go-kit实践之4:go-kit微服务熔断机制的实现
在微服务架构中,每一个微服务都是一个独立的业务功能单元,而一个应用一般由多个微服务组成,微服务之间的交互是通过RPC(远程过程调用)完成。
比如,我们的应用是微服务A调用微服务B和微服务C来完成的,而微服务B又需要调用微服务D,微服务D又需要调用微服务E。如果在调用的链路上对微服务E的调用,响应时间过长或者服务不可用,那么对微服务D的调用就会占用越来越多的系统资源,进而引起微服务D的系统崩溃,微服务D的不可用,又会连锁反应的引起微服务B崩溃,进而微服务A崩溃,最终导致整个应用不可用。这也就是所谓的“雪崩效应”。
介绍
go-kit 提供了三种熔断
1、 gobreaker
2、 handy
3、 hystrix-go
hystrix用的比较多,我们来介绍下go-kit中hystrix的使用方法
go-kit的hystrix
Middleware的实现
1、 Hystrix返回Middleware 此中间件会在原来的endPoint包一层Hystrix的endPoint
2、 hystrix通过传入的commanName获取对应的Hystrix的设置,并设置run失败时运行的fallback函数为nil
3、 我们也可以自己实现middleware包装endPoint
func Hystrix(commandName string) endpoint.Middleware {
return func(next endpoint.Endpoint) endpoint.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, request interface{}) (response interface{}, err error) {
var resp interface{}
if err := hystrix.Do(commandName, func() (err error) {
resp, err = next(ctx, request)
return err
}, nil); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return resp, nil
}
}
}客户端hystrix配置
1、Timeout 【请求超时的时间】
2、ErrorPercentThreshold【允许出现的错误比例】
3、SleepWindow【熔断开启多久尝试发起一次请求】
4、MaxConcurrentRequests【允许的最大并发请求数】
5、RequestVolumeThreshold 【波动期内的最小请求数,默认波动期10S】
commandName := "my-endpoint"
hystrix.ConfigureCommand(commandName, hystrix.CommandConfig{
Timeout: 1000 * 30,
ErrorPercentThreshold: 1,
SleepWindow: 10000,
MaxConcurrentRequests: 1000,
RequestVolumeThreshold: 5,
})
增加熔断中间件的包装
breakerMw := circuitbreaker.Hystrix(commandName)
//增加熔断中间件
reqEndPoint = breakerMw(reqEndPoint)实例
1、protobuf文件及生成对应的go文件
syntax = "proto3";
// 请求书详情的参数结构 book_id 32位整形
message BookInfoParams {
int32 book_id = 1;
}
// 书详情信息的结构 book_name字符串类型
message BookInfo {
int32 book_id = 1;
string book_name = 2;
}
// 请求书列表的参数结构 page、limit 32位整形
message BookListParams {
int32 page = 1;
int32 limit = 2;
}
// 书列表的结构 BookInfo结构数组
message BookList {
repeated BookInfo book_list = 1;
}
// 定义 获取书详情 和 书列表服务 入参出参分别为上面所定义的结构
service BookService {
rpc GetBookInfo (BookInfoParams) returns (BookInfo) {}
rpc GetBookList (BookListParams) returns (BookList) {}
}生成对应的go语言代码文件:protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. book.proto (其中:protobuf文件名为:book.proto)
注:由于演示熔断机制,也就是Server出现问题的时候进行熔断,因此本文Server端代码可以不用。
2、Client端代码
package main
import (
"MyKit"
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/afex/hystrix-go/hystrix"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/circuitbreaker"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/endpoint"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/log"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/sd"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/sd/etcdv3"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/sd/lb"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"io"
"time"
)
func main() {
var (
//注册中心地址
etcdServer = "127.0.0.1:2379"
//监听的服务前缀
