手写一个基于NIO的迷你版Tomcat
笔者也建立的自己的公众号啦,平时会分享一些编程知识,欢迎各位大佬支持~
扫码或微信搜索北风IT之路关注

本文公众号地址:手写一个基于NIO的迷你版Tomcat
在很久之前看到了一篇文章写一个迷你版的Tomcat,觉得还是很有意思的,于是也跟着手敲了一遍,果不其然得出了想要的hello world,但是他这个是基于BIO的,正好最近看了并发编程的书,于是尝试将这位大佬的代码改一改,于是就有了这个基于NIO的迷你Tomcat。
源代码已更新至我的Github:https://github.com/tzfun/MyTomcat
BIO和NIO
BIO是同步阻塞IO,在实际场景中大部分时间消耗在了IO等待上了,比较消耗资源,所以这种IO方式逐渐被替代了,具体介绍这里不再赘述。取而代之的是NIO(New IO),它是一种同步非阻塞式的IO,它通过Selector自旋式或回调式的方式去处理准备好数据的Channel,Channel即通道,相当于BIO中的流,它不存在花费大量时间去IO等待,从而大大提升了吞吐量。Tomcat在老版本也是基于BIO的,后续版本更新也全部替换为NIO。
项目结构
项目结构和原作者的结构几乎一样,只是代码实现不一样,具体结构看下图:
Request和Response
Tomcat主要是Http服务,所以处理的协议是Http协议,那么Http的头部信息由请求行、请求头部、空行、请求数据组成,只需要拆分这些数据即可处理http请求,这里我只是简单的处理了一下,其他详细内容看注释。
Request
package mytomcat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 14:45 2019/4/21
*/
public class MyRequest {
private String url;
private String method;
private HashMap<String,String> param = new HashMap<>();
public MyRequest(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException{
// 从契约获取通道
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
String httpRequest = "";
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(16*1024); // 从堆内存中获取内存
int length = 0; // 读取byte数组的长度
length = channel.read(bb); // 从通道中读取数据到ByteBuffer容器中
if (length < 0){
selectionKey.cancel(); // 取消该契约
}else {
httpRequest = new String(bb.array()).trim(); // 将ByteBuffer转为String
String httpHead = httpRequest.split("\n")[0]; // 获取请求头
url = httpHead.split("\\s")[1].split("\\?")[0]; // 获取请求路径
String path = httpHead.split("\\s")[1]; // 请求全路径,包含get的参数数据
method = httpHead.split("\\s")[0];
// 一下是拆分get请求的参数数据
String[] params = path.indexOf("?") > 0 ? path.split("\\?")[1].split("\\&") : null;
if (params != null){
try{
for (String tmp : params){
param.put(tmp.split("\\=")[0],tmp.split("\\=")[1]);
}
}catch (NullPointerException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(this);
}
bb.flip();
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyRequest{" +
"url='" + url + '\'' +
", method='" + method + '\'' +
", param=" + param +
'}';
}
}
Response
package mytomcat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 14:49 2019/4/21
*/
public class MyResponse {
private SelectionKey selectionKey;
public MyResponse(SelectionKey selectionKey){
this.selectionKey = selectionKey;
}
public void write(String content) throws IOException{
// 拼接相应数据包
StringBuffer httpResponse = new StringBuffer();
httpResponse.append("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n")
.append("Content-type:text/html\n")
.append("\r\n")
.append("")
.append(content)
.append("");
// 转换为ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(httpResponse.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); // 从契约获取通道
long len = channel.write(bb); // 向通道中写入数据
if (len == -1){
selectionKey.cancel();
}
bb.flip();
channel.close();
selectionKey.cancel();
}
}
Servlet和Mapping映射类及其配置类
在Java web开发中都会遇到Servlet和Mapping的配置,这些是必备的元素,Servlet负责定义处理请求和响应的方法,它是一个抽象类。
Servlet
package mytomcat;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 14:53 2019/4/21
*/
public abstract class MyServlet {
public abstract void doGet(MyRequest myRequest,MyResponse myResponse);
public abstract void doPost(MyRequest myRequest,MyResponse myResponse);
public void service(MyRequest myRequest,MyResponse myResponse){
if (myRequest.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("POST")){
doPost(myRequest,myResponse);
}else if (myRequest.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("GET")){
doGet(myRequest,myResponse);
}
}
}
Mapping映射是负责将某些请求路径分发到各自处理类进行处理,那么就需要一个配置类,以下是ServletMapping类的定义和Config类。
ServletMapping
package mytomcat;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 14:59 2019/4/21
*/
public class ServletMapping {
private String servletName;
private String url;
private String clazz;
public ServletMapping(String servletName, String url, String clazz) {
this.servletName = servletName;
this.url = url;
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public String getServletName() {
return servletName;
}
public void setServletName(String servletName) {
this.servletName = servletName;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(String clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
}
ServletMappingConfig
package mytomcat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 15:01 2019/4/21
*/
public class ServletMappingConfig {
public static List<ServletMapping> servletMappingList = new ArrayList<>();
