lwip mqtt + mbed TLS
https://mcuoneclipse.com/2017/04/17/tutorial-secure-tls-communication-with-mqtt-using-mbedtls-on-top-of-lwip/
Tutorial: Secure TLS Communication with MQTT using mbedTLS on top of lwip
Posted on April 17, 2017 by Erich Styger
One of the most important aspects of the ‘IoT’ world is having a secure communication. Running MQTT on lwip (see “MQTT with lwip and NXP FRDM-K64F Board“) is no exception. Despite of the popularity of MQTT and lwip, I have not been able to find an example using a secure TLS connection over raw/native lwip TCP :-(. Could it be that such an example exists, and I have not found it? Or that someone implemented it, but has not published it? Only what I have found on the internet are many others asking for the same kind of thing “running MQTT on lwip with TLS”, but there was no answer? So I have to answer my question, which seems to be a good thing anyway: I can learn new things the hard way :-).
Block diagram MQTT Application with TLS using lwip
Outline
This article describes how to enable a bare-metal (no RTOS) in RAW/native (no sockets, TCP only) lwip application running the MQTT protocol with TLS.
The project used in this article is available on GitHub: https://github.com/ErichStyger/mcuoneclipse/tree/master/Examples/MCUXpresso/FRDM-K64F/FRDM-K64F_lwip_lwip_mqtt_bm
The project runs a MQTT client application which initiates TLS handshaking and then communicates securely with a Mosquitto broker.
Prerequisites: Software/Tools
In this article I have used the following software and tools:
- MQTT broker running with TLS on port 8883, e.g. see Enable Secure Communication with TLS and the Mosquitto Broker
- MCUXpresso IDE v10.0.0 b344: http://www.nxp.com/mcuxpresso/ide
- MCUXpresso SDK for FRDM-K64F: https://mcuxpresso.nxp.com/ which includes
- lwip 2.0.0
- mbed TLS 2.3.0
- MQTT lwip stub from lwip 2.0.2: https://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/lwip/
- mbed TLS 2.4.2 (Apache): https://tls.mbed.org/download
- Optional: Processor Expert v3.2.0 (see “MCUXpresso IDE: Installing Processor Expert into Eclipse Neon“)
- TCP based (raw) example, e.g. the lwip tcp ping application (or the project from MQTT with lwip and NXP FRDM-K64F Board).
But any other software/tool combination should do it too :-).
mbed TLS
As outlined in “Introduction to Security and TLS (Transport Layer Security)“, I have selected mbed TLS because its licensing terms are very permissive (Apache).
Get mbed TLS from https://tls.mbed.org/download (I recommend the Apache version as it is permissive).
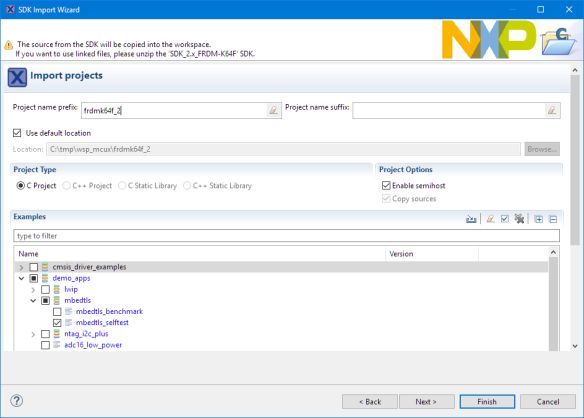
Another way is to get it from the NXP MCUXpresso SDK for the FRDM-K64F. Use the ‘import SDK examples’ function from the quickstart panel and import the mbedtls_selftest example. The advantage of this method is that it comes with the random number generator drivers (RNG):
mbed tls in MCUXpresso SDK
Adding mbedTLS
From the mbed TLS distribution, add the ‘mbedtls’ folder to the project. You need
- mbedtls\include\mbedtls
- mbedtls\library
The mbed TLS implementation uses a ‘port’ which takes advantage of the hardware encryption unit of the on the NXP Kinetis K64F device. That ‘port’ is part of the MCUXpresso SDK, place it inside mbedtls\port.
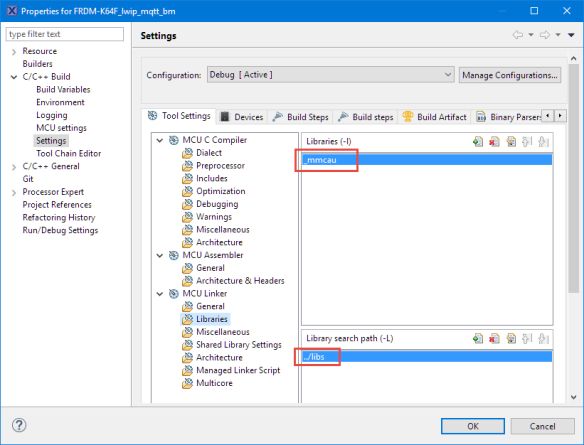
And finally I need the driver for the mmCAU (Memory-Mapped Cryptographic Acceleration Unit) of the NXP Kinetis device:
- mmcau_common: common mmCAU files and interface
- \libs\lib_mmcau.a: library with cryptographic routines
![]()
mbedtls and MCUXpresso SDK Files
The mbed configuration file is included with a preprocessor symbol. Add the following to compiler Preprocessor defined symbols:
MBEDTLS_CONFIG_FILE='"ksdk_mbedtls_config.h"'
MBEDTLS_CONFIG_FILE Macro
Next, add the following to compiler include path settings so it can find all the needed header files:
"${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/mbedtls/port/ksdk}"
"${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/mbedtls/include/mbedtls}"
"${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/mbedtls/include}"
"${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/mmcau_common}"
mbedtls includes
And add the mmCAU library to the linker options so it gets linked with the application (see “Creating and using Libraries with ARM gcc and Eclipse“):
mmCAU Library Linker Options
Last but not least, make sure that the random number generator (RNG) source files of the MCUXpresso SDK are part of the project:
- drivers/fsl_rnga.c
- drivers/fsl_rnga.h
Random Number Generator Sources
This completes the files and settings to add mbed TLS to the project :-).
