【Flink博客阅读】 Flink 作业执行深度解析(WordCount) 读后实战总结
Flink 作业执行解析
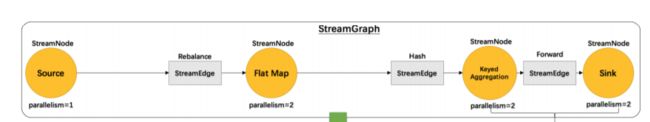
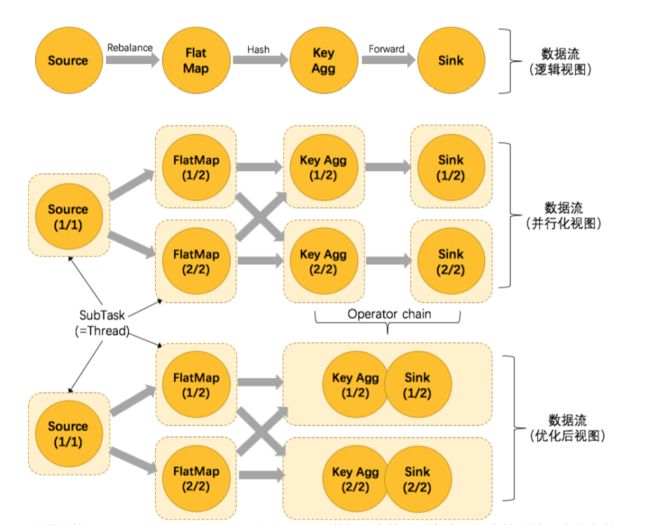
所有有关Flink作业执行的介绍都包含以下的这个流程,今天我们就是实战一些这些转换是如何完成的?
StreamGraphClass representing the streaming topology. It contains all the information necessary to build the jobgraph for the execution. 这个类表示流处理的拓扑结构,包含构造JobGraph的所有信息,从而满足任务执行。JobGraph:JobGraph代表Flink的dataflow程序,处于JobManager接受的底层。来自更高级别API的所有程序都将转换为JobGraphs。在此之前,都是在client里面进行运行的。并且可以根据ExplainPlan获取执行计划ExecutionGraph:ExecutionGraph是JobGraph的并行化版本,是调度层(Schduler)最核心的数据结构。- 物理执行计划
- StreamGraph: 流处理节点拓扑图
- JobGraph: Flink的数据流图。
- JobGraph 属性
-
Operator : 算子,理解为function定义。
-
Transformation: 转换,包含输入、算子、与输出,理解为一个完整的流程,function runtime。
示例程序
flink-examples-streaming工程下面的org.apache.flink.streaming.examples.wordcount.WordCount
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Checking input parameters
final MultipleParameterTool params = MultipleParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
// set up the execution environment
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// make parameters available in the web interface
env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params);
// get input data
DataStream<String> text = null;
if (params.has("input")) {
// union all the inputs from text files
for (String input : params.getMultiParameterRequired("input")) {
if (text == null) {
text = env.readTextFile(input);
} else {
text = text.union(env.readTextFile(input));
}
}
Preconditions.checkNotNull(text, "Input DataStream should not be null.");
} else {
System.out.println("Executing WordCount example with default input data set.");
