Towards Open-Set Identity Preserving Face Synthesis
[1803.11182] Towards Open-Set Identity Preserving Face Synthesis
文章目录
- Abstract
- 1. Introduction
- (1)与其他网络对比
- (2)本文原理
- 2. Related work
- 3. 保留身份信息的GAN
- 3.1 身份信息和属性信息的分离
- 3.1.1 提取身份向量
- 3.1.2 提取属性向量
- 3.2 对网络G,C,D的非对称训练
- 3.3 非监督训练
- 3.4 全局目标函数
- 4. 实验
- 4.1 框架分析
- 4.2 KL散度损失
- 4.3 脸部属性转移
- 4.4 人脸属性调整
- 4.5 人脸对抗实例检测
- 5. 总结
Abstract
Previous identity preserving face synthesis processes are largely confined to synthesizing faces with known identities that are already in the training dataset. Our proposed framework does not need to annotate the attributes of faces in any way. It is trained with an asymmetric loss function to better preserve the identity and stabilize the training process. It can also effectively leverage large amounts of unlabeled training face images to further improve the fidelity of the synthesized faces for subjects that are not presented in the labeled training face dataset.
-
之前的保留身份的人脸合成过程都限制于数据集中已知身份的人脸合成,而本文可训练数据集外的人脸。
-
本文提出的架构不需要对人脸属性做任何标注。
-
本文采用非对称函数来更好的保留身份信息和使训练过程稳定。
-
可高效率利用大量的无标签脸部图片来提高合成的质量。
1. Introduction
(1)与其他网络对比
Many previous works have attempted to synthesize face images of a specific person. For example, TP-GAN [14] and FF-GAN [36] attempt to synthesize the frontal view of a face from a single face image. DR-GAN [33] can change the pose of an input face image. However, these methods can only manipulate limited types of attributes, such as poses. These methods also require full annotation of attributes for training the models. More recent work, such as CVAE- GAN [4], can produce a variety of attribute changes. Nevertheless, it is not able to synthesize a face with an identity outside the training dataset.
-
许多之前的工作尝试合成特定的人脸。比如TP-GAN, FF-GAN(通过单一脸部图像合成正脸图像), DR-GAN(改变输入脸部图像的表情)。
但这些方法都仅能修改某种限定属性,而且要求输入图片属性的所有标注来训练模型。
-
CVAE-GAN可以修改很多属性,但不能合成来自训练集以外的人脸。
(2)本文原理
To synthesize a face with an identity outside the training dataset, we require one input image of that subject to produce an identity vector, and any other input face image to extract an attribute vector capturing, e.g., pose, emotion, illumination, and even background. We then combine the identity vector and the attribute vector to synthesize a new face of the subject with the extracted attribute.
To this end, we propose a framework based on Generative Adversarial Networks to disentangle identity and attributes given a face image, and recombine different identities and attributes for identity preserving face synthesis.
我们需要一个主体的输入图像来提供一个身份向量,和其他输入的脸部图像来提取一个属性向量捕获,比如姿态、感情等。然后我们将这些身份向量和提取到的属性向量合成来合成主体的新脸部。
末端的GAN用来分离给定脸部图片的身份和属性,并将不同的身份和属性重组来做保留身份的脸部合成。
We use two loss functions: 1) a reconstruction loss of the attribute image, and 2) a KL divergence loss defined on the attribute vector. These functions enforce that network A extracts the attribute information.We take full advantage of recent advancements in face recognition, and use the softmax loss on top of network I to encode the identity into an attribute independent vector representation. Therefore, in order to reconstruct the input, network A is forced to extract the attribute information. Meanwhile, we add a KL divergence loss to regularize the attribute vector, such that it dose not contain identity information.
Inspired by the CVAE-GAN [4], we adopt a new asymmetric loss function. More specifically, we adopt a cross-entropy loss when training the discriminative network D, and the classification network C, and use a pairwise feature matching loss when updating the generative network G. This does a better job of preserving the identity while stabilizing the training process.