MQTT without TLS
In an application with MQTT, the MQTT communication protocol is handled between the application and the stack:
Application stack with MQTT
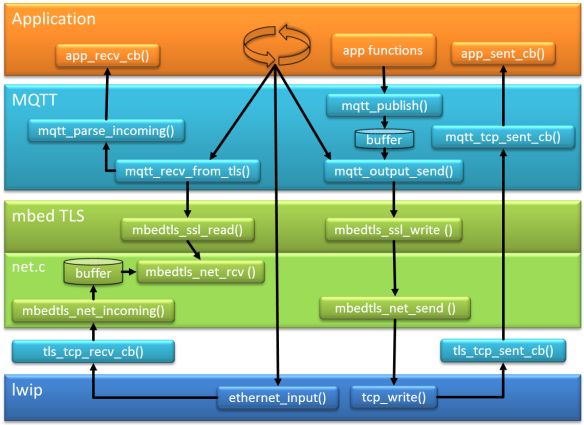
The block diagram below shows the general flow of the MQTT application interacting with lwip in RAW (tcp) mode. With lwip the application has basically two call backs:
- recv_cb(): callback called when we receive a packet from the network
- sent_cb(): callback called *after* a packet has been sent
There is yet another call back, the error callback. To keep things simple, I ignore that callback here.s
MQTT Application with lwip
In raw/bare metal mode, the application calls ethernet_input() which calls the ‘received’ callback. With using MQTT, the MQTT parses the incoming data and passes it to the application (e.g. CONNACK message).
If the application is e.g. sending a PUBLISH request, that TCP message is constructed by the MQTT layer and put into a buffer (actually a ring buffer). That data is only sent if the mqtt_output_send() is called (which is not available to the application). mqtt_output_send() is called for ‘sending’ functions like mqtt_publish() or as a side effect of the mqtt_tcp_sent_cb() callback which is called after a successful tcp_write(). The MQTT sent_cb() is forwarded to the application sent_cb() callback.
MQTT with TLS
The TLS encryption is happening between the application/MQTT part and the TCP/IP (lwip) layers. That way it is transparent between the protocol and the physical layer:
![]()
MQTT Application with Encryption
While things look easy from the above block diagram, it is much more complex to get the cryptographic library working between MQTT and lwip:
- mbed TLS needs to be initialized properly
- The application needs to first start the TLS handshaking, adding an extra state to the application state handling
- All calls to the lwip TCP layer needs to be replaced with calls to the mbedtls_ssl layer
- The communication flow is not any more ‘send one message, receive one sent_cb() callback). Because the TLS layer is doing the handshaking, multiple messages will be transmitted and received, so the call backs need to be separated too.
- Without the TLS layer, the communication flow is more synchronous, and received messages are directly passed up to the application layer. With the TLS between, there is the need for an extra buffering of the incoming messages.
- Messages to be sent from the MQTT layer are already buffered in the non-TLS version. To ensure that they are sent, an extra function mqtt_output.send() has been added.
Block diagram of MQTT Application with TLS on top of lwip
I’m not very happy with that mqtt_output_send() method, but that’s the best I was able to come up to get things working. I might need to refactor this.
To make the above working, I had the tweak the existing MQTT implementation with comes with lwip. Several things should be considered for a general refactoring or done with extra callbacks. I might be able to implement and improve it over the next weeks.
All the needed changes in the application to support TLS are enabled with the following macro inside mqtt_opts.h:
#ifndef MQTT_USE_TLS #define MQTT_USE_TLS 1 /*!< 1: enable TLS/SLL support; 0: do not use TLS/SSL */ #endif
The following sections explain the implementation in more details.
Random Number Generator
Before using the random number generator, it needs to be initialized:
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
/* initialize random number generator */
RNGA_Init(RNG); /* init random number generator */
RNGA_Seed(RNG, SIM->UIDL); /* use device unique ID as seed for the RNG */
if (TLS_Init()!=0) { /* failed? */
printf("ERROR: failed to initialize for TLS!\r\n");
for(;;) {} /* stay here in case of error */
}
#endif
TLS Initialization
To use the mbed TLS library, several objects have to be initialized at application startup:
static mbedtls_entropy_context entropy;
static mbedtls_ctr_drbg_context ctr_drbg;
static mbedtls_ssl_context ssl;
static mbedtls_ssl_config conf;
static mbedtls_x509_crt cacert;
static mbedtls_ctr_drbg_context ctr_drbg;
static int TLS_Init(void) {
/* inspired by https://tls.mbed.org/kb/how-to/mbedtls-tutorial */
int ret;
const char *pers = "ErichStyger-PC";
/* initialize the different descriptors */
mbedtls_ssl_init( &ssl );
mbedtls_ssl_config_init( &conf );
mbedtls_x509_crt_init( &cacert );
mbedtls_ctr_drbg_init( &ctr_drbg );
mbedtls_entropy_init( &entropy );
if( ( ret = mbedtls_ctr_drbg_seed( &ctr_drbg, mbedtls_entropy_func, &entropy,
(const unsigned char *) pers,
strlen(pers ) ) ) != 0 )
{
printf( " failed\n ! mbedtls_ctr_drbg_seed returned %d\n", ret );
return -1;
}
/*
* First prepare the SSL configuration by setting the endpoint and transport type, and loading reasonable
* defaults for security parameters. The endpoint determines if the SSL/TLS layer will act as a server (MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_SERVER)
* or a client (MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_CLIENT). The transport type determines if we are using TLS (MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_STREAM)
* or DTLS (MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_DATAGRAM).
