Redis源码分析(四)——跳表zskiplist
跳跃表(skiplist)是一种随机化的数据,这种数据结构以有序的方式在层次化的链表中保存元素,其效率可以和平衡数媲美,并且其实现比平衡树简单得多。
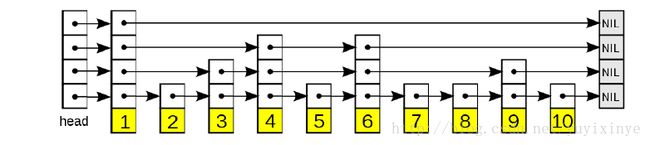
SkipList基本结构示意图
如图,跳表的主要构成:
* 表头(head):负责维护跳表的节点指针。
* 跳表节点:保存着元素值,以及多个层结构。
* 层:保存着一个前向节点指针,以及一个该节点在改层的前向跨越的节点计数。高层的指针越过的节点数 量大等于低层的指针,为了提高查找效率,程序总是从高层 先开始访问,然后随着元素范围的缩小,逐 渐降到低层。
*表尾(tail):全部由NULL组成,表示跳表的末尾。
Reids实现的跳表,有如下特点:
1、按score值比较排序存放,允许多个不同member的score值重复。
2、在进行对比操作时,不仅要检查score值,还要检查member,以唯一确定元素。
3、每个节点都带有高度为1层(最底层)的后退节点,用于从表尾方向向表头迭代。
前面在分析Leve了DB时对其跳表实现做过较浅的分析http://blog.csdn.net/yuyixinye/article/details/39314381。。在此对跳表的主要API函数进行剖析。
主要在redis.h/t_zset.c两个文件。
基本数据结构 redis.h:
//跳表节点
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
robj *obj;//member对象
double score;//分值 作为索引
struct zskiplistNode *backward;//后向指针
struct zskiplistLevel {//节点所在的层
struct zskiplistNode *forward;//前向指针
unsigned int span;//该层向前跨越的节点数量
} level[]; //节点层结构 数组
} zskiplistNode;
//跳表
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;//头节点 尾节点
unsigned long length;//节点数量
int level;//目前表内节点的最大层数
} zskiplist;
/* Struct to hold a inclusive/exclusive range spec by score comparison. */
//一个score的范围min max的结构体。区间开/闭?
typedef struct {
double min, max;
int minex, maxex;//是否min和max包含在区间中 /* are min or max exclusive? */
} zrangespec;
/* Struct to hold an inclusive/exclusive range spec by lexicographic comparison. */
//一个字典顺序的范围 开/闭
typedef struct {
robj *min, *max; /* May be set to shared.(minstring|maxstring) */
int minex, maxex; /* are min or max exclusive? */
} zlexrangespec;
/********************************************/
//跳表API函数
zskiplist *zslCreate(void);//创建并初始化一个新的跳表
void zslFree(zskiplist *zsl);//释放给定跳表
//将一个包含给定score和member的新节点插入到指定跳表
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, robj *obj);
//
unsigned char *zzlInsert(unsigned char *zl, robj *ele, double score);
//删除指定节点
int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, robj *obj);
//找到跳表中第一个符合给定范围的节点
zskiplistNode *zslFirstInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range);
//创建一给定score和member的跳表节点,该节点的层数为level(该层数是随机生成的)
zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, robj *obj) {
zskiplistNode *zn = zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));
zn->score = score;
zn->obj = obj;
return zn;
}
zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {
int j;
zskiplist *zsl;
zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));//分配空间
zsl->level = 1;//初始化跳表中节点最大层数为1
zsl->length = 0;//初始化节点数为0
zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL);//头节点默认为32层,所有节点层数不得超过该值。该跳表之多可存储2^32个元素
for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {//初始化头结点的 层结构数组,都指向NULL,即尾节点
zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;
zsl->header->level[j].span = 0; //跳表为空,因此所有跨度为0
}
zsl->header->backward = NULL;//初始化节点 后向指针为null
zsl->tail = NULL;//尾节点始终由NULL组成,因此每当前进到NULL时即表明到了末尾
return zsl;
}
//释放给定节点
void zslFreeNode(zskiplistNode *node) {
decrRefCount(node->obj);//递减引用计数
zfree(node);//释放
}
//释放跳表 注意:从最底层(跨度始终为0 ,因此保证不会遗漏节点)向后逐个节点释放。
void zslFree(zskiplist *zsl) {
zskiplistNode *node = zsl->header->level[0].forward, *next;
zfree(zsl->header);//释放头节点
while(node) {//从最底层向后逐个节点释放
next = node->level[0].forward;
zslFreeNode(node);
node = next;
}
zfree(zsl);
}
/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create.