Ⅰ. 使用了两个损失函数:
(1)定义在属性图片上的重构损失。在I网络的顶端使用softmax损失函数来将身份编码为一个独立于属性的向量表示。
(2)定义在属性向量上的KL散度损失。在提取属性信息的A网络上加入一个KL散度损失来正则化属性向量,使其不包含身份信息。
Ⅱ. 采用了一种新的不对称的损失函数。
(1)在训练判别器D和分类器C的时候采用交叉熵损失;
(2)在更新生成器G的时候采用成堆的特征匹配损失。
本文的网络可以高效利用大量的无标签脸部训练图片来提高合成数据集中没有的脸的保真度。这些无标签数据可以增大类内和类间人脸分布差异以提高合成人脸的多样性,所以生成的人脸在姿态和表情上有更大的变化。
2. Related work
In contrast, this paper proposes an Identity PreservingGenerative Adversarial Network framework, which does not require any attribute annotations. This framework disentangles the identity and attributes representations, and then uses different recombinations of representations for identity preserving face synthesis. This disentaglement allows us to synthesize faces with identities outside what is presented in the training datasets. This addresses a serious limitation of a previous deep generative model-based identity preserving face synthesis method [4]. It simply can not generate faces of identities outside the training dataset.
对比之下,本文提出了一种保留身份的GAN,它并不要求任何属性注释。本文的结构将身份和属性分离,然后使用不同表示形式的组合来做保留身份的人脸合成。这种分离使我们可以合成训练集中没有的人脸,而其他的方法不能。
3. 保留身份信息的GAN
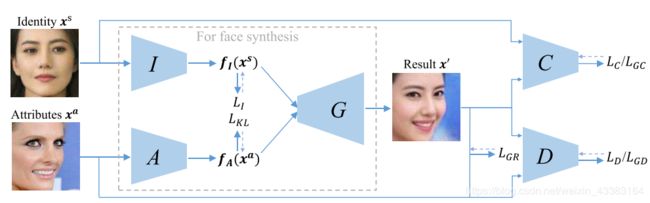
实线:输入输出 虚线:损失函数
I I I从图片 x s x^s xs中提取身份向量 f I ( x s ) f_I(x^s) fI(xs)。从属性图片中提取属性向量 f A ( x a ) f_A(x^a) fA(xa)。G通过组合身份向量和属性向量 [ f I ( x s ) T , f A ( x a ) T ] T [f_I(x^s)^T, f_A(x^a)^T]^T [fI(xs)T,fA(xa)T]T来生成一个新的脸部图片 x ′ x' x′。C通过后验概率 P ( c ∣ x s ) P(c|x^s) P(c∣xs)来保留身份信息,其中c是身份信息x^s的主体(类别/标签)。判别网络D用来区分真实图片和生成图片。
3.1 身份信息和属性信息的分离
In our training data, we only have the annotation of the identity of each face, without any annotation of the attribute information. Extracting the identity vector is relatively straightforward. Here, we take full advantage of recent improvement in face recognition.
训练数据有身份信息的标注,没有属性信息的标注。
3.1.1 提取身份向量
给定脸部图片的身份信息 { x i s , c i } ( x i s \{x_i^s,c_i\}(x_i^s {xis,ci}(xis是身份向量, c i c_i ci是类别),我们使用softmax损失来训练网络身份向量提取网络I,使其做脸部分类的工作。相同的个体拥有大致相同的特征(身份向量)。I的损失函数: L I = − E x ∼ P r [ l o g P ( c ∣ x s ) ] L_I=-\mathbb{E}_{x\sim P_r}[logP(c|x^s)] LI=−Ex∼Pr[logP(c∣xs)],然后我们用I最后一个池化层的响应作为特征向量。
3.1.2 提取属性向量
采用完全无监督的方式训练A,训练过程中采用两个损失函数:重建损失和KL散度损失。
-
重建损失
这里我们有两种情况:主体图像xs与属性图像xa相同和不同。两种情况中,我们都需要x’来重构属性图像x^a,但是有不同的损失权重。重构损失函数表达式为:其中 λ \lambda λ是重构损失权重。
