数据结构:哈夫曼编码(详解)
文章目录
- 前言
- 哈夫曼构造全过程
- 结果展示
- GBK
- UTF-8
- 确立编码
- 函数和全局变量
- 结点详解
- 带头结点优化使用
- 文件读取
- 关于insert深究
- 建树
- 编码
- 加密
- 解密
- 后记
- 完整代码
前言
该代码能够在编译环境 codeblocks 16.01 及 DEV-C++ 5.11 中能够正确运行。关于 cmd gcc 命令行编译或者 Linux 环境下的编译运行。请使用以下命令。
gcc main.c -finput-charset=UTF-8 -fexec-charset=GBK -o main
main.c 是需要编译的文件。
-finput-charset=UTF-8 编译文件对应的编码信息。
-fexec-charset=GBK 指定编译的方式。
main 可执行文件的名字。
注:读取文件为 GBK 格式。
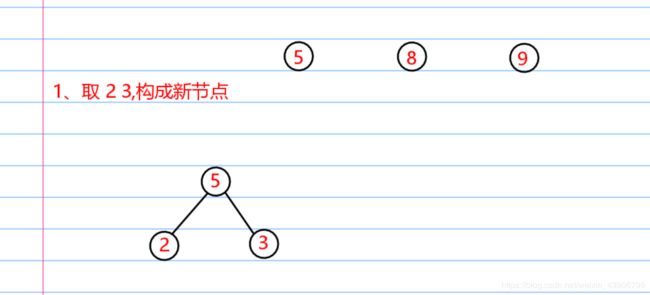
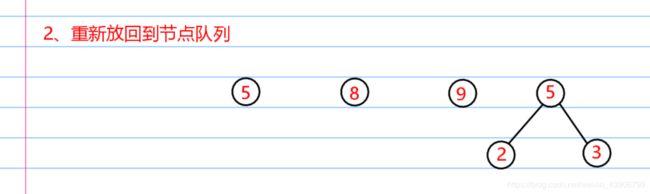
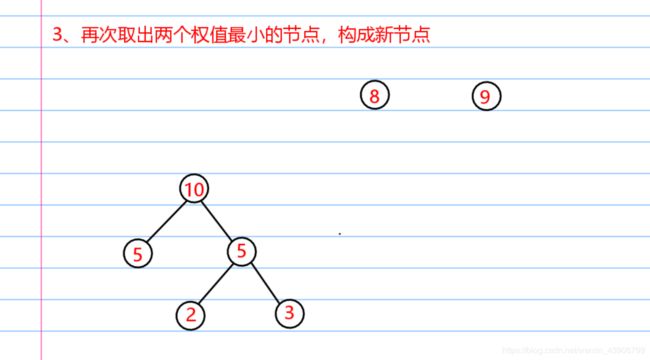
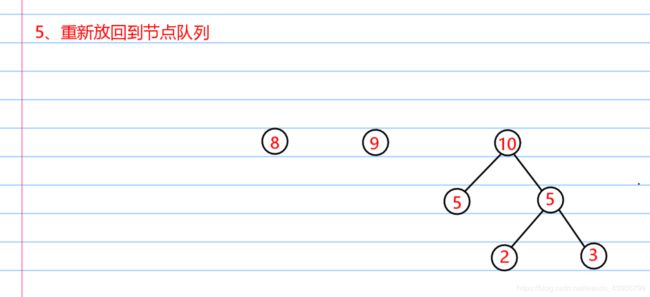
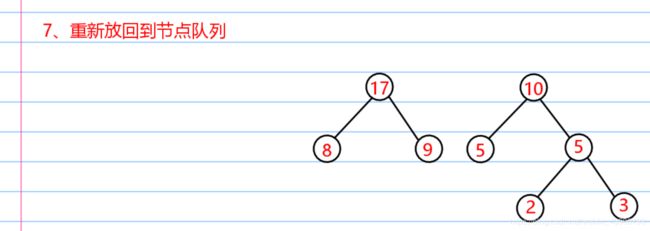
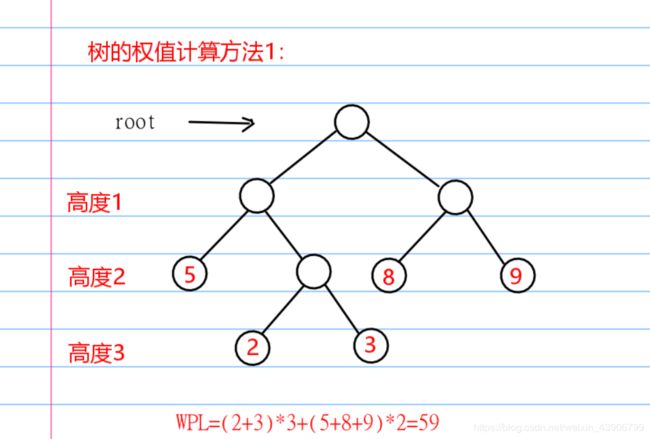
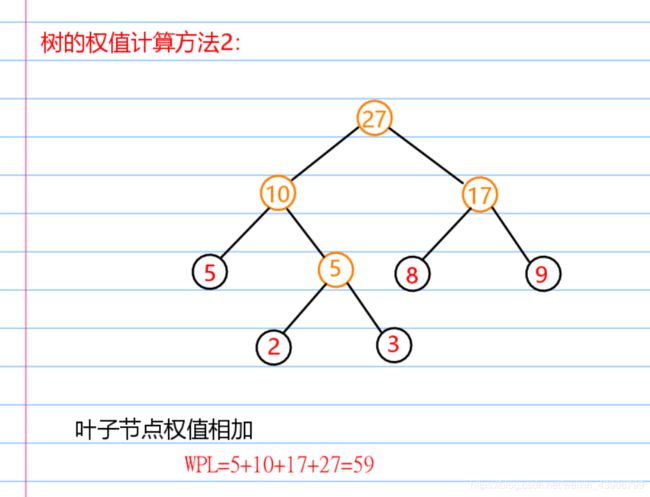
哈夫曼构造全过程
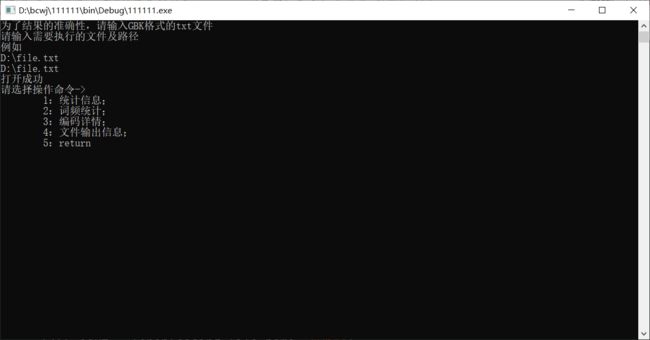
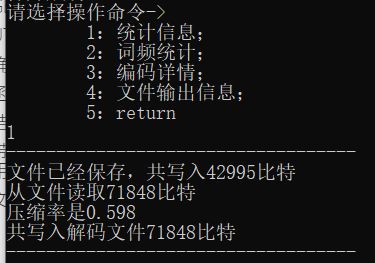
结果展示
数据文件包含GBK格式下的 中文字符,英文字符,特殊字符等
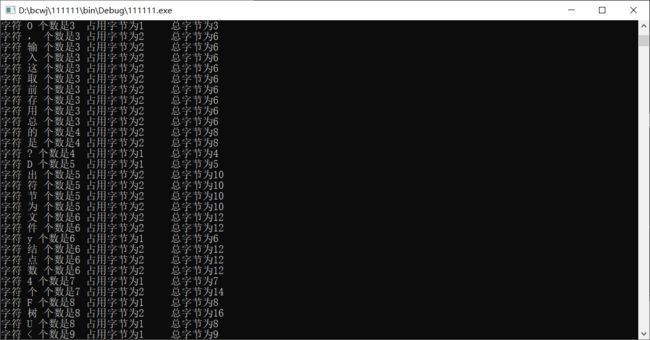
词频统计
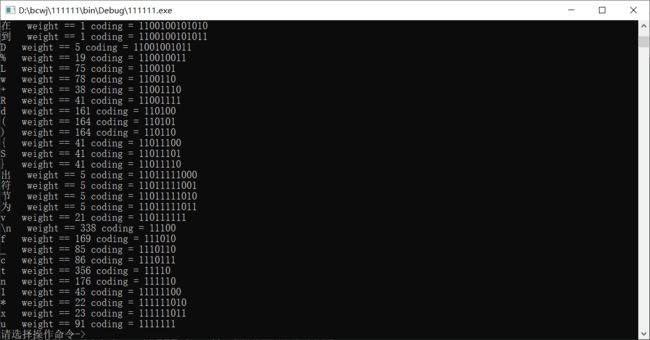
编码展示
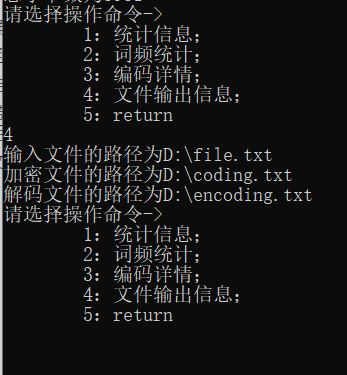
文件输出路径信息(在输入的父级目录下,动态改变)
原读取文件展示
加密文件展示
解码文件展示及对比
GBK
字符有一字节和双字节编码,00–7F范围内是第一个字节,和ASCII保持一致,此范围内严格上说有96个文字和32个控制符号。
之后的双字节中,前一字节是双字节的第一位。总体上说第一字节的范围是81–FE(也就是不含80和FF),第二字节的一部分领域在40–7E,其他领域在80–FE。
具体来说,定义的是下列字节:
| 范围 | 第1字节 | 第2字节 | 编码数 | 字数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水准GBK/1 | A1–A9 |
A1–FE |
846 | 717 |
| 水准GBK/2 | B0–F7 |
A1–FE |
6,768 | 6,763 |