static {
servletMappingList.add(new ServletMapping("helloWorld","/world","mytomcat.HelloWorldServlet"));
}
}
当然一般这个配置是通过xml文件去配置的。
下面是处理/world请求的处理类
package mytomcat;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 14:57 2019/4/21
*/
public class HelloWorldServlet extends MyServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(MyRequest myRequest, MyResponse myResponse) {
try{
myResponse.write("get hello world");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void doPost(MyRequest myRequest, MyResponse myResponse) {
try{
myResponse.write("post hello world");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Tomcat核心启动类
Tomcat的启动类是它的核心,其中包含初始化Mapping、监听端口、处理请求和响应等,我与原作者的主要区别也就是在这一部分,用NIO替换了BIO的接收数据模式,采用线程池处理数据。
MyTomcat
package mytomcat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author beifengtz
* www.beifengtz.com
* location: mytomcat.javase_learning
* Created in 15:03 2019/4/21
*/
public class MyTomcat {
private int port = 8080;
private Map<String, String> urlServletMap = new HashMap<>();
private Selector selector;
private ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public MyTomcat() {
}
public MyTomcat(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws IOException {
// 初始化映射关系
initServletMapping();
// 启动Selector
selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
// 启动Channel
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 配置非阻塞选择
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
// 监听端口
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress(port);
ssc.socket().bind(isa);
// 将Channel绑定到Selector上,并选择准备模式为Accept,此处可能会失败,后续可再次开启
SelectionKey acceptKey = ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("MyTomcat is started...");
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<MyRequest> requestList = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<MyResponse> responseList = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
while (true) {
selector.select(); // 等待Channel准备数据
Set readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator i = readyKeys.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = (SelectionKey) i.next();
i.remove(); // 从集合中移除,防止重复处理
if (sk.isAcceptable()) { // 如果键的接收状态未正常打开,再次尝试打开
doAccept(sk);
} else if (sk.isValid() && sk.isReadable()) { // 可读
requestList.add(getRequest(sk));
// 切换准备状态
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
} else if (sk.isValid() && sk.isWritable()) { // 可写
responseList.add(getResponse(sk));
// 切换准备状态
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 等待一对请求和响应均准备好时处理
if (!requestList.isEmpty() && !responseList.isEmpty()) {
dispatch(requestList.poll(), responseList.poll());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 如果没有正常开启接收模式
* 尝试开启接收模式
* @param selectionKey
*/
private void doAccept(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel;
try {
clientChannel = server.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey clientKey = clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 从通道中获取请求并进行包装
*
* @param selectionKey
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
private MyRequest getRequest(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
return new MyRequest(selectionKey); // 包装request
}
/**
* 从通道中获取响应并进行包装
*
* @param selectionKey
* @return
*/
private MyResponse getResponse(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
return new MyResponse(selectionKey); // 包装response
}
/**
* 初始化Servlet的映射对象
*/
private void initServletMapping() {
for (ServletMapping servletMapping : ServletMappingConfig.servletMappingList) {
urlServletMap.put(servletMapping.getUrl(), servletMapping.getClazz());
}
}
/**
* 请求调度
*
* @param myRequest
* @param myResponse
*/
private void dispatch(MyRequest myRequest, MyResponse myResponse) {
if (myRequest == null) return;
if (myResponse == null) return;
String clazz = urlServletMap.get(myRequest.getUrl());
try {
if (clazz == null) {
myResponse.write("404");
return;
}
es.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Class<MyServlet> myServletClass = (Class<MyServlet>) Class.forName(clazz);
MyServlet myServlet = myServletClass.newInstance();
myServlet.service(myRequest, myResponse);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new MyTomcat().start();
}
}
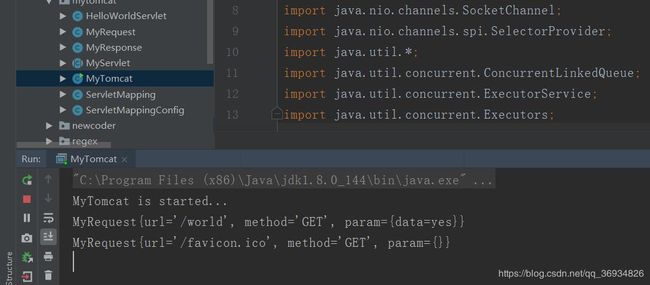
测试
当我们在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/world?data=yes时,成功得到了预期的结果