*/
if( ( ret = mbedtls_ssl_config_defaults( &conf,
MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_CLIENT,
MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_STREAM,
MBEDTLS_SSL_PRESET_DEFAULT ) ) != 0 )
{
printf( " failed\n ! mbedtls_ssl_config_defaults returned %d\n\n", ret );
return -1;
}
/* The authentication mode determines how strict the certificates that are presented are checked. */
mbedtls_ssl_conf_authmode(&conf, MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_NONE ); /* \todo change verification mode! */
/* The library needs to know which random engine to use and which debug function to use as callback. */
mbedtls_ssl_conf_rng( &conf, mbedtls_ctr_drbg_random, &ctr_drbg );
mbedtls_ssl_conf_dbg( &conf, my_debug, stdout );
mbedtls_ssl_setup(&ssl, &conf);
if( ( ret = mbedtls_ssl_set_hostname( &ssl, "ErichStyger-PC" ) ) != 0 )
{
printf( " failed\n ! mbedtls_ssl_set_hostname returned %d\n\n", ret );
return -1;
}
/* the SSL context needs to know the input and output functions it needs to use for sending out network traffic. */
mbedtls_ssl_set_bio(&ssl, &mqtt_client, mbedtls_net_send, mbedtls_net_recv, NULL);
return 0; /* no error */
}
Notice that with I’m using MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_NONE. I need to change this in a next iteration, see “Tuturial: mbedTLS SLL Certificate Verification with Mosquitto, lwip and MQTT“.
Application Main Loop
The application runs in an endless loop. To keep things simple, it uses a timer/timestamp to connect and then periodically publish MQTT data:
static void DoMQTT(struct netif *netifp) {
uint32_t timeStampMs, diffTimeMs;
#define CONNECT_DELAY_MS 1000 /* delay in seconds for connect */
#define PUBLISH_PERIOD_MS 10000 /* publish period in seconds */
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_IDLE;
timeStampMs = sys_now(); /* get time in milli seconds */
for(;;) {
LED1_On();
diffTimeMs = sys_now()-timeStampMs;
if (MQTT_state==MQTT_STATE_IDLE && diffTimeMs>CONNECT_DELAY_MS) {
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_DO_CONNECT; /* connect after 1 second */
timeStampMs = sys_now(); /* get time in milli seconds */
}
if (MQTT_state==MQTT_STATE_CONNECTED && diffTimeMs>=PUBLISH_PERIOD_MS) {
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_DO_PUBLISH; /* publish */
timeStampMs = sys_now(); /* get time in milli seconds */
}
MqttDoStateMachine(&mqtt_client); /* process state machine */
/* Poll the driver, get any outstanding frames */
LED1_Off();
ethernetif_input(netifp);
sys_check_timeouts(); /* Handle all system timeouts for all core protocols */
}
}
With ethernetif_input() it polls for any incoming TCP packets. With sys_check_timeouts() it checks for any timeout and for example sends periodic PINGREQ messages to the MQTT broker.
Application State Machine
The application state machine goes through init, connect and TLS handshake sequence, follwed by a periodic PUBLISH:
static void MqttDoStateMachine(mqtt_client_t *mqtt_client) {
switch(MQTT_state) {
case MQTT_STATE_INIT:
case MQTT_STATE_IDLE:
break;
case MQTT_STATE_DO_CONNECT:
printf("Connecting to Mosquito broker\r\n");
if (mqtt_do_connect(mqtt_client)==0) {
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_DO_TLS_HANDSHAKE;
#else
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
#endif
} else {
printf("Failed to connect to broker\r\n");
}
break;
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
case MQTT_STATE_DO_TLS_HANDSHAKE:
if (mqtt_do_tls_handshake(mqtt_client)==0) {
printf("TLS handshake completed\r\n");
mqtt_start_mqtt(mqtt_client);
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
}
break;
#endif
case MQTT_STATE_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
if (mqtt_client_is_connected(mqtt_client)) {
printf("Client is connected\r\n");
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_CONNECTED;
} else {
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
mqtt_recv_from_tls(mqtt_client);
#endif
}
break;
case MQTT_STATE_CONNECTED:
if (!mqtt_client_is_connected(mqtt_client)) {
printf("Client got disconnected?!?\r\n");
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_DO_CONNECT;
}
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
else {
mqtt_tls_output_send(mqtt_client); /* send (if any) */
mqtt_recv_from_tls(mqtt_client); /* poll if we have incoming packets */
}
#endif
break;
case MQTT_STATE_DO_PUBLISH:
printf("Publish to broker\r\n");
my_mqtt_publish(mqtt_client, NULL);
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_CONNECTED;
break;
case MQTT_STATE_DO_DISCONNECT:
printf("Disconnect from broker\r\n");
mqtt_disconnect(mqtt_client);
MQTT_state = MQTT_STATE_IDLE;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
In the MQTT_STATE_CONNECTED it calls mqtt_tls_output_send() to send any outstanding MQTT packets. It uses mqqt_recv_from_tls() to poll any incoming TCP packets.