| 水准GBK/3 | 81–A0 |
40–FE (7F除外) |
6,080 | 6,080 |
| 水准GBK/4 | AA–FE |
40–A0 (7F除外) |
8,160 | 8,160 |
| 水准GBK/5 | A8–A9 |
40–A0 (7F除外) |
192 | 166 |
| 用户定义 | AA–AF |
A1–FE |
564 | |
| 用户定义 | F8–FE |
A1–FE |
658 | |
| 用户定义 | A1–A7 |
40–A0 (7F除外) |
672 | |
| 合计: | 23,940 | 21,886 |
双字节符号可以表达的64K空间如下图所示。绿色和黄色区域是GBK的编码,红色是用户定义区域。没有颜色区域是不正确的代码组合。
UTF-8
- 对于UTF-8编码中的任意字节B,如果B的第一位为0,则B独立的表示一个字符(ASCII码);
- 如果B的第一位为1,第二位为0,则B为一个多字节字符中的一个字节(非ASCII字符);
- 如果B的前两位为1,第三位为0,则B为两个字节表示的字符中的第一个字节;
- 如果B的前三位为1,第四位为0,则B为三个字节表示的字符中的第一个字节;
- 如果B的前四位为1,第五位为0,则B为四个字节表示的字符中的第一个字节;
因此,对UTF-8编码中的任意字节,根据第一位,可判断是否为ASCII字符;根据前二位,可判断该字节是否为一个字符编码的第一个字节;根据前四位(如果前两位均为1),可确定该字节为字符编码的第一个字节,并且可判断对应的字符由几个字节表示;根据前五位(如果前四位为1),可判断编码是否有错误或数据传输过程中是否有错误。
确立编码
通过上面可以发现,GBK 编码中文字符少,但是都是双字节,也就是高位和低位。第一个双字节的开始是 81 对应十进制的 129 。
而 UTF-8 编码少数汉字是3个字节,多数汉字是4个字节,统计起来真的不方便,存储都不能存储,怎么统计出现的频率。
于是选择 GBK 编码。
函数和全局变量
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| void insert(LIST head, LIST tmp) | 有序插入结点 |
| LIST find_and_insert(LIST head, LIST tmp) | 弹出内部的结点,然后调用insert函数 |
| void output(LIST head) | 输出这个读取文件的所有字符统计情况 |
| LIST init_LIST(int high, int low, int weight) | 初始化链表信息 |
| TREE tree_node_init(int high, int low, int weight) | 初始化哈夫曼树各个结点 |
| TREE build_tree(LIST head) | 建立哈夫曼树 |
| void print_huffman_pre(TREE Tree) | 前序输出 |
| void update_tree(TREE Tree) | 更新树的信息,也即更新编码信息 |
