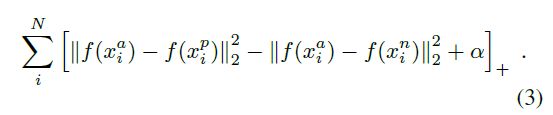Triplet Loss 和 Center Loss详解和pytorch实现
最近在学习ReID相关的算法,为了提高ReID的性能通常会采用softmax loss 联合 Triplet Loss和Center Loss来提高算法的性能。
本文对Triplet Loss和Cnetr Loss做一个总结,以简洁的方式帮助理解。
Triplet Loss和Center Loss都是从人脸识别领域里面提出来的,后面在各种图像检索任务中被广泛应用。
想要了解Triplet Loss和Center Loss算法原文的可以查看我之前的博客,对论文做了详细翻译。
《FaceNe: Triplet Loss》 《Center Loss》
1,Triplet Loss
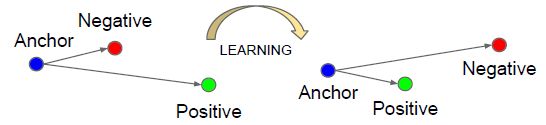
如上图所示,Triplet Loss 是有一个三元组
a: anchor 表示训练样本。
p: positive 表示预测为正样本。
n: negative 表示预测为负样本。
triplet loss的作用:用于减少positive(正样本)与anchor之间的距离,扩大negative(负样本)与anchor之间的距离。基于上述三元组,可以构建一个positive pair
所以我们希望:D(a, p) < D(a, n)。进一步希望在一定距离上(margin) 满足这个情况:D(a, p) + margin < D(a, n)
对于一个样本经过网络有:
对于训练时有这么几种情况:
(a)easy triplets:loss = 0,D(a, p) + margin < D(a, n),positive pair 的距离远远小于于negative pair的距离。即,类内距离很小,类间很大距离,这种情况不需要优化。
(b)hard triplets:D(a, n) < D(a, p) ,positive pair 的距离大于于negative pair的距离,即类内距离大于类间距离。这种情况比较难优化。
(c)semi-hard triplets:D(a, p) < D(a, n) < D(a, p) + margin。positive pair的距离和negative pair的距离比较高近。即,
当为 semi-hard triplets 时, D(a, p) + margin - D(a, n) > 0产生loss。得到要优化的损失函数。
对于Triplet Loss的梯度:
![]()
训练的时候:早期为了网络loss平稳,一般选择easy triplets进行优化,后期为了优化训练关键是要选择hard triplets,他们是活跃的,因此可以帮助改进模型。
pytorch源码实现:
class TripletLoss(nn.Module):
"""Triplet loss with hard positive/negative mining.
Reference:
Hermans et al. In Defense of the Triplet Loss for Person Re-Identification. arXiv:1703.07737.
Imported from ``_.
Args:
margin (float, optional): margin for triplet. Default is 0.3.
"""
def __init__(self, margin=0.3,global_feat, labels):
super(TripletLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
self.ranking_loss = nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=margin)
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
"""
Args:
inputs (torch.Tensor): feature matrix with shape (batch_size, feat_dim).
targets (torch.LongTensor): ground truth labels with shape (num_classes).
"""
n = inputs.size(0)
# Compute pairwise distance, replace by the official when merged
dist = torch.pow(inputs, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(n, n)
dist = dist + dist.t()
dist.addmm_(1, -2, inputs, inputs.t())
dist = dist.clamp(min=1e-12).sqrt() # for numerical stability
# For each anchor, find the hardest positive and negative
mask = targets.expand(n, n).eq(targets.expand(n, n).t())
dist_ap, dist_an = [], []
for i in range(n):
dist_ap.append(dist[i][mask[i]].max().unsqueeze(0))
dist_an.append(dist[i][mask[i] == 0].min().unsqueeze(0))
dist_ap = torch.cat(dist_ap)
dist_an = torch.cat(dist_an)
# Compute ranking hinge loss
y = torch.ones_like(dist_an)
return self.ranking_loss(dist_an, dist_ap, y) 训练的时候对每一个样本选择hardest triplet 进行训练。
2,Center Loss
center loss是在triplet之后提出来的。triplet学习的是样本间的相对距离,没有学习绝对距离,尽管考虑了类间的离散性,但没有考虑类内的紧凑性。对于triplet loss举一个例子。设margin = 0.3,D(a, p) = 0.3 , D(a, n) = 0.5 怎triplet loss = 0.1。而当D(a, p) = 1.3 D(a, n) = 1.5时,triplet loss仍然等于0.1,这相当于,内类之间不够紧凑(距离还不够小)。
所以Center Loss希望可以通过学习每个类的类中心,使得类内的距离变得更加紧凑。
 表示深度特征的第
表示深度特征的第 ![]() 类中心。理想情况下,
类中心。理想情况下,![]() 应该随着深度特性的变化而更新。
应该随着深度特性的变化而更新。
训练时:第一是基于mini-batch执行更新。在每次迭代中,计算中心的方法是平均相应类的特征(一些中心可能不会更新)。第二,避免大扰动引起的误标记样本,用一个标量 α 控制中心的学习速率,一般这个α 很小(如,0.005)。
pytorch源码实现:
class CenterLoss(nn.Module):
"""Center loss.
Reference:
Wen et al. A Discriminative Feature Learning Approach for Deep Face Recognition. ECCV 2016.
Args:
num_classes (int): number of classes.
feat_dim (int): feature dimension.
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=751, feat_dim=2048, use_gpu=True):
super(CenterLoss, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.feat_dim = feat_dim
self.use_gpu = use_gpu
if self.use_gpu:
self.centers = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.num_classes, self.feat_dim).cuda())
else:
self.centers = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.num_classes, self.feat_dim))
def forward(self, x, labels):
"""
Args:
x: feature matrix with shape (batch_size, feat_dim).
labels: ground truth labels with shape (num_classes).
"""
assert x.size(0) == labels.size(0), "features.size(0) is not equal to labels.size(0)"
batch_size = x.size(0)
distmat = torch.pow(x, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(batch_size, self.num_classes) + \
torch.pow(self.centers, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(self.num_classes, batch_size).t()
distmat.addmm_(1, -2, x, self.centers.t())
classes = torch.arange(self.num_classes).long()
if self.use_gpu: classes = classes.cuda()
labels = labels.unsqueeze(1).expand(batch_size, self.num_classes)
mask = labels.eq(classes.expand(batch_size, self.num_classes))
print(mask)
dist = []
for i in range(batch_size):
print(mask[i])
value = distmat[i][mask[i]]
value = value.clamp(min=1e-12, max=1e+12) # for numerical stability
dist.append(value)
dist = torch.cat(dist)
loss = dist.mean()
return loss实际场景,可以利用triplet loss和center loss联合训练优化模型。详细操作可以参我之前阅读的ReID论文中的方法。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40671425/article/details/93885584