Connecting to the Broker
The following is the connection code to the broker:
static int mqtt_do_connect(mqtt_client_t *client) {
ip4_addr_t broker_ipaddr;
struct mqtt_connect_client_info_t ci;
err_t err;
IP4_ADDR(&broker_ipaddr, configBroker_ADDR0, configBroker_ADDR1, configBroker_ADDR2, configBroker_ADDR3);
memset(client, 0, sizeof(mqtt_client_t)); /* initialize all fields */
/* Setup an empty client info structure */
memset(&ci, 0, sizeof(ci));
/* Minimal amount of information required is client identifier, so set it here */
ci.client_id = configMQTT_CLIENT_NAME;
ci.client_user = configMQTT_CLIENT_USER;
ci.client_pass = configMQTT_CLIENT_PWD;
ci.keep_alive = 60; /* timeout */
/* Initiate client and connect to server, if this fails immediately an error code is returned
otherwise mqtt_connection_cb will be called with connection result after attempting
to establish a connection with the server.
For now MQTT version 3.1.1 is always used */
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
client->ssl_context = &ssl;
err = mqtt_client_connect(client, &broker_ipaddr, MQTT_PORT_TLS, mqtt_connection_cb, 0, &ci);
#else
err = mqtt_client_connect(client, &broker_ipaddr, MQTT_PORT, mqtt_connection_cb, 0, &ci);
#endif
/* For now just print the result code if something goes wrong */
if(err != ERR_OK) {
printf("mqtt_connect return %d\n", err);
return -1; /* error */
}
return 0; /* ok */
}
At this state, the only difference between TLS and unencrypted communication is that it uses uses a different port (8883 instead of 1883) and that it stores the SSL context in the client descriptor. Inside mqtt_client_connect(), it will directly call the tcp_connect() function.
Connection Callback
If the TCP connection succeeds, it calls the connection callback:
/**
* TCP connect callback function. @see tcp_connected_fn
* @param arg MQTT client
* @param err Always ERR_OK, mqtt_tcp_err_cb is called in case of error
* @return ERR_OK
*/
static err_t
mqtt_tcp_connect_cb(void *arg, struct tcp_pcb *tpcb, err_t err)
{
mqtt_client_t* client = (mqtt_client_t *)arg;
if (err != ERR_OK) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(MQTT_DEBUG_WARN,("mqtt_tcp_connect_cb: TCP connect error %d\n", err));
return err;
}
/* Initiate receiver state */
client->msg_idx = 0;
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
/* Setup TCP callbacks */
tcp_recv(tpcb, tls_tcp_recv_cb);
tcp_sent(tpcb, tls_tcp_sent_cb);
tcp_poll(tpcb, NULL, 0);
LWIP_DEBUGF(MQTT_DEBUG_TRACE,("mqtt_tcp_connect_cb: TCP connection established to server, starting TLS handshake\n"));
/* Enter MQTT connect state */
client->conn_state = TLS_HANDSHAKING;
/* Start cyclic timer */
sys_timeout(MQTT_CYCLIC_TIMER_INTERVAL*1000, mqtt_cyclic_timer, client);
client->cyclic_tick = 0;
#else
/* Setup TCP callbacks */
tcp_recv(tpcb, mqtt_tcp_recv_cb);
tcp_sent(tpcb, mqtt_tcp_sent_cb);
tcp_poll(tpcb, mqtt_tcp_poll_cb, 2);
LWIP_DEBUGF(MQTT_DEBUG_TRACE,("mqtt_tcp_connect_cb: TCP connection established to server\n"));
/* Enter MQTT connect state */
client->conn_state = MQTT_CONNECTING;
/* Start cyclic timer */
sys_timeout(MQTT_CYCLIC_TIMER_INTERVAL*1000, mqtt_cyclic_timer, client);
client->cyclic_tick = 0;
/* Start transmission from output queue, connect message is the first one out*/
mqtt_output_send(client, &client->output, client->conn);
#endif
return ERR_OK;
}
In TLS mode, it configures the special call backs for tls handling (tls_rcp_recv_cb() and tls_tcp_sent_cb()) and moves the connection state into TLS_HANDSHAKING mode.
Receiver Callback
Because the normal receiver callback mqtt_tcp_recv_cb() does not work with the TLS layer, I have implemented a function which reads from the TLS layer:
Note that the error handling is not completed yet!