| void save_file(TREE *a, int right, TREE Tree) | 保存文件 |
| void to_free_tree(TREE Tree) | 释放树 |
| void to_free_list(LIST head) | 释放链表 |
| void coding() | 编码/加密 |
| void decoding(); | 解码 |
| TREE queue[1000]; | 哈夫曼叶子结点信息/密文==密码 |
| int sum_bit_coding = 0; | //编码bit |
| int sum_bit_decoding = 0; | //解码bit |
| char file_in[100]; | 输入文件及路径 |
| char file_out[100]; | 输出文件及路径 |
| void init_main(); | 封装/交互 |
结点详解
typedef struct node *LIST;
typedef struct node *TREE;
struct node
{
int high;
int low;
int weight;
int code_index;
char code[100];
TREE Left;
TREE Right;
LIST NEXT;
};
对于每一个需要储存的字符(结点)信息,我们首先标记的是字符对应的十进制整数值。
这里分为高位和低位,主要是为了汉字服务。
高位储存0-127 ASSIC 码的所有字符。
如果高位读取到汉字 > 128 ,那么低位储存下一个字节的信息,也就是说,高位和低位共同储存一个汉字。
weight 储存权重也就是统计字符的个数。
code_index 编码指针
code[100] 编码数组
构建哈夫曼所需要的左右孩子,构建链表需要的NEXT指针
带头结点优化使用
前面的多项式的原理和实现讲解,已经说的很清楚了,头结点有没有的区别和不同之处。
对应博客链接 多项式运算
头结点的二次使用。
head->high 用来存储 ASSIC 0-127 出现的字符总个数 计算输入bits使用。
head->low 用来存储 汉字 出现的字符总个数 计算输入bits使用。
Tree->weight 用来记录不重复的字符个数;即链表的总长度(头结点不算);又即记录当前构造哈夫曼树的时候的队列剩余的结点个数。
这样的好处是,不用在额外变量记录信息。
文件读取
首先初始化文件指针。
读取方式是按照字符读取,也就是一个一个字节的读取。
但是这个地方我们,需要判断是否是汉字,也就是高位,如果是,读取低位,同存储到这个结点里面,输出的时候同时输出高位和低位就行了。
int ch;
while((ch = fgetc(P)) != EOF)
{
LIST tmp = init_LIST(ch, -1, 1);
if(ch > 128)
tmp->low = fgetc(P);
insert(head, find_and_insert(head, tmp));
}
关于insert深究
基本的插入方法有头插法和尾插法,这个在之前的实验中说过了。