当 x s 与 x a x^s与x^a xs与xa相同时,输出的 x ′ x' x′也一定与这两者相同。假定一个身份信息有很多不同的脸部图像,那么身份向量 f I ( x ) f_I(x) fI(x)几乎对所有的样本都大致相同。但是使用不同样本的 f I ( x ) 和 f A ( x ) f_I(x)和f_A(x) fI(x)和fA(x)的重构是不同的。因此,重构损失使属性编码网络 A A A学习不同的属性表示 f A ( x ) f_A(x) fA(x)。
当身份图片和属性图片不同时,我们不能明确知道重构结果看起来应该是什么样。但是我们可以期望重构结果与属性图片 x a x^a xa类似,比如背景、全图光亮、姿势等。所以我们采用一个权值相对较小的像素重建损失来保留其属性。我们将 λ \lambda λ设为0.1。而后的实验也证明,如果设定一个大的权值\lambda,结果会很差。
-
KL散度损失
To help the attributes encoder network learn better representations, we also add a KL divergence loss to regularize the attribute vector with an appropriate prior P(z) . The KL divergence loss will limit the distribution range of the attribute vector, such that it dose not contain much identity information, if at all. For each input face image, the network A outputs the mean µ and covariance of the latent vector. We use the KL divergence loss to reduce the gap between the prior P(z) and the learned distributions, i.e., L K L = 1 2 ( μ T μ + ∑ j − 1 J ( e ϵ − ϵ − 1 ) ) L_{KL}=\frac{1}{2}(\mu ^T\mu+\sum_{j-1}^J(e^{\epsilon}-\epsilon-1)) LKL=21(μTμ+∑j−1J(eϵ−ϵ−1))
we sample the attribute vector using z = μ + r ⊙ e ε z = \mu + r ⊙ e^ε z=μ+r⊙eε in the training phase, where r ∼ N ( 0 , I ) r ∼ N(0, I) r∼N(0,I) is a random vector and ⊙ represents the element-wise multiplication.加入KL损失,使用 P ( z ) N ( 0 , 1 ) P(z)~N(0, 1) P(z) N(0,1)来正则化属性向量。KL散度损失可以限制属性向量的范围使其不包含太多身份信息。对于每个输入的脸部图片,A(提取属性特征)网络输出均值μ和协方差。使用KL散度损失可以降低先验概率P(z)和学习到的分布之间的差异。
公式解读:μ为均值,j为向量ε的第j个元素。
采用z来对属性向量取样,其中r是高斯随机向量,r与 e ε e^ε eε做逐元素乘法。
3.2 对网络G,C,D的非对称训练
-
生成网络G和辨别网络D——成对特征匹配(针对属性向量)
为了解决梯度消失问题,向生成器G提出pairwise feature matching objective(成对特征匹配目标),匹配真假图片在辨别器D中的特征。令 f D ( x ) f_D(x) fD(x)表示辨别器D中间层特征(为了简化,采用辨别网络D最后一层FC层的输入),则采用欧几里得距离衡量辨别网络中生成图片和属性图片的特征: L G D = 1 2 ∣ ∣ f D ( x ′ ) − f D ( x a ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 L_{GD}=\frac{1}{2}||f_D(x')-f_D(x^a)||^2_2 LGD=21∣∣fD(x′)−fD(xa)∣∣22。 -
分类网络C——最大化身份信息匹配正确的概率(针对身份向量)
(1)身份信息与标签的正确匹配分类网络C尝试区分不同身份的脸部图像,即最小化损失函数 L C = − E x ∼ P x [ l o g P ( c ∣ x s ) ] L_C=-\mathbb{E}_{x\sim P_x}[logP(c|x^s)] LC=−Ex∼Px[logP(c∣xs)]
(2)身份信息与生成网络G生成图片的正确匹配