prefix = "/services/book/"
ctx = context.Background()
)
//对hystrix进行配置
commandName:="my_endpoint"
hystrix.ConfigureCommand(commandName,hystrix.CommandConfig{
Timeout:1000*3, //超时
MaxConcurrentRequests:100, //最大并发的请求数
RequestVolumeThreshold:5,//请求量阈值
SleepWindow:10000, //熔断开启多久尝试发起一次请求
ErrorPercentThreshold:1, //误差阈值百分比
})
breakerMw:=circuitbreaker.Hystrix(commandName) //定义熔断器中间件
options := etcdv3.ClientOptions{
DialTimeout: time.Second * 3,
DialKeepAlive: time.Second * 3,
}
//连接注册中心
client, err := etcdv3.NewClient(ctx, []string{etcdServer}, options)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
logger := log.NewNopLogger()
//创建实例管理器, 此管理器会Watch监听etc中prefix的目录变化更新缓存的服务实例数据
instancer, err := etcdv3.NewInstancer(client, prefix, logger)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
//创建端点管理器, 此管理器根据Factory和监听的到实例创建endPoint并订阅instancer的变化动态更新Factory创建的endPoint
endpointer := sd.NewEndpointer(instancer, reqFactory, logger) //reqFactory自定义的函数,主要用于端点层(endpoint)接受并显示数据
//创建负载均衡器
balancer := lb.NewRoundRobin(endpointer)
/**
我们可以通过负载均衡器直接获取请求的endPoint,发起请求
reqEndPoint,_ := balancer.Endpoint()
*/
/**
也可以通过retry定义尝试次数进行请求
*/
reqEndPoint := lb.Retry(3, 100*time.Second, balancer) //请求次数为3,时间为10S(时间需要多于服务器限流时间3s)
//增加熔断中间件
reqEndPoint=breakerMw(reqEndPoint)
//现在我们可以通过 endPoint 发起请求了
req := struct{}{}
for i:=0;i<20;i++ { //发生20次请求
ctx=context.Background()
if _, err = reqEndPoint(ctx, req); err != nil {
//panic(err)
fmt.Println("当前时间: ", time.Now().Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05.99"),"\t第",i+1,"次")
fmt.Println(err)
time.Sleep(1*time.Second)
}
}
}
//通过传入的 实例地址 创建对应的请求endPoint
func reqFactory(instanceAddr string) (endpoint.Endpoint, io.Closer, error) {
return func(ctx context.Context, request interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
conn, err := grpc.Dial(instanceAddr, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
panic("connect error")
}
defer conn.Close()
bookClient := book.NewBookServiceClient(conn)
bi, _ := bookClient.GetBookInfo(context.Background(), &book.BookInfoParams{BookId: 1})
fmt.Println("获取书籍详情")
fmt.Println("bookId: 1", " => ", "bookName:", bi.BookName)
fmt.Println("请求服务成功: ", instanceAddr,"当前时间为:",time.Now().Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05.99"))
/*bl, _ := bookClient.GetBookList(context.Background(), &book.BookListParams{Page: 1, Limit: 10})
fmt.Println("获取书籍列表")
for _, b := range bl.BookList {
fmt.Println("bookId:", b.BookId, " => ", "bookName:", b.BookName)
}*/
return nil, nil
}, nil, nil
}
3、运行及分析
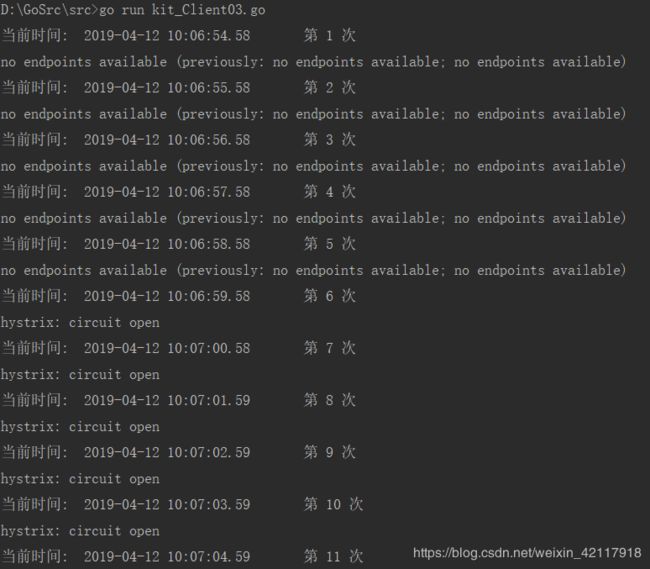
直接运行Client端(不用启动etcd、Server),效果如下:
通过上面的输出记录可以验证我们的配置:
1、 前5条波动期内的错误,没有触发circuit开启(RequestVolumeThreshold:5,//请求量阈值)
2、 circuit开启后请求熔断生效(输出内容:hystrix: circuit open)
3、 circuit开启10S后,SleepWindow测试发起请求设置生效(第16次输出的内容;设置:SleepWindow:10000, //熔断开启多久尝试发起一次请求)