* The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
* (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher
* levels are less likely to be returned. */
//为新创建节点返回一个介于[1,ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL=32]之间的随机层数
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1;
while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))
level += 1;
return (levelheader;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {//从顶层往下
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];//每次下沉到新一层,开始时该新位置所跨过的总节点数
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
compareStringObjects(x->level[i].forward->obj,obj) < 0))) {//继续在该层向后移
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;//该层下沉位置还没找到,继续递增
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
/* we assume the key is not already inside, since we allow duplicated
* scores, and the re-insertion of score and redis object should never
* happen since the caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table
* if the element is already inside or not. */
level = zslRandomLevel();//为新节点随机生成 层数
if (level > zsl->level) {//如果新节点层数大于当前跳表所有节点中的最大层数
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {//更新新增层数的相关部分
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
zsl->level = level;//更新跳表当前最大层数
}
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,obj);//创建新节点
//将新节点插入到前面找到的跳表中的位置
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) { //从最底层开始连接插入
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);//填充新节点的前向跨度
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;//更新下沉节点下沉层的前向节点
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
//递增新节点前面比其层数更大节点的较大层结果的跨度
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];//更新新节点的后退指针。 后腿指针始终在最底层后后
if (x->level[0].forward)//更新节点的前向节点的后退指针
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
zsl->length++;
return x;
}
/* Internal function used by zslDelete, zslDeleteByScore and zslDeleteByRank */
//删除节点。 过渡函数 update数组由调用函数传入
void zslDeleteNode(zskiplist *zsl, zskiplistNode *x, zskiplistNode **update) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < zsl->level; i++) {//更新下沉层的前向指针和前向跨度
if (update[i]->level[i].forward == x) {
update[i]->level[i].span += x->level[i].span - 1;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x->level[i].forward;
} else {
update[i]->level[i].span -= 1;
}
}
if (x->level[0].forward) {//更新删除节点的相邻前向节点的后向指针
x->level[0].forward->backward = x->backward;
} else {
zsl->tail = x->backward;
}
while(zsl->level > 1 && zsl->header->level[zsl->level-1].forward == NULL)//更新跳表最大节点层数
zsl->level--;
zsl->length--;//递减节点数
}
/* Delete an element with matching score/object from the skiplist. */
//删除指定节点,存在该节点并删除返回1,如果不存在则返回0.
int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, robj *obj) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;//下沉转折节点
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {//遍历查找删除节点的位置,并记录每层的下沉节点,最后一个记录的节点即目标节点的前面一个节点
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
compareStringObjects(x->level[i].forward->obj,obj) < 0)))
x = x->level[i].forward;
update[i] = x;
}
/* We may have multiple elements with the same score, what we need
* is to find the element with both the right score and object. */
//表中可能有多个有相同score的节点,因此我们需要寻找score和member都相同的节点
x = x->level[0].forward;//x为目标节点
if (x && score == x->score && equalStringObjects(x->obj,obj)) {
zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);
zslFreeNode(x);
return 1;
}
return 0; /* not found */
}
//判断value是否大于给定区间的最小值
static int zslValueGteMin(double value, zrangespec *spec) {
return spec->minex ? (value > spec->min) : (value >= spec->min);
}
//判断value是否小于给定区间最大值
static int zslValueLteMax(double value, zrangespec *spec) {
return spec->maxex ? (value < spec->max) : (value <= spec->max);
}
/* Returns if there is a part of the zset is in range. */
//判断是否存在一部分元素的score在给定区间的中(给定区间时,需要设置区间的左右端点的开闭)
int zslIsInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range) {
zskiplistNode *x;
/* Test for ranges that will always be empty. */
//是否为0区间,若是返回0
if (range->min > range->max ||
(range->min == range->max && (range->minex || range->maxex)))//minex/maxex为真表示不包含区间的左/右端点
return 0;
x = zsl->tail;//不清楚:跳表的tail始终未null,还是指向跳表最后一个节点?
if (x == NULL || !zslValueGteMin(x->score,range))//如果跳表最后一个节点小于区间左端点,返回0
return 0;
x = zsl->header->level[0].forward;
if (x == NULL || !zslValueLteMax(x->score,range))//如果跳表第一个节点大于区间右端点,返回0
return 0;
//否则必然有部分或全部节点在给定区间内,返回1
return 1;
}
/* Find the first node that is contained in the specified range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
//返回在给定区间中的第一个节点指针,如果不存在则返回NULL
//注意效率: 只当确定有部分元素在给定区间中时才去遍历查找,从而避免盲目的遍历
zskiplistNode *zslFirstInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range) {
zskiplistNode *x;
int i;
/* If everything is out of range, return early. */
//首先判断是否 没有任何元素在区间中,如果是则及时返回,从而避免了无用了遍历查找过程!