err_t mqtt_recv_from_tls(mqtt_client_t *client) {
int nof;
mqtt_connection_status_t status;
struct pbuf p;
/*! \todo check if can we really use rx_buffer here? */
nof = mbedtls_ssl_read(client->ssl_context, client->rx_buffer, sizeof(client->rx_buffer));
if (nof>0) {
printf("mqtt_recv_from_tls: recv %d\r\n", nof);
memset(&p, 0, sizeof(struct pbuf)); /* initialize */
p.len = nof;
p.tot_len = p.len;
p.payload = client->rx_buffer;
status = mqtt_parse_incoming(client, &p);
if (status!=MQTT_CONNECT_ACCEPTED) {
return ERR_CONN; /* connection error */ /*! \todo In case of communication error, have to close connection! */
}
}
return ERR_OK;
}
TLS Sent Callback
For every packet sent, the callback tsl_tcp_sent_cb() gets called:
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
/**
* TCP data sent callback function. @see tcp_sent_fn
* @param arg MQTT client
* @param tpcb TCP connection handle
* @param len Number of bytes sent
* @return ERR_OK
*/
static err_t tls_tcp_sent_cb(void *arg, struct tcp_pcb *tpcb, u16_t len)
{
printf("tls_tcp_sent_cb\r\n");
return mqtt_tcp_sent_cb(arg, tpcb, 0); /* call normal (non-tls) callback */
}
#endif /*MQTT_USE_TLS */
It call the corresponding callback in the MQTT layer:
/**
* TCP data sent callback function. @see tcp_sent_fn
* @param arg MQTT client
* @param tpcb TCP connection handle
* @param len Number of bytes sent
* @return ERR_OK
*/
static err_t
mqtt_tcp_sent_cb(void *arg, struct tcp_pcb *tpcb, u16_t len)
{
mqtt_client_t *client = (mqtt_client_t *)arg;
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(tpcb);
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(len);
if (client->conn_state == MQTT_CONNECTED) {
struct mqtt_request_t *r;
printf("mqtt_tcp_sent_cb: and MQTT_CONNECTED\r\n");
/* Reset keep-alive send timer and server watchdog */
client->cyclic_tick = 0;
client->server_watchdog = 0;
/* QoS 0 publish has no response from server, so call its callbacks here */
while ((r = mqtt_take_request(&client->pend_req_queue, 0)) != NULL) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(MQTT_DEBUG_TRACE,("mqtt_tcp_sent_cb: Calling QoS 0 publish complete callback\n"));
if (r->cb != NULL) {
r->cb(r->arg, ERR_OK);
}
mqtt_delete_request(r);
}
/* Try send any remaining buffers from output queue */
mqtt_output_send(client, &client->output, client->conn);
}
return ERR_OK;
}
Net.c Functions
The interface to the network/lwip layer for mbed TLS is implemented in net.c.
The receiving function puts the incoming data into a ring buffer and returns the number of bytes received
/*
* Read at most 'len' characters
*/
int mbedtls_net_recv( void *ctx, unsigned char *buf, size_t len )
{
struct mqtt_client_t *context;
context = (struct mqtt_client_t *)ctx;
if(context->conn == NULL) {
return( MBEDTLS_ERR_NET_INVALID_CONTEXT );
}
if (RNG1_NofElements()>=len) {
printf("mbedtls_net_recv: requested nof: %d, available %d\r\n", len, (int)RNG1_NofElements());
if (RNG1_Getn(buf, len)==ERR_OK) {
return len; /* ok */
}
}
return 0; /* nothing read */
}
The sending function writes the data with tcp_write():
/*
* Write at most 'len' characters
*/
int mbedtls_net_send( void *ctx, const unsigned char *buf, size_t len )
{
struct mqtt_client_t *context;
context = (struct mqtt_client_t *)ctx;
int err;
if(context->conn == NULL) {
return( MBEDTLS_ERR_NET_INVALID_CONTEXT );
}
printf("mbedtls_net_send: len: %d\r\n", len);
err = tcp_write(context->conn, buf, len, TCP_WRITE_FLAG_COPY /*| (wrap ? TCP_WRITE_FLAG_MORE : 0)*/);
if (err!=0) {
return MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_WRITE;
}
return len; /* >0: no error */
}
Sending MQTT Messages
With TLS, sending MQTT messages is using mbedtls_ssl_write() instead of tcp_write():
/**
* Try send as many bytes as possible from output ring buffer
* @param rb Output ring buffer
* @param tpcb TCP connection handle
*/
static void
mqtt_output_send(mqtt_client_t *client, struct mqtt_ringbuf_t *rb, struct tcp_pcb *tpcb)
{
err_t err;
int nof;
u8_t wrap = 0;
u16_t ringbuf_lin_len = mqtt_ringbuf_linear_read_length(rb);
u16_t send_len = tcp_sndbuf(tpcb);
LWIP_ASSERT("mqtt_output_send: tpcb != NULL", tpcb != NULL);
if (send_len == 0 || ringbuf_lin_len == 0) {
return;
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(MQTT_DEBUG_TRACE,("mqtt_output_send: tcp_sndbuf: %d bytes, ringbuf_linear_available: %d, get %d, put %d\n",
send_len, ringbuf_lin_len, ((rb)->get & MQTT_RINGBUF_IDX_MASK), ((rb)->put & MQTT_RINGBUF_IDX_MASK)));
if (send_len > ringbuf_lin_len) {
/* Space in TCP output buffer is larger than available in ring buffer linear portion */
send_len = ringbuf_lin_len;
/* Wrap around if more data in ring buffer after linear portion */
wrap = (mqtt_ringbuf_len(rb) > ringbuf_lin_len);
}
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
printf("mqtt_output_send: mbedtls_ssl_write: bytes %d\r\n", send_len);
