spring官方文档学习
(注:阅读学习spring官方文档做的笔记,如有不对的地方,还望指出)
IOC
也称为依赖注入(DI)。
在org.springframework.beans和org.springframework.context包是spring框架的IOC容器的基础。
该BeanFactory接口提供了一种能够管理任何类型对象的高级配置机制。
ApplicationContext(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.1.6.RELEASE/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/ApplicationContext.html)是BeanFactory的子接口。
- 更容易与spring的AOP功能集成
- 消息资源处理
- 事件发布
- 特定WebApplicationContext于应用程序层的上下文,例如在WEB应用程序中使用的上下文。
在spring中,构成应用程序主干并由spring IOC容器管理的对象称为bean。
bean是一个由spring IOC容器实例化、组装和管理的对象。
bean及其之间的依赖关系反映在容器使用的配置元数据中。
Container容器
ApplicationContext接口代表spring IOC容器,负责实例化、配置和组装bean。
容器通过读取配置元数据获取有关要实例化、配置和组装的对象的指令、配置元数据以XML、JAVA注释或JAVA代码表示。
ApplicationContext spring提供了几种接口的实现。在应用程序中,通常会创建一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.1.6.RELEASE/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/support/ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.html)或者FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.1.6.RELEASE/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/support/FileSystemXmlApplicationContext.html)。
简单的配置web.xml模板:
contextConfigLocation
/WEB-INF/daoContext.xml /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
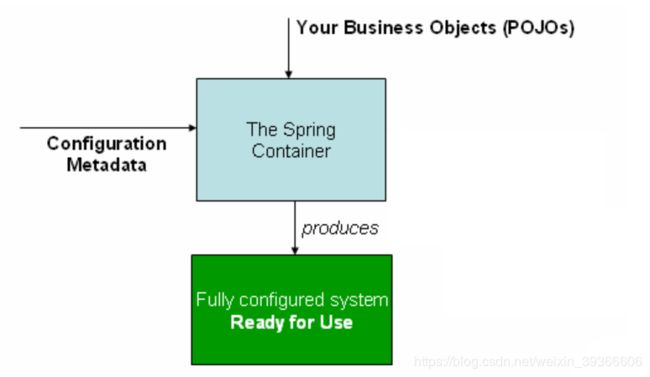
下图为spring工作的高级视图。
配置元数据
如上图所示,spring IOC容器使用一种配置元数据。此配置元数据表示作为应用程序的开发人员告诉spring容器如何在应用程序中实例化、配置和组装对象。
配置元数据的方式:
- 基于XML格式配置
- 基于JAVA的配置,例如@Cnofiguration(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/annotation/Configuration.html),@Bean(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/annotation/Bean.html),@Import(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/annotation/Import.html),@DependsOn(https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/context/annotation/DependsOn.html)
- 基于注释的配置
基于XML的配置元数据将这些bean配置为顶级
JAVA配置通常是将@Bean使用在@Configuration类中带注释的方法中。
基于XML的配置元数据的基本结构:
- id属性是一个标识单个bean的字符串
- class属性定义bean的类型并使用完全限定的类名
实例化容器
提供给ApplicationContext构造函数的位置路径是资源字符串,它允许容器从各种外部资源(如本地文件系统、JAVA等)加载配置元数据CLASSPATH
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");services.xml配置文件:
daos.xml配置文件:
在上面的示例中,服务层由PetStoreServiceImpl类和2个数据访问对象JpaAccountDao、JpaItemDao类组成。
id和ref之间的联系表现了协作对象之间的依赖关系。
也可使用一个或多个
例如:
在上面的例子中,外部bean是从services.xml、messageSource.xml、themeSource.xml三个文件中加载。
所有位置路径都与执行导入的定义文件有关。因此services.xml必须与执行导入的文件位于相同的目录或类路径位置,messageSource.xml、themeSource.xml必须位于resources文件位置下,可以忽略前“/”,鉴于是相对路径,最好不要使用“/”。
Groovy Bean定义DSL
bean定义也可以在Spring的Groovy Bean定义DSL中表示,如Grails。通常,此类配置位于“.groovy”文件中,其结构如下:
beans {
dataSource(BasicDataSource) {
driverClassName = "org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"
url = "jdbc:hsqldb:mem:grailsDB"
username = "sa"
password = ""
settings = [mynew:"setting"]
}
sessionFactory(SessionFactory) {
dataSource = dataSource
}
myService(MyService) {
nestedBean = { AnotherBean bean ->
dataSource = dataSource
}
}
}使用容器
使用ApplicationContext的方法 getBean方法获取bean的实例。
T getBean(String name, Class requiredType) 例如:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class);
List userList = service.getUsernameList(); 如果是Groovy配置,如下:
ApplicationContext context = new GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy", "daos.groovy");针对Groovy的XML配置:
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.xml", "daos.xml");
context.refresh();或者
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
new GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.groovy", "daos.groovy");
context.refresh();