System.out.println("Use --input to specify file input.");
// get default test text data
text = env.fromElements(WordCountData.WORDS);
}
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts =
// split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1)
text.flatMap(new Tokenizer())
// group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1"
.keyBy(0).sum(1);
// emit result
if (params.has("output")) {
counts.writeAsText(params.get("output"));
} else {
System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path.");
counts.print();
}
// execute program
env.execute("Streaming WordCount");
}
Flink Client
WordCount程序
text = env.fromElements(WordCountData.WORDS);
DataStream> counts =
// split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1)
text.flatMap(new Tokenizer())
// group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1"
.keyBy(0).sum(1);
初始化
初始化是之前当前程序的定义,主要是整个数据流的定义元数据收集
Source
FlatMap
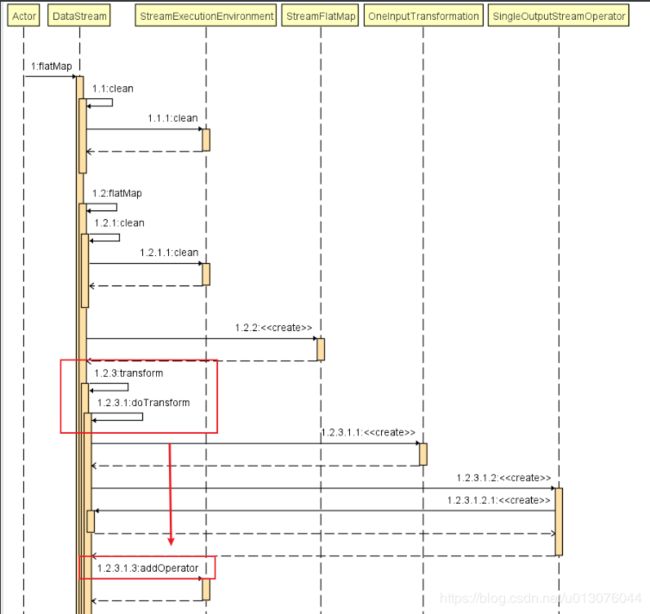
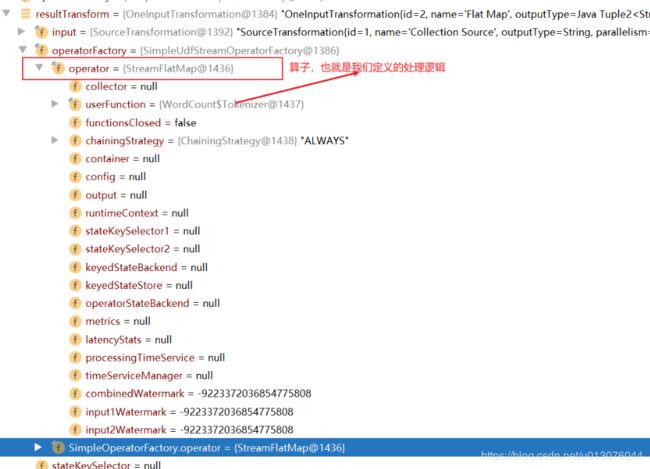
- (1) 首先调用DataStream的FlatMap方法 => transform 方法
DataStream#doTransform
-
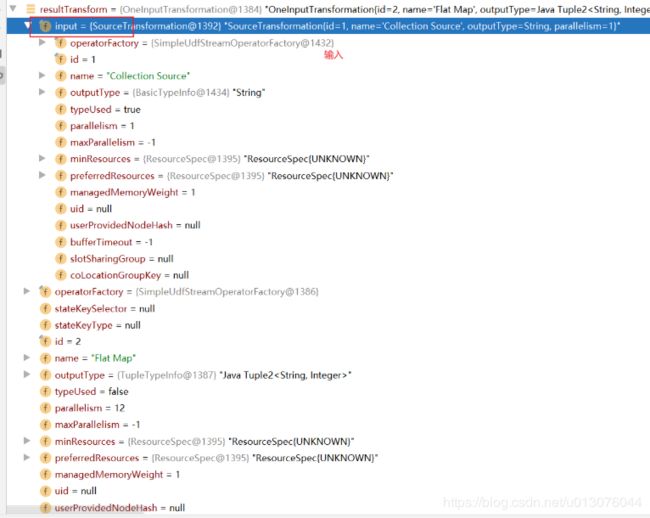
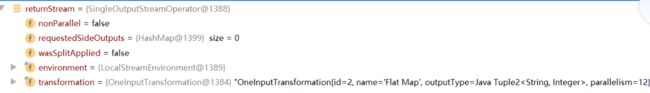
(2)创建Transformation(包含输入实例、算子 、输出)
-
(3)创建结果流
-
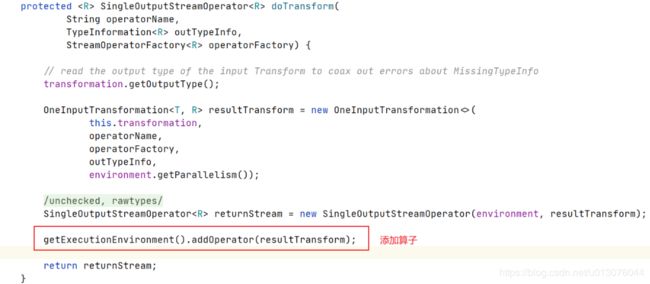
(4)添加算子到当前上下文
public void addOperator(Transformation transformation) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(transformation, "transformation must not be null."); this.transformations.add(transformation); } -
(5)返回结果流
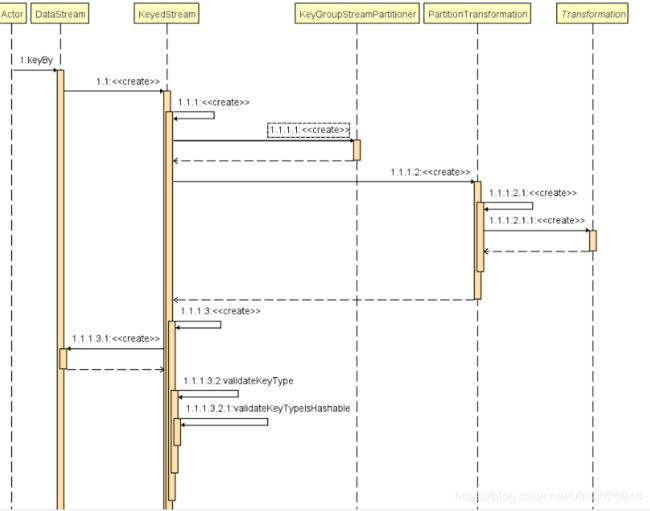
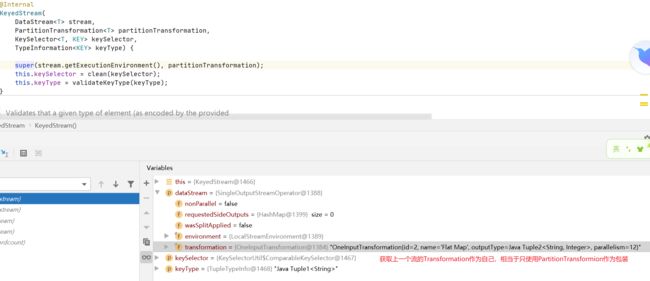
keyBy
sum
sum还是在当前的dataStream流上面。
需要注意的是,有些 transform 操作并不会生成StreamNode 如 PartitionTransformtion,而是生成个虚拟节点。
