android-5.0 sensor框架简介
1.sensor框架
Android Sensor 主要包括3 大部分,各个部分的主要功能如下:
Application Framework
这一部分主要包括Sensor Manager,功能是为Application提供 Java API接口,以便Application可以开启所需的 Sensor 并获取数据。
Libraries
这一部分主要有Sensor Service和Sensor HAL(硬件抽象层)构成,Sensor Service主要实现了Sensor 数据流和控制流,Sensor HAL实现了 Sensor 的具体操作和数据获取功能。同时,它还进行虚拟 Sensor,电子罗盘等相关的算法处理过程。此模块通常以一个动态链接库的形式提供。
Linux Kernel
这一部分是 Sensor 的驱动程序,通过I2C接口读写sensor的寄存器来进行sensor的控制和数据读取。
2.Sensor Manager
该类主要封装了 Sensor 相关的 API ,提供给 Application 使用。
文件路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SensorManager.java
SystemSensorManager
该类主要实现 SensorManager 控制和数据获取的逻辑。
文件路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SystemSensorManager.java
android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
该文件负责 jave 层和 native 层通信的 JNI 实现,上层的 Java 代码通过 JNI 调用 Native 层提供的服务。
文件路径:frameworks/base/core/jni/android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
SensorManager.cpp
Sensor 在 Native 层的客户端,负责与服务端 SensorService.cpp 的通信
文件路径:frameworks/native/libs/gui/SensorManager.cpp
3.Sensor Service
SensorService文件路径:frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorService.cpp
BinderService
BinderService是Android Service框架的主要类,它提供了Service生命周期管理、进程间通信、请求响应处理等功能。Android中的绝大部分 Service都会继承此类。
文件路径:frameworks/native/include/binder/BinderService.h
BnSensorServer
该类提供类 Sensor 信息获取以及SensorEventConnection 创建的功能。
文件路径:frameworks/native/include/gui/ISensorServer.h
SensorEventConnection
SensorEventConnection 是 Sensor 数据的传输通道,当 Client 开始监听某一个 Sensor 是,一个对应的 SensorEventConnection 将会被创建,Server 端在接收到 Sensor 数据后,通过写入到 SensorEventConnection 传递给 Client 端。
文件路径:frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISensorEventConnection.cpp
Bittube
该类为单向字节管道,提供进程间单向数据通信功能。SensorEventConnection 是基于 Bittube 实现的。
文件路径:frameworks/native/libs/gui/BitTube.cpp
SensorDevice
该类负责管理和维护系统中的所有Sensor,封装了 Sensor 的使能、配置、数据读取等功能。
文件路径:frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorDevice.cpp
4.Sensor HAL
HAL相关代码:
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h
vendor/mediatek/proprietary/hardware/sensor/sensors.c
vendor/mediatek/proprietary/hardware/sensor/nusensors.cpp
vendor/mediatek/proprietary/hardware/sensor/hwmsen_chip_info.c
Android 定义了一系列 Sensor HAL 接口,实际的 Sensor HAL 库需要实现这些接口,主要的接口如下:
4.1 SensorList
SensorList 定义了 HAL 层提供的 Sensor,提供 Sensor 类型、供应商、功耗等信息。同时,HAL 层需要实现获取 SensorList 的回调接口。
struct sensor_t sSensorList[MAX_NUM_SENSOR] =
{
#ifdef CUSTOM_KERNEL_ACCELEROMETER
{
.name = ACCELEROMETER,
.vendor = ACCELEROMETER_VENDER,
.version = 3,
.handle = ID_ACCELEROMETER+ID_OFFSET,
.type = SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER,
.maxRange = ACCELEROMETER_RANGE,//32.0f,
.resolution = ACCELEROMETER_RESOLUTION,//4.0f/1024.0f,
.power = ACCELEROMETER_POWER,//130.0f/1000.0f,
.minDelay = 10000,
.maxDelay = 1000000,
.reserved = {}
},
#endif
#if defined(CUSTOM_KERNEL_ALSPS) || defined(CUSTOM_KERNEL_PS)
{
.name = PROXIMITY,
.vendor = PROXIMITY_VENDER,
.version = 1,
.handle = ID_PROXIMITY+ID_OFFSET,
.type = SENSOR_TYPE_PROXIMITY,
.maxRange = PROXIMITY_RANGE,//1.00f,
.resolution = PROXIMITY_RESOLUTION,//1.0f,
.power = PROXIMITY_POWER,//0.13f,
.reserved = {}
},
#endif
......
