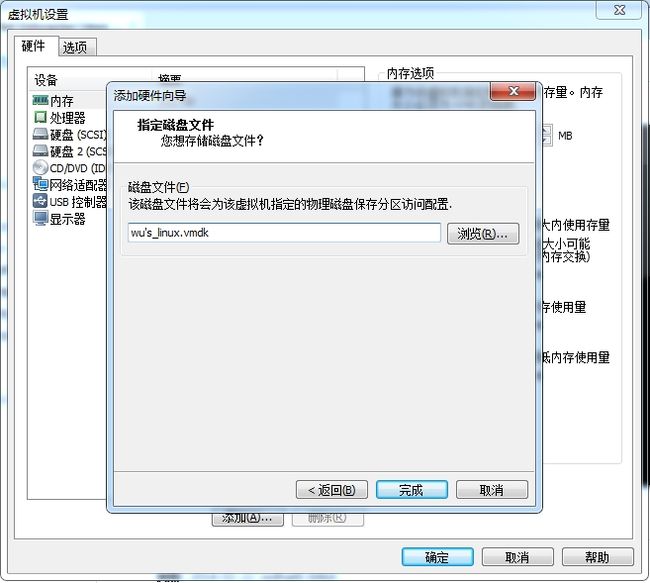
给新磁盘取个名字保存。
2、进入系统给新硬盘分区
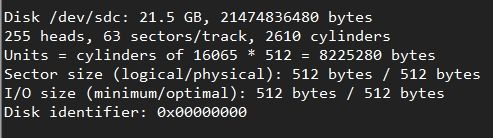
2.1、使用fdisk -l 命令查看磁盘情况。
我的新硬盘是/dev/sdc
2.2、给/dev/sdc分区,分两个区就行了,先创建一个100M的分区,再创建一个10G的分区,分区步骤不在此讨论。
2.3、给新分区格式化
mke2fs -t ext3 /dev/sdc1 mke2fs -t ext3 /dev/sdc2
3、挂载两个分区
3.1、把/dev/sdc1挂载到/mnt/boot目录,/dev/sdc2挂载至/mnt/sysroot目录
mount -t ext3 /dev/sdc1 /mnt/boot mount -t ext3 /dev/sdc2 /mnt/sysroot
分区挂载成功。
4、给新硬盘安装grub引导程序
grub安装成功,grub把新硬盘识别为hd2,不过在目标机上我们还是要使用hd0。
5、复制宿主机的内核文件和initrd文件到/mnt/boot目录
cp /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64 /mnt/boot cp /boot/initramfs-2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64.img /mnt/boot
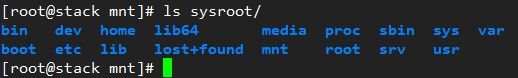
6、接着在目标机的根目录,也就是当前主机的/mnt/sysroot目录创建Linux所需要的各目录。
mkdir -pv /mnt/sysroot/{etc/rc.d,usr,var,proc,sys,dev,lib,lib64,bin,sbin,boot,srv,mnt,media,home,root}
7、写个简单的shell脚本,用来完成命令移植工作,脚本代码如下:
#!/bin/bash
#
# If directroy does't exist will be make directory.
makeDir(){
local dirPath=`dirname $1`
if ! [ -d $dirPath ];then
mkdir -p $dirPath
fi
}
cpMain(){
commandPath=`which --skip-alias $commandChar`
desDir='/mnt/sysroot'
libPath=`ldd $commandPath|grep -o '/[^[:space:]].*\{1,\}[[:space:]]'`
# Copy the command file to the new directory.
cpCommandCount=0
cpError=0
makeDir $desDir$commandPath
if cp $commandPath $desDir$commandPath; then
let cpCommandCount+=1
else
echo "Copy $commandPath file error."
let cpError+=1
fi
# Copy the command library to the new directory.
cpLibCount=0
for partLibPath in $libPath; do
makeDir $desDir$partLibPath
if cp $partLibPath $desDir$partLibPath ; then
let cpLibCount+=1
else
echo "Copy the $partLibPath error."