nof = mbedtls_ssl_write(client->ssl_context, mqtt_ringbuf_get_ptr(rb), send_len);
if (nof==send_len) {
err = ERR_OK;
} else {
err = ERR_BUF; /* just assign an error */
}
#else
err = tcp_write(tpcb, mqtt_ringbuf_get_ptr(rb), send_len, TCP_WRITE_FLAG_COPY | (wrap ? TCP_WRITE_FLAG_MORE : 0));
#endif
if ((err == ERR_OK) && wrap) {
mqtt_ringbuf_advance_get_idx(rb, send_len);
/* Use the lesser one of ring buffer linear length and TCP send buffer size */
send_len = LWIP_MIN(tcp_sndbuf(tpcb), mqtt_ringbuf_linear_read_length(rb));
#if MQTT_USE_TLS
printf("mbedtls_ssl_write: bytes %d\r\n", send_len);
nof = mbedtls_ssl_write(client->ssl_context, mqtt_ringbuf_get_ptr(rb), send_len);
if (nof==send_len) {
err = ERR_OK;
} else {
err = ERR_BUF; /* just assign an error */
}
#else
err = tcp_write(tpcb, mqtt_ringbuf_get_ptr(rb), send_len, TCP_WRITE_FLAG_COPY);
#endif
}
if (err == ERR_OK) {
mqtt_ringbuf_advance_get_idx(rb, send_len);
/* Flush */
tcp_output(tpcb);
} else {
LWIP_DEBUGF(MQTT_DEBUG_WARN, ("mqtt_output_send: Send failed with err %d (\"%s\")\n", err, lwip_strerr(err)));
}
}
Summary
In order to get MQTT working with TLS/SLL and lwip, I had to deep dive into how TLS and lwip works. I have to admit that things were not as easy as I thought as both MQTT and TLS are new to me, and I only had used lwip as a ‘black box’. The current implementation is very likely not ideal, not that clean and lacks some error handling. But it ‘works’ fine so far with a local Mosquitto broker. Plus I have learned a lot new things. I plan to clean it up more, add better error handling, plus to add FreeRTOS in a next step. Will see how it goes :-).
I hope this is useful for you. I have pushed the application for the NXP FRDM-K64F board on GitHub (https://github.com/ErichStyger/mcuoneclipse/tree/master/Examples/MCUXpresso/FRDM-K64F/FRDM-K64F_lwip_lwip_mqtt_bm). I plan to update/improve/extend the implementation, so make sure you check the latest version on GitHub.
I hope you find this useful to add TLS to your MQTT application with lwip.
There is an alterative lwip API which should be easier to use with TLS. I have found that one after writing this article: http://git.savannah.nongnu.org/cgit/lwip.git/tree/src/include/lwip/altcp.h
How to add server certificate verification, see my next article: “Tuturial: mbedTLS SLL Certificate Verification with Mosquitto, lwip and MQTT“.
Happy Encrypting
LINKS
- MQTT: http://mqtt.org/
- lwip: https://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/lwip/
- mbed TLS library: https://tls.mbed.org/
- mbed TLS tutorial: https://tls.mbed.org/kb/how-to/mbedtls-tutorial
- TLS/SSL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security
- MQTT on NXP FRDM-K64F: MQTT with lwip and NXP FRDM-K64F Board
- Introduction to TLS: Introduction to Security and TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Enable TLS in Mosquitto Broker: Enable Secure Communication with TLS and the Mosquitto Broker
- Project used in this article on GitHub: https://github.com/ErichStyger/mcuoneclipse/tree/master/Examples/MCUXpresso/FRDM-K64F/FRDM-K64F_lwip_lwip_mqtt_bm
- Tuturial: mbedTLS SLL Certificate Verification with Mosquitto, lwip and MQTT
- TLS Security: https://dzone.com/articles/tls-security-tlsssl-explained
- TLS and web certificates explained: https://dzone.com/articles/a-look-at-tls-transport-layer-security
- Understanding security in IoT: https://dzone.com/articles/understanding-security-in-iot-ssltls
- Understanding Transport Layer Security: https://dzone.com/articles/understanding-transport-layer
Advertisements
SHARE THIS:
- Tumblr
- Telegram
- Skype
RELATED
MQTT with lwip and NXP FRDM-K64F BoardIn "ARM"
Introduction to Security and TLS (Transport Layer Security)In "Embedded"
Tutorial: lwip with FreeRTOS and the Freescale FRDM-K64F BoardIn "ARM"
This entry was posted in ARM, Building, Cortex, CPU's, Eclipse, Embedded, FRDM-K64F120M, gcc, Kinetis, MCUXpresso, MCUXpresso IDE, MQTT, NXP, Processor Expert, SDK, Tutorial and tagged arm gcc, cryptography, Eclipse, FRDM-K64F, gnu gcc, mbed, mbedTLS, MCUXpresso, MCUXpresso IDE, mmCAU, NXP, open source projects, Processor Expert, SDK, software, software project, SSL, technology, TLS, Tutorial by Erich Styger. Bookmark the permalink.
About Erich Styger
Embedded is my passion....
View all posts by Erich Styger →
27 THOUGHTS ON “TUTORIAL: SECURE TLS COMMUNICATION WITH MQTT USING MBEDTLS ON TOP OF LWIP”
-
 Carl on April 17, 2017 at 21:43 said:
Carl on April 17, 2017 at 21:43 said:Thanks, Erich. Will have to give it ago. Have you played with FNET https://github.com/butok/FNET/ at all? Found that a while ago when looking for lwip alternatives. looks like that has mbed tls built in too.
Like
Reply ↓
-
 Luca Gotti on April 18, 2017 at 15:23 said:
Luca Gotti on April 18, 2017 at 15:23 said:Hi Erich,
Compliments for gettin it running !