}
static int sensors__get_sensors_list(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list)
{
ALOGD(" sSensorList addr =%p, module addr =%p\r\n",sSensorList,module);
ALOGD(" ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList) =%d SENSORS_NUM=%d MAX_NUM_SENSOR=%d \r\n",ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList), SENSORS_NUM, MAX_NUM_SENSOR);
*list = sSensorList;
return ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList);
}
HAL 层需要定义一个 sensors_module_t,供系统在启动时加载 Sensor HAL 动态库。sensors_module_t 向上层注册获取 SensorList 和获取 Sensor 控制接口的相关回调函数。
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
.open = open_sensors
};
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "MTK SENSORS Module",
.author = "Mediatek",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list,
};
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
ALOGD("%s: name: %s! fwq debug\r\n", __func__, name);
return init_nusensors(module, device);
}
4.3 Sensor 控制和数据获取接口
HAL 层还需要提供实际控制和获取 Sensor 数据的接口,SensorService 中对 Sensor 的控制和数据的获取最终会调用到这些接口。
struct sensors_poll_context_t {
struct sensors_poll_device_1 device;// must be first
sensors_poll_context_t();
~sensors_poll_context_t();
int activate(int handle, int enabled);
int setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns);
int pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count);
int batch(int handle, int flags, int64_t samplingPeriodNs, int64_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs);
int flush(int handle);
.....
}
static int poll__close(struct hw_device_t *dev)
{
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
if (ctx) {
delete ctx;
}
return 0;
}
static int poll__activate(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int enabled) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->activate(handle-ID_OFFSET, enabled);
}
static int poll__setDelay(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int64_t ns) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->setDelay(handle-ID_OFFSET, ns);
}
static int poll__poll(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->pollEvents(data, count);
}
static int poll__batch(struct sensors_poll_device_1 *dev,
int handle, int flags, int64_t samplingPeriodNs, int64_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->batch(handle-ID_OFFSET, flags, samplingPeriodNs, maxBatchReportLatencyNs);
