树莓派检测运动目标并辨识类别代码备忘
rgbhistogram.py
import cv2
class RGBHistogram:
def __init__(self, bins):
self.bins = bins
def describe(self, image, mask = None):
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
hist = cv2.calcHist([image], [0, 1, 2],
mask, self.bins, [0, 256, 0, 256, 0, 256])
cv2.normalize(hist, hist)
return hist.flatten()classifier.py
from __future__ import print_function
from rgbhistogram import RGBHistogram
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn import svm
###from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import numpy as np
import argparse
import glob
import cv2
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--images", required = True,
help = "path to the image dataset")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--masks", required = True,
help = "path to the image masks")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
print(args)
imagePaths = sorted(glob.glob(args["images"] + "/*.jpg"))
maskPaths = sorted(glob.glob(args["masks"] + "/*.jpg"))
data = []
target = []
#print(imagePaths)
desc = RGBHistogram([16, 16, 16])
for (imagePath, maskPath) in zip(imagePaths, maskPaths):
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
if image.ndim==2:
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
features = desc.describe(image)
data.append(features)
target.append('A')
print(imagePath)
mask = cv2.imread(maskPath)
if mask.ndim==2:
mask = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
features = desc.describe(mask)
data.append(features)
target.append('B')
print(maskPath)
#print(target)
targetNames = np.unique(target)
le = LabelEncoder()
target = le.fit_transform(target)
(trainData, testData, trainTarget, testTarget) = train_test_split(data, target,test_size = 0.1, random_state = 1)
model = smv.SVC(gamma=0.5, C=1.)
###model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 25, random_state = 42)
model.fit(trainData, trainTarget)
joblib.dump(model, "svm_model.model")
model = joblib.load("svm_model.model")
print(classification_report(testTarget, model.predict(testData),target_names = targetNames))
for i in np.random.choice(np.arange(0, len(maskPaths)), 10):
imagePath = maskPaths[i]
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
#mask = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
features = desc.describe(image)
type = le.inverse_transform(model.predict([features]))[0]
print(imagePath)
print("I think this type is a {}".format(type.upper()))
cv2.imshow("image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)执行方式:
python classify.py –image train_data /A –mask train_data /B
准备训练数据如下:
A类数据:
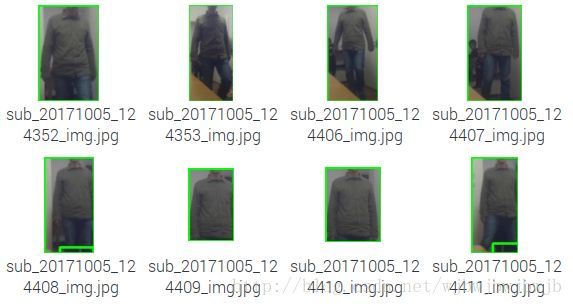
B类数据:

执行训练结果如下:

detectCamera.py
from sklearn.externals import joblib
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from rgbhistogram import RGBHistogram
import argparse
import datetime
import imutils
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-v", "--video", help="path to the video file")
ap.add_argument("-a", "--min-area", type=int, default=500, help="minimum area size")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
model = joblib.load("svm_model.model")
target = []
target.append('A')
target.append('B')
targetNames = np.unique(target)
le = LabelEncoder()
target = le.fit_transform(target)
desc = RGBHistogram([16, 16, 16])
# if the video argument is None, then we are reading from webcam
if args.get("video", None) is None:
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
time.sleep(0.25)
# otherwise, we are reading from a video file
else:
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(args["video"])
# initialize the first frame in the video stream
firstFrame = None
frameCount = 0
# loop over the frames of the video
while True:
# grab the current frame and initialize the occupied/unoccupied
# text
#d1 = datetime.datetime.now()
(grabbed, org_frame) = camera.read()
#d = datetime.datetime.now() - d1
#print("#consuming %dms" % (d.microseconds/1000))
text = "Unoccupied"
# if the frame could not be grabbed, then we have reached the end
# of the video
if not grabbed:
break
frameCount = frameCount+1
if frameCount%10 > 0:
continue
d1 = datetime.datetime.now()
# resize the frame, convert it to grayscale, and blur it
#frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=640)
frame = cv2.resize(org_frame,(320,240),interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (7, 7), 0)
# if the first frame is None, initialize it
if firstFrame is None:
firstFrame = gray
continue
# compute the absolute difference between the current frame and
# first frame
frameDelta = cv2.absdiff(firstFrame, gray)
thresh = cv2.threshold(frameDelta, 25, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
# dilate the thresholded image to fill in holes, then find contours
# on thresholded image
thresh = cv2.dilate(thresh, None, iterations=2)
(_, cnts, _) = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
area = 0;
# loop over the contours
for c in cnts:
# if the contour is too small, ignore it
if cv2.contourArea(c) < args["min_area"]:
continue
# compute the bounding box for the contour, draw it on the frame,
# and update the text
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
if area < w * h:
area = w * h
(bx,by,bw,bh) = (x,y,w,h);
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
text = "Occupied"
# draw the text and timestamp on the frame
#cv2.putText(frame, "Room Status: {}".format(text), (10, 20),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 2)
#cv2.putText(frame, datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %I:%M:%S"),
# (10, frame.shape[0] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.35, (0, 0, 255), 1)
if area > 0:
print("x %d, y %d, w %d, h %d" % (bx, by, bw,by))
cropImg = frame[by:by+bh, bx:bx+bw]
features = desc.describe(cropImg)
type = le.inverse_transform(model.predict([features]))[0]
print("I think this is a {}".format(type.upper()))
cv2.imwrite(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("captured_imgs/sub_%Y%m%d_%I%M%S_img.jpg"),cropImg)
d = datetime.datetime.now() - d1
print("consuming %dms" % (d.microseconds/1000))
if cmp(text,"Occupied") == 0 :
cv2.imwrite(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("captured_imgs/%Y%m%d_%I%M%S_img.jpg"),frame)
# show the frame and record if the user presses a key
cv2.imshow("Security Feed", frame)
#cv2.imshow("Thresh", thresh)
#cv2.imshow("Frame Delta", frameDelta)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
# if the `q` key is pressed, break from the lop
if key == ord("q"):
break
# cleanup the camera and close any open windows
camera.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()执行方式:
python detectCamera.py测试效果如下:
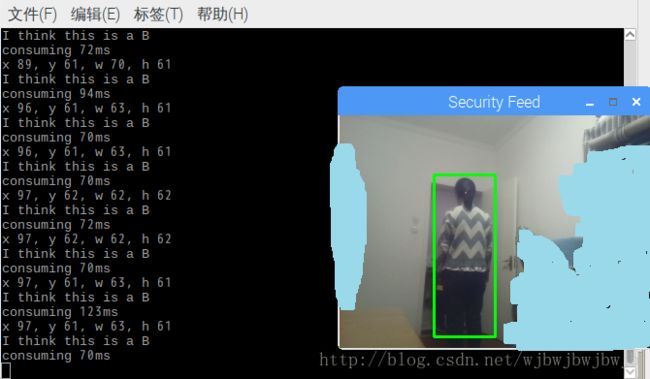
参考:
1. https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/05/25/basic-motion-detection-and-tracking-with-python-and-opencv/
2. http://opencv.org/new-opencv-books.html
3. Practical Python and OpenCV, Case Studies, 3rd Edition.pdf