I expect that my implementation ( MQX based ) should be a little bit simpler since RTCS give socket support with asyncronous receive and sending of the TCP/IP packets.
Anyway, thank very much for all these article about MQTT and SSL : they are really inspiring and offer also a list of useful links.Luca
Like
Reply ↓
-
Pingback: Tuturial: mbedTLS SLL Certificate Verification with Mosquitto, lwip and MQTT | MCU on Eclipse
-
 amanda shen on May 27, 2017 at 05:16 said:
amanda shen on May 27, 2017 at 05:16 said:Hi Erich,
Great introduction! It’s very useful.
I have one question about the reduce RAM usage part.
The size of MBEDTLS_MPI_MAX_SIZE is reduced from 1024(default) to 512. I dont know what is MPI. How can you decide the 512 is enough? Can you give me some clues?
Thanks!Like
Reply ↓
-
 Erich Stygeron May 27, 2017 at 09:31 said:
Erich Stygeron May 27, 2017 at 09:31 said:Hi Amanda,
see https://tls.mbed.org/kb/how-to/reduce-mbedtls-memory-and-storage-footprint.
MPI stands for Message Passing Interface, and that define is used in many places for buffers. It basically describes the maxiumum number of bytes which can be passed in a single message.
Basically it means that the keys exchanged should not be larger than 512 bytes.
I hope this helps,
ErichLike
Reply ↓
-
-
 Driss Baddouri on April 23, 2018 at 14:22 said:
Driss Baddouri on April 23, 2018 at 14:22 said:It is possible to use MQTT mbedTLS with ESP8266 ?
Like
Reply ↓
-
 Erich Stygeron April 23, 2018 at 17:37 said:
Erich Stygeron April 23, 2018 at 17:37 said:You mean connecting from a NXP FRDM board (e.g. FRDM-K64F) with an MQTT client using mbedTLS to a MQTT server running on a ESP8266? Not done that, but I don’t see a reason why this would not work if the software on the ESP8266 is properly running the protocol.
Like
Reply ↓
-
-
 Richmond Umagat on July 7, 2018 at 19:13 said:
Richmond Umagat on July 7, 2018 at 19:13 said:Where are the certificates loaded? I didnt found where the CA, certificate and private key are passed.
– Richmond
Like
Reply ↓
-
 Ahmed on October 17, 2018 at 12:25 said:
Ahmed on October 17, 2018 at 12:25 said:Hi Erich,
I’m trying since months to follow your amazing tutorial step by step. I bought all materials and installed all tools on Linux, and I’m trying to connect the board with a local mosquitto broker (in my PC).
My two Questions:
1- How to configure the board (client-publisher) with the local mosquitto broker?
Note:
In “config.h” I made in /* broker settings */ CONFIG_USE_BROKER_LOCAL (1) and CONFIG_USE_BROKER_HSLU (0), and for /* client configuration settings */ I gave my PC settings in not WORK_NETZWORK. And in /* connection settings to broker */ I set again my PC settings (HOST_NAME, HOST_IP) in CONFIG_USE_BROKER_LOCAL. Unfortunatly I could not see the result becuse it was a problem in the debugging.2- How to make a correct debug, every time I make debug I get this message in the “Debugger Console” of MCUXpresso:
“GNU gdb (GNU Tools for Arm Embedded Processors 7-2017-q4-major) 8.0.50.20171128-git
Copyright (C) 2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type “show copying”
and “show warranty” for details.
This GDB was configured as “–host=x86_64-linux-gnu –target=arm-none-eabi”.
Type “show configuration” for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
.
For help, type “help”.
Type “apropos word” to search for commands related to “word”.Program stopped.
ResetISR () at ../startup/startup_mk64f12.c:460
460 void ResetISR(void) {Temporary breakpoint 1, main () at ../source/lwip_mqtt.c:844
844 SYSMPU_Type *base = SYSMPU;”And before I ge this message in the Console “[MCUXpresso Semihosting Telnet console for ‘FRDM-K64F_lwip_mqtt_bm LinkServer Debug’ started on port 52358 @ 127.0.0.1]”
The Console writes this:
“MCUXpresso IDE RedlinkMulti Driver v10.2 (Jul 25 2018 11:28:11 – crt_emu_cm_redlink build 555)
Reconnected to existing link server
Connecting to probe 1 core 0:0 (using server started externally) gave ‘OK’
============= SCRIPT: kinetisconnect.scp =============
Kinetis Connect Script
DpID = 2BA01477
Assert NRESET
Reset pin state: 00
Power up Debug
MDM-AP APID: 0x001C0000
MDM-AP System Reset/Hold Reset/Debug Request
MDM-AP Control: 0x0000001C
MDM-AP Status (Flash Ready) : 0x00000032
Part is not secured
MDM-AP Control: 0x00000014
Release NRESET
Reset pin state: 01
MDM-AP Control (Debug Request): 0x00000004
MDM-AP Status: 0x0001003A
MDM-AP Core Halted
============= END SCRIPT =============================
Probe Firmware: MBED CMSIS-DAP (MBED)
Serial Number: 024002014D87DE5BB07923E3
VID:PID: 0D28:0204
USB Path: /dev/hidraw0
Using memory from core 0:0 after searching for a good core
debug interface type = Cortex-M3/4 (DAP DP ID 2BA01477) over SWD TAP 0
processor type = Cortex-M4 (CPU ID 00000C24) on DAP AP 0
number of h/w breakpoints = 6
number of flash patches = 2
number of h/w watchpoints = 4
Probe(0): Connected&Reset. DpID: 2BA01477. CpuID: 00000C24. Info:
Debug protocol: SWD. RTCK: Disabled. Vector catch: Disabled.
