认识C语言的动态内存分配
文章目录
- 1. 引言
- 2. 动态内存分配
- 2.1 malloc()和calloc()的使用方法
- 2.2 malloc()和calloc()的区别
- 2.3 free()和realloc()
- 参考文献
1. 引言
数组是存储在连续内存位置的项的集合,在实际使用中,往往需要增加或减少数组长度,这种情况下出现了动态内存分配(Dynamic Memory Allocation)。在程序运行时,改变数据结构(例如数组)大小的过程就被定义为C语言的动态内存分配。在 /usr/include/stdlib.h 头文件中,C定义了4个函数,以方便C编程中的动态内存分配,它们是malloc()、calloc()、realloc()和free(),分别用于分配、重新分配和释放内存。
2. 动态内存分配
2.1 malloc()和calloc()的使用方法
malloc(memory allocation的缩写)方法用于动态分配具有指定大小的单个大块内存。它返回void类型的指针,其指针类型可以灵活转换,同时使用默认garbage value(内存中存储的随机值)初始化内存块。其语法格式为:
ptr = (指针转换格式*) malloc(分配的字节数)
例如:
ptr = (int*) malloc(100 * sizeof(int));
一般情况下int占用4字节,整个语句会分配400字节的内存,指针ptr以int形式存储首字节的地址。如果空间不足,则分配失败并返回空(NULL)指针。示例:
#include正常情况下打印分配的内存内容及地址:
Please input the number of memory, the suggest range is [0,256]: 2
ptr[0] = 0, ptr address is 0x16eb010
ptr[1] = 0, ptr address is 0x16eb014
如果需要分配的内存过大,返回空指针:
Please input the number of memory, the suggest range is [0,256]: 999999999
Your input number is out of range.
calloc(continuous allocation的缩写)方法与malloc()类似,用于动态分配指定类型的指定数量的内存块。它用默认值“0”初始化每个块。语法格式为:
ptr = (指针转换格式*)calloc(元素总数, 单一元素所占字节数);
2.2 malloc()和calloc()的区别
程序将它的可用内存分为3部分来存储变量:存储静态变量的静态存储区、存储自动变量的栈、存储动态分配变量的堆。静态变量的生命周期贯穿程序始终;自动变量位于函数代码块中,随着函数的逐层调用开始占用内存,随着函数调用结束反向释放内存,符合栈后进先出的特点;动态分配变量的特点是可以在一个函数中创建内存块,在其他函数中释放,存取灵活的同时会造成内存使用的碎片化,所以动态内存往往导致进程比使用栈内存慢。
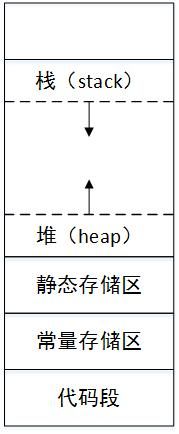
malloc()和calloc()是动态分配内存的库函数,这意味着在程序执行时从堆(heap)中分配内存。它们的区别不大:
- 初始化:malloc()不初始化分配的内存,如果在初始化内存之前访问内存内容,可能会得到 segmentation fault error 或是 garbage value;calloc()分配内存并将内存块初始化为0。
- 当malloc()分配单一元素的内存大小时,配合memset()函数实现与calloc()相同的功能。
ptr = malloc(size);
memset(ptr, 0, size);
一般使用malloc()而不是calloc(),因为malloc()比calloc()快,除非需要将内存初始化为0。如果需要复制内存,malloc将是一个更好的选择。
2.3 free()和realloc()
free()方法用于动态地取消分配内存。使用函数malloc(和calloc()分配的内存不会自行释放分配。因此,每当动态内存分配发生时,都会通过free()方法释放内存来减少内存的浪费。语法为:
free(ptr);
realloc(reallocation)方法用于动态更改以前分配的内存大小。换言之,如果先前借助malloc或calloc分配的内存不足,则可以使用realloc动态扩大变量占用的内存。原有内存块将保持现有值,新块将使用默认garbage value初始化。语法为:
ptr = realloc(ptr, newSize);
where ptr is reallocated with new size 'newSize'.
参考文献
[1] RishabhPrabhu.Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free() and realloc()[EB/OL].https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dynamic-memory-allocation-in-c-using-malloc-calloc-free-and-realloc/,2020-01-01.
[2] chakradharkandula, shubham_singh, Navfal, HarshitHiremath.Difference Between malloc() and calloc() with Examples[EB/OL].https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-malloc-and-calloc-with-examples/,2020-01-01.
[3] ElementLS.堆栈的知识[EB/OL].https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34681978,2018-03-21.