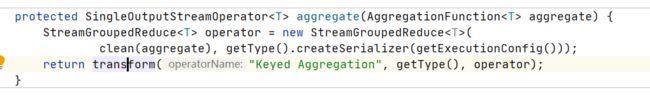
调用transform即可flatmap一样。会把自己作为transformations。
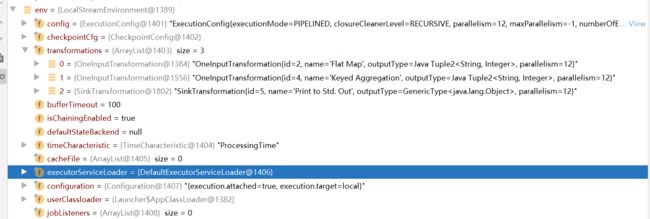
最终配置总览
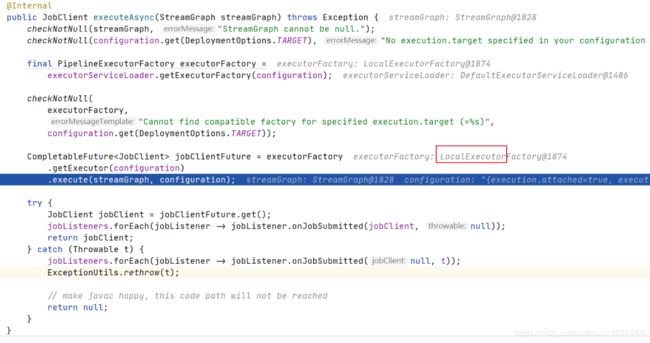
执行提交
env.execute("Streaming WordCount");
===>
public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobName, "Streaming Job name should not be null.");
return execute(getStreamGraph(jobName));
}
生成StreamGraph(Pipeline)
public StreamGraph getStreamGraph(String jobName, boolean clearTransformations) {
StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraphGenerator().setJobName(jobName).generate();
if (clearTransformations) {
this.transformations.clear();
}
return streamGraph;
}
Generate全图
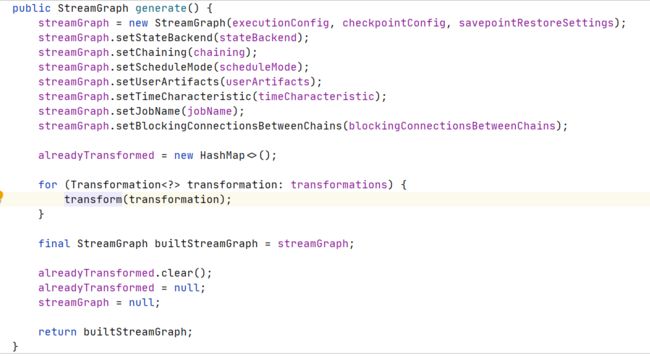
拓扑图的生成逻辑,循环处理每一个节点
Generate Transformation
这里对操作符的类型进行判断,并以此调用相应的处理逻辑.简而言之,
处理的核心:是递归的将该节点和节点的上游节点加入图
private Collection<Integer> transform(Transformation<?> transform) {
if (alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) {
return alreadyTransformed.get(transform);
}
LOG.debug("Transforming " + transform);
if (transform.getMaxParallelism() <= 0) {
// if the max parallelism hasn't been set, then first use the job wide max parallelism
// from the ExecutionConfig.
int globalMaxParallelismFromConfig = executionConfig.getMaxParallelism();
if (globalMaxParallelismFromConfig > 0) {
transform.setMaxParallelism(globalMaxParallelismFromConfig);
}
}
// call at least once to trigger exceptions about MissingTypeInfo
transform.getOutputType();
Collection<Integer> transformedIds;
if (transform instanceof OneInputTransformation<?, ?>) {
transformedIds = transformOneInputTransform((OneInputTransformation<?, ?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof TwoInputTransformation<?, ?, ?>) {