let cpError+=1
fi
done
}
while true;do
read -p "Enter a command: " commandChar
if [[ "$commandChar" == "quit" ]];then
exit 0
fi
! which $commandChar &> /dev/null && echo "Command not found." && exit 1
cpMain
done
#if [ "$cpError" -eq 0 ];then
# echo -e "Copy command file: $cpCommandCount.\nCopy library file: $cpLibCount. \nCopy successfully!"
#else
# echo -e "Copy command file: $cpCommandCount.\nCopy library file: $cpLibCount. \n$cpError file copy failed."
#fi
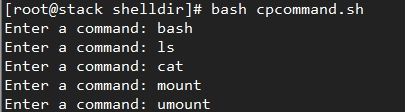
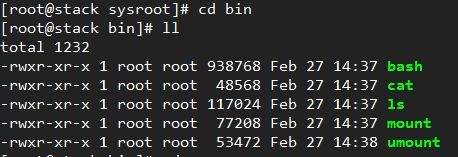
把我们经常要用到的若干命令移植到/mnt/sysroot目录中。
暂时先移这么多吧。
8、系统的大体框架弄好了,接下来我们手动配置一个grub.conf配置文件
我们先把默认的init程序使用bash代替,测试一下。
文件保存后,为了防止缓存没有写入,记得执行几个sync命令。
9、新建一个虚拟机
9.1、操作系统选择Other Linux
9.2、在选择磁盘时,选择刚才我们新加的那块硬盘。
10、目标主机创建好后,因为两部主机都使用了那块新硬盘,此时我们先把宿主机关闭,把目标机开启测试。
10.1、开机测试,看到了grub的菜单。
10.2、如果没有出错,开机后会直接进入shell的命令行界面。
OK,没有出错。
11、一个微型Linux系统就快完成了,不过现在还不能连接网络,没有init程序,先退出系统,回到宿主机上,给他添加网络功能。
11.1、使用 lsmod命令查找一下宿主机的网卡模块
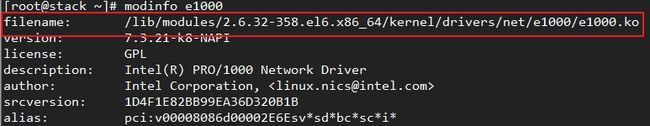
11.2、使用 modinfo 命令查看网卡模块的详细信息,以此获得网卡模块的所在路径。
11.3、在/mnt/sysroot/lib目录创建一个模块目录。
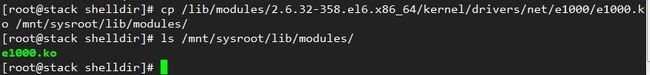
11.4、复制宿主机的网卡模块到/mnt/sysroot/lib/modules目录。
cp /lib/modules/2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/e1000/e1000.ko /mnt/sysroot/lib/modules/
12、执行刚才的shell脚本,复制一些网络命令及模块安装命令到目标机的目录。
13、网络模块创建好了,我们可以手动创建一个init程序了。
13.1、在/mnt/sysroot/sbin目录下创建一个init脚本文件
#!/bin/bash # echo -e " \tWelcome to \033[33mXiaoWu's \033[0mLinux " mount -n -t proc proc /proc mount -n -t sysfs sysfs /sys mount -n -o remount,rw /dev/sda2 / /bin/bash
首先输出一行欢迎信息,然后挂载两个系统内核必需要挂载的分区,再以读写的方式重新挂载一下根分区。
13.2、给脚本添加执行权限
最后执行sync命令,进入目标机测试一下。
13.3、开机测试一下
13.4、安装网卡模块
insmod /lib/modules/e1000.ko
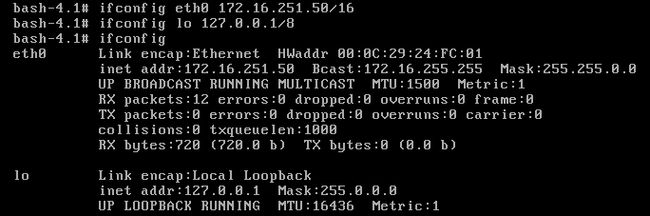
13.5、设置IP地址,测试网络
网络可以使用。
14、最后把添加网卡模块的步骤也写入init文件,让他开机就能连接网络。
#!/bin/bash # echo -e " \tWelcome to \033[33mXiaoWu's \033[0mLinux " mount -n -t proc proc /proc mount -n -t sysfs sysfs /sys mount -n -o remount,rw /dev/sda2 / insmod /lib/modules/e1000.ko ifconfig lo 127.0.0.0/8 ifconfig eth0 172.16.251.50/16 ! [[ -f "/etc/issue" ]] && echo " Modify by CentOS release 6.4 (Final) XiaoWu's Linux Good good study!Day day up! http://wubinary.51cto.com " > /etc/issue /bin/bash
一切就绪,开机测试一下。。。
OK,系统裁剪成功!