这次的实验还是采用有序尾插法。
因为要统计权值,也就是字符出现的次数,同时哈夫曼树读取两个结点的时候也是要读取权值最小的,所以,直接采用有序尾插法,如果这个字符出现在这个链表怎么办?我这个地方处理方式是 find_and_insert(head, tmp),有的话返回该结点,同时权值++,没用的话吗,返回一个初始化的结点,无论哪种结果,都需要重新插入原有的链表。维持链表的有序状态。
LIST find_and_insert(LIST head, LIST tmp)
{
//统计汉字和其它字符的不重复个数
if(tmp->low != -1) head->low++;
else head->high++;
LIST P = head;
while(P->NEXT)
{
//这个字符相同
if(P->NEXT->high == tmp->high)
{
//汉字相同情况
if(P->NEXT->low != -1 && tmp->low != -1 && P->NEXT->low == tmp->low)
{
//取出当前结点
LIST found = init_LIST(P->NEXT->high, P->NEXT->low, P->NEXT->weight + 1);
//删除
LIST del = P->NEXT;
P->NEXT = P->NEXT->NEXT;
del->NEXT = NULL;
free(del);
return found;
}
if(P->NEXT->low == -1 && tmp->low == -1)
{
//取出当前结点
LIST found = init_LIST(P->NEXT->high, P->NEXT->low, P->NEXT->weight + 1);
//删除
LIST del = P->NEXT;
P->NEXT = P->NEXT->NEXT;
del->NEXT = NULL;
free(del);
return found;
}
}
P = P->NEXT;
}
return tmp;
}
void insert(LIST head, LIST tmp)
{
LIST P = head;
while(P->NEXT)
{
if(tmp->weight < P->NEXT->weight)
break;
P = P->NEXT;
}
//找不到位置
if(!P->NEXT)
{
P->NEXT = tmp;
return;
}
//insert
tmp->NEXT = P->NEXT;
P->NEXT = tmp;
}
建树
上面都是基本的统计情况,包括文件读入,存储,字频统计。
完成之后,就是最重要的环节,建树。
首先把LIST 复制为 TREE(TREE 可以使用链表的所以方法,同时该树,附带头结点,并且权值升序)
基本思路非常明确了,就是不断的取出结点,然后构建成一个树,然后插入到TREE里面。
因为之前我们已经写好了insert函数,所以把结点插入进去还是有序。
同时。之前我们提到 头结点的优化用法 weight 的使用 这个地方就用到了。