if (!zslIsInRange(zsl,range)) return NULL;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* Go forward while *OUT* of range. */
while (x->level[i].forward &&
!zslValueGteMin(x->level[i].forward->score,range))
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* This is an inner range, so the next node cannot be NULL. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
redisAssert(x != NULL);
/* Check if score <= max. */
if (!zslValueLteMax(x->score,range)) return NULL;
return x;
}
/* Find the last node that is contained in the specified range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
//返回在给定区间中的最后一个节点指针。 如果没有节点在该区间中返回null
zskiplistNode *zslLastInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range) {
zskiplistNode *x;
int i;
/* If everything is out of range, return early. */
if (!zslIsInRange(zsl,range)) return NULL;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* Go forward while *IN* range. */
while (x->level[i].forward &&
zslValueLteMax(x->level[i].forward->score,range))
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* This is an inner range, so this node cannot be NULL. */
redisAssert(x != NULL);
/* Check if score >= min. */
if (!zslValueGteMin(x->score,range)) return NULL;
return x;
}
/* Delete all the elements with score between min and max from the skiplist.
* Min and max are inclusive, so a score >= min || score <= max is deleted.
* Note that this function takes the reference to the hash table view of the
* sorted set, in order to remove the elements from the hash table too. */
//删除跳表中在给定区间中的所有节点(基于score的比较),返回删除的节点个数。 同时在字典有序集中也把这些节点删除
unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByScore(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range, dict *dict) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned long removed = 0;//删除的元素计数
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {//记录每层小于(小等于)给定区间左端点的临界节点
while (x->level[i].forward && (range->minex ?
x->level[i].forward->score <= range->min :
x->level[i].forward->score < range->min))
x = x->level[i].forward;
update[i] = x;
}
/* Current node is the last with score < or <= min. */
x = x->level[0].forward;//x即为跳表中大于(区间不包括左端点)或者大等于(区间包括左端点)的第一个节点
/* Delete nodes while in range. */
while (x &&
(range->maxex ? x->score < range->max : x->score <= range->max))//当x确实在给定区间中,则删除该节点
{
zskiplistNode *next = x->level[0].forward;
zslDeleteNode(zsl,x,update);
dictDelete(dict,x->obj);//在字典集中删除该节点的member
zslFreeNode(x);//释放该节点
removed++;//计数递增
x = next;//目标节点更新为next节点
}
return removed;
}
//删除跳表中在给定区间中的所有节点(基于member的字典顺序的比较),返回删除的节点个数。 同时在字典有序集中也把这些节点删除
unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByLex(zskiplist *zsl, zlexrangespec *range, dict *dict) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned long removed = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
!zslLexValueGteMin(x->level[i].forward->obj,range))
x = x->level[i].forward;
update[i] = x;
}
/* Current node is the last with score < or <= min. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
/* Delete nodes while in range. */
while (x && zslLexValueLteMax(x->obj,range)) {
zskiplistNode *next = x->level[0].forward;
zslDeleteNode(zsl,x,update);
dictDelete(dict,x->obj);
zslFreeNode(x);
removed++;
x = next;
}
return removed;
}
/* Delete all the elements with rank between start and end from the skiplist.
* Start and end are inclusive. Note that start and end need to be 1-based */
//删除跳表中在给定区间中的所有节点(索引区间,为闭区间),返回删除的节点个数。 同时在字典有序集中也把这些节点删除
//注意:索引从1开始(header视为第一个节点)
unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned int start, unsigned int end, dict *dict) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned long traversed = 0, removed = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward && (traversed + x->level[i].span) < start) {
traversed += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
traversed++;
x = x->level[0].forward;
while (x && traversed <= end) {
zskiplistNode *next = x->level[0].forward;
zslDeleteNode(zsl,x,update);
dictDelete(dict,x->obj);
zslFreeNode(x);
removed++;
traversed++;
x = next;
}
return removed;
}
/* Find the rank for an element by both score and key.
* Returns 0 when the element cannot be found, rank otherwise.
* Note that the rank is 1-based due to the span of zsl->header to the
* first element. */
//查找给定节点的索引
//注意:索引从1开始(header视为第一个节点)
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, robj *o) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long rank = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
compareStringObjects(x->level[i].forward->obj,o) <= 0))) {
rank += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* x might be equal to zsl->header, so test if obj is non-NULL */
if (x->obj && equalStringObjects(x->obj,o)) {
return rank;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* Finds an element by its rank. The rank argument needs to be 1-based. */
//查找给定索引的节点。 索引基于1
zskiplistNode* zslGetElementByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned long rank) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long traversed = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward && (traversed + x->level[i].span) <= rank)
{
traversed += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
if (traversed == rank) {
return x;
}
}
return NULL;
} 疑问: 尾(tail)初始化时里面全部存放NULL,后来插入节点后,tail始终是全NULL,以表示跳表的末尾,还是指向了跳表的最后一个节点?(应该是前者,但是那样有些代码没有理解明白)