}
static int poll__flush(struct sensors_poll_device_1 *dev,
int handle) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->flush(handle-ID_OFFSET);
}
int init_nusensors(hw_module_t const* module, hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
sensors_poll_context_t *dev = new sensors_poll_context_t();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_1));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
#if defined(SENSOR_BATCH_SUPPORT) || defined(CUSTOM_KERNEL_SENSORHUB)
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1;
#else
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0;
#endif
dev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;
dev->device.batch = poll__batch;
dev->device.flush = poll__flush;
*device = &dev->device.common;
status = 0;
return status;
}
5.Sensor Framework的初始化流程
5.1 SensorService 初始化
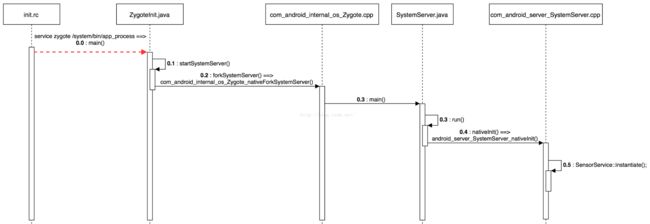
Kernel 在启动完成后,会执行 init 程序,该程序接着解析 init.rc 文件,启动 zygote,最终会执行 Zyoteinit.java 中的 main 函数。
在 Zygoteinit 的main 函数执行过程中,会调用 startSystemServer 接口,该接口最终会调用 native 层的 nativeforkSystemServer 接口,进而启动 SystemServer ,调用其 main 函数。
在 SystemServer 的 main 函数中,会调用对应的 nativeInit 接口。在 nativeInit 中,会创建第一个 SensorService 实例。当 SensorService 第一个实例创建时,其 onFirstRef 接口将会被调用。
在 SensorService 的 onFirstRef 接口中,会创建 SensorDevice 的实例。在 SensorDevice 的构造函数中,会调用 hw_get_module 接口加载 Sensor HAL 的动态库,接着调用 Sensor HAL 提供的 open 接口,执行 Sensor HAL 的初始化。 接着 SensorService 通过 SensorDevice,调用 Sensor HAL 提供的 get_sensors_list 接口,获取所支持的 Sensor 信息。 而后,SensorService 会创建一个 Looper 和 SensorEventAckReceiver。其中 Looper 用于 enable sensor 后,进行数据的接收;而 SensorEventAckReceiver 则用于在 dispatch wake up sensor event 给上层后,接收上层返回的确认ACK。 至此,SensorService 初始化完毕。
5.2 Sensor Manager 初始化
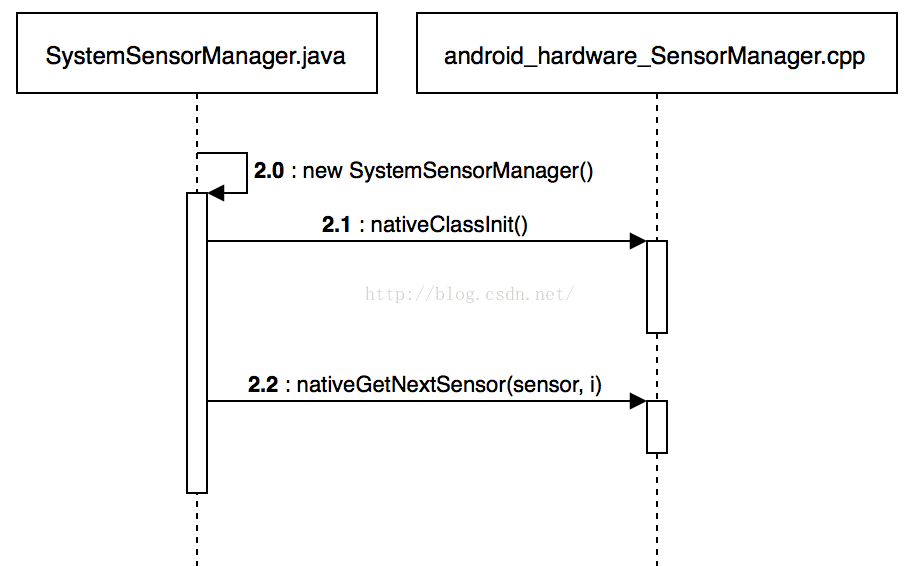
APP 在获取 Sensor 数据前,需要获取一个 SensorManager 对象。而在其构造函数中,会先调用 nativeClassInit 和 nativeGetNextSensor 获取系统支持的所有 Sensor 的参数(注:nativeClassInit 只会调用一次),包括名称、类型等参数。后续的相关接口,会用到这些参数。
6.Sensor Framework的数据流程分析
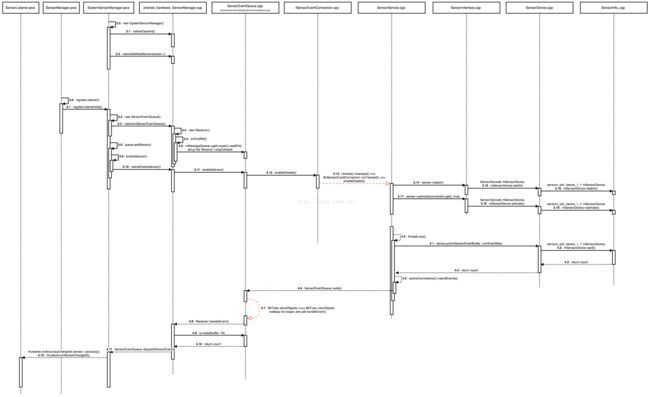
当上层调用 registerListener 接口时,相应的 sensor 就会被 enable。SensorService 在调用 HAL 提供的 enable 接口前,会先调用 batch 接口,对 sensor 的采样率、数据上报频率等进行配置。另外,如果 sensor 已经被 enable 了,那么 SensorService 就只调用 batch 和 flush 接口。 SensorService 在 onFirstRef 时创建了一个 Looper,该 Looper 的执行线程会调用 poll 接口,并阻塞在 sensor 的数据管道,当 sensor 有数据返回时,SensorService 会通过 SensorEventQueue 发送到上层,并最终分发到各个 listener。