Content of CoreSight Debug ROM(s):
RBASE E00FF000: CID B105100D PID 04000BB4C4 ROM dev (type 0x1)
ROM 1 E000E000: CID B105E00D PID 04000BB00C ChipIP dev SCS (type 0x0)
ROM 1 E0001000: CID B105E00D PID 04003BB002 ChipIP dev DWT (type 0x0)
ROM 1 E0002000: CID B105E00D PID 04002BB003 ChipIP dev FPB (type 0x0)
ROM 1 E0000000: CID B105E00D PID 04003BB001 ChipIP dev ITM (type 0x0)
ROM 1 E0040000: CID B105900D PID 04000BB9A1 CoreSight dev TPIU type 0x11 Trace Sink – TPIU
ROM 1 E0041000: CID B105900D PID 04000BB925 CoreSight dev ETM type 0x13 Trace Source – core
ROM 1 E0042000: CID B105900D PID 04003BB907 CoreSight dev ETB type 0x21 Trace Sink – ETB
ROM 1 E0043000: CID B105900D PID 04001BB908 CoreSight dev CSTF type 0x12 Trace Link – Trace funnel/router
Inspected v.2 On chip Kinetis Flash memory module FTFE_4K.cfx
Image ‘Kinetis SemiGeneric Feb 17 2017 17:24:02’
Opening flash driver FTFE_4K.cfx
Sending VECTRESET to run flash driver
Flash variant ‘K 64 FTFE Generic 4K’ detected (1MB = 256*4K at 0x0)
Closing flash driver FTFE_4K.cfx
NXP: MK64FN1M0xxx12
( 65) Chip Setup Complete
Connected: was_reset=true. was_stopped=true
Awaiting telnet connection to port 3330 …
GDB nonstop mode enabled
Opening flash driver FTFE_4K.cfx (already resident)
Sending VECTRESET to run flash driver
Flash variant ‘K 64 FTFE Generic 4K’ detected (1MB = 256*4K at 0x0)
Writing 142880 bytes to address 0x00000000 in Flash”I hope you can help.
Like
Reply ↓
-
 Erich Stygeron October 18, 2018 at 18:21 said:
Erich Stygeron October 18, 2018 at 18:21 said:1) in lwip_app.c you can onfigure the IP address of the broker (I have not used DHCP for this)
2) I recommend you use the SEGGER J-Link firmware instead
I hope this helps,
ErichLike
Reply ↓
-
 Ahmedon October 18, 2018 at 18:55 said:
Ahmedon October 18, 2018 at 18:55 said:Hi Erich,
thanks for your reply.
I didn’t find any file with the name lwip_app.c!Like
Reply ↓
-
 Ahmedon October 19, 2018 at 13:58 said:
Ahmedon October 19, 2018 at 13:58 said:Hi Erich,
1- I’m not working on mqtt-FreeRTOS without mbedtls but with mbedtls “FRDM-K64F_lwip_lwip_mqtt_bm”. I think, I can configure the IP address in /source/config.h file.2- When MCUXpresso searches for a propes then it findes only LinkServer type. So I have no chance to make with SEGGER J-Link.
Like
Reply ↓
-
-
-
 Mattia on December 10, 2018 at 11:30 said:
Mattia on December 10, 2018 at 11:30 said:Hello Erich,
first, thank you very much for such a good job. Do you think is it possible not to use the RNG1 Module? how should I modify the mbedtls_net_recv?
Thank you,Like
Reply ↓
-
 Mattiaon December 10, 2018 at 16:13 said:
Mattiaon December 10, 2018 at 16:13 said:To be more precise, I see that, porting this example in another microcontroller, the mbedtls_net_recv always has no data in the RNG1 Ringbuffer. Could you explain how it is used?
Thank you,
MattiaLike
Reply ↓
-
 Erich Stygeron December 10, 2018 at 16:29 said:
Erich Stygeron December 10, 2018 at 16:29 said:In that case it means that you are not receiving the data. Have you tried to run it on a K64F as well?
Like
Reply ↓
-
 Mattiaon December 10, 2018 at 17:08 said:
Mattiaon December 10, 2018 at 17:08 said:I’m waiting for the MCUXpresso to be available to download, then I will test on my K64F.
However, I can’t understand very well the firmware.
if (RNG1_Getn(buf, len)==ERR_OK)
{
return len; /* ok */
}But who writes on buf?
The strange thing is that with no TLS the program is perfect, so it seems that some union between TLS and TCP is missing.
Like
-
 Erich Stygeron December 11, 2018 at 05:47 said:
Erich Stygeron December 11, 2018 at 05:47 said:Search for RNG1_Putn in the project.
Like
-
 Mattiaon December 11, 2018 at 13:39 said:
Mattiaon December 11, 2018 at 13:39 said:I found what the problem was: it seems that tcp_write didn’t send data. I put a tcp_output, now it works!
Thanks,
MattiaLike
-
-
-
 Erich Stygeron December 10, 2018 at 16:28 said:
Erich Stygeron December 10, 2018 at 16:28 said:You can use whatever you like. The RNG1 is a simple implementation of a ring buffer, but you can replace it with your own implementation too.
Like
Reply ↓
-
What do you think?
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
FOLLOW ME ON TWITTER
My Tweets
Blog at WordPress.com.
- Follow