为了生成保留身份信息的脸部图片,依然采用该方法以激励 x ′ x' x′和 x s x^s xs在分类网络C中具有相同特征表示。令 f C ( x ) f_C(x) fC(x)表示分类网络C的中间层的输出特征(采用分类网络C最后一个全连接层的输入),特征重构函数损失为 L G C = 1 2 ∣ ∣ f C ( x ’ ) − ∣ f C ( x s ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 L_{GC}=\frac{1}{2}||f_C(x’)-|f_C(x^s)||^2_2 LGC=21∣∣fC(x’)−∣fC(xs)∣∣22。
-
总结说明
(1)组合多层特征仅仅可以稍微提升生成网络G保留身份信息的能力;(2)身份提取网络I和分类网络C共享参数,且可通过脸部分类网络预训练以加快收敛速度。
3.3 非监督训练
生成训练集中没有的脸部图片这一任务要求生成网络G覆盖所有脸部的类内和类间差异。而带标签的训练集在大小、姿势、光照等方面受限,即不具有多样性。所以在网站上随机收集一百万张人脸图像,并用人脸检测器定位人脸。
没有标签的图像可用作(1)身份图片。由于没有标签,所以不加 L I 和 L C L_I和L_C LI和LC。即固定I和C对其他部分进行训练;(2)属性图片。训练方式不变。
3.4 全局目标函数
最终的损失函数是以上所有损失函数的和。即使损失函数很多,但是每个网络只与损失函数的一部分有关,所以很好训练。
训练中将每一次迭代分为两步:(1)重建过程,即 x s = x a x^s=x^a xs=xa;(2)转换过程,即 x a ≠ x s x^a \neq x^s xa=xs。
4. 实验
对每张图片检测其脸部区域,然后对齐并调整尺寸为128*128像素。
对网络 I , C , A I, C, A I,C,A采用VGG网络。 I 和 C I和C I和C共享参数以加快收敛。 G G G是一个反向VGG结构。其池化层改为上采样层,卷积层改为去卷积层。 D D D采用与DCGAN相同的网络结构。批量归一化层用在每个卷积层和去卷积层之后。
4.1 框架分析
为了理解网络每一部分的工作效果,我们采用不同的损失函数组合。在此对比了五种可能:(1)去掉 L G D L_{GD} LGD(2)去掉 L G C L_{GC} LGC(3)去掉transformation训练过程(4)去掉无监督学习过程(5)所有部分都包含的最佳模型。
在数据集中选取了1万个身份,对于每一个身份主体,选取六张照片(这些照片都不在我们的训练集中),一张存放在gallery中,五张用于queries。利用每个queries和随机选取五张属性图片生成五张新的图片,然后寻找gallery中与生成图片最相似的脸,测量其top 1精度。
对于不在数据集中的身份信息,在Multi-PIE中选取六种属性图片。对数据集中的每个人,其中一种属性的脸部作为gallery,queries是原始的脸部图片和剩余五种属性图片生成的图片。

表格显示,每一种成分都对网络做了提升。其中 L G C L_{GC} LGC提升最大。同时我们也衡量了使用真实query图像时的top-1精度,我们的生成图像获得了类似的结果。

图片3显示了量化结果。我们发现去掉transformation训练过程会导致生成结果丢失很多属性细节,尤其是表情信息。去掉 L G D L_{GD} LGD损失会导致生成图片的模糊。去掉 L G C L_{GC} LGC使生成图片无法保留身份信息。加上无监督学习后生成图片表现更好,比如最后一行第一张图片,嘴张得更大。
4.2 KL散度损失
在这里讨论KL散度损失可以移除属性向量中的身份信息。
首先训练有无KL散度损失的连个模型。将数据集中的脸部随机分为两部分,一部分作为训练集,另一部分为验证集。用A提取属性向量,用MLP(多层感知机)训练分类模型来区分不同身份主体的脸部特征。同样测量其top-1精度。

结果如图,有KL散度损失的模型在验证集上top-1精度更低,即不具有更少的身份信息。
4.3 脸部属性转移
脸部属性转移的目标是生成一张组合了 x s x^s xs身份信息和 x a x^a xa属性信息的图片KaTeX parse error: Expected group after '^' at position 2: x^̲'。实验生成两种脸部图片:身份信息在与不在训练集中的脸部图片。
如图,两种表现都很好。
另外本文网络还可以用于脸部对正。即输入一张正脸作为属性图片,网络可以生成保留身份信息的正脸图片。对比之前的工作,本文网络可以保留光照和肤色。
4.4 人脸属性调整
这一部分用来证明生成图片的属性会随潜在向量而不断变化。我们称之为脸部属性调整。
首先选取一对图片 x 1 x_1 x1, x 2 x_2 x2,并用A提取其属性向量 z 1 z_1 z1, z 2 z_2 z2。令 z = α z 1 + ( 1 − α ) z 2 , α ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] z=\alpha z_1+(1-\alpha)z_2, \alpha \in [0, 1] z=αz1+(1−α)z2,α∈[0,1].我们可以逐渐改变其姿态、表情、光照。效果如图。

4.5 人脸对抗实例检测
对抗性实例使系统的安全性存在风险,这一部分用来证明本文的网络不需修改就可用于人脸对抗实例检测。
略。