记录的是当前队列(森林)(TREE)里面的结点个数(不包含头结点)。
当结点树为1,说明该队列(森林)(TREE)只有一棵树,也就是要求的哈夫曼树。
void coding(TREE Tree)
{
while(Tree->weight > 1)
{
TREE t1 = Tree->NEXT;
Tree->NEXT = Tree->NEXT->NEXT;
TREE t2 = Tree->NEXT;
Tree->NEXT = Tree->NEXT->NEXT;
//add t1 and t2 to t; 合并树
TREE t = tree_node_init(-1, -1, t1->weight + t2->weight);
//左树
t->Left = t1;
//右树
t->Right = t2;
insert(Tree, t);
Tree->weight--;
}
}
编码
树建好了,怎么样才能编码啊,毫无疑问是 层序遍历 编码,因为这样比较简单。
如果从该节点向左,则左孩子的编码为该节点编码 + '0’
如果从该节点向右,则右孩子的编码为该节点编码 + '1’
void update_tree(TREE Tree)
{
TREE a[1000];
int left = 0, right = 0;
if(!Tree) return;
a[right++] = Tree->NEXT;
while(left < right)
{
//左
if(a[left]->Left)
{
a[right++] = a[left]->Left;
strcpy(a[left]->Left->code, a[left]->code);
a[left]->Left->code_index = strlen(a[left]->code);
a[left]->Left->code[a[left]->Left->code_index++] = '0';
//a[left]->Left->code[a[left]->Left->code_index] = '\0';
}
//右
if(a[left]->Right)
{
a[right++] = a[left]->Right;
strcpy(a[left]->Right->code, a[left]->code);
a[left]->Right->code_index = strlen(a[left]->code);
a[left]->Right->code[a[left]->Right->code_index++] = '1';
//a[left]->Right->code[a[left]->Right->code_index] = '\0';
}
left++;
}
save_file(a, right, Tree);
}
加密
直接读取字符,然后写入该字符的密文。
解密
因为是前缀码,该二进制信息唯一,所以不断向后读取字符,然后对比编码信息就行。
后记
window 换行符 \r\n
所以需要特判 if ch == '\n';printf("\r\n")
建树的时候,树是Tree->NEXT开始。(含头结点)。
完整代码
#include