transformedIds = transformTwoInputTransform((TwoInputTransformation<?, ?, ?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof SourceTransformation<?>) {
// .......... 省略
// need this check because the iterate transformation adds itself before
// transforming the feedback edges
if (!alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) {
alreadyTransformed.put(transform, transformedIds);
}
if (transform.getBufferTimeout() >= 0) {
streamGraph.setBufferTimeout(transform.getId(), transform.getBufferTimeout());
} else {
streamGraph.setBufferTimeout(transform.getId(), defaultBufferTimeout);
}
if (transform.getUid() != null) {
streamGraph.setTransformationUID(transform.getId(), transform.getUid());
}
if (transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash() != null) {
streamGraph.setTransformationUserHash(transform.getId(), transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash());
}
if (!streamGraph.getExecutionConfig().hasAutoGeneratedUIDsEnabled()) {
if (transform instanceof PhysicalTransformation &&
transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash() == null &&
transform.getUid() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Auto generated UIDs have been disabled " +
"but no UID or hash has been assigned to operator " + transform.getName());
}
}
if (transform.getMinResources() != null && transform.getPreferredResources() != null) {
streamGraph.setResources(transform.getId(), transform.getMinResources(), transform.getPreferredResources());
}
streamGraph.setManagedMemoryWeight(transform.getId(), transform.getManagedMemoryWeight());
return transformedIds;
}
创建节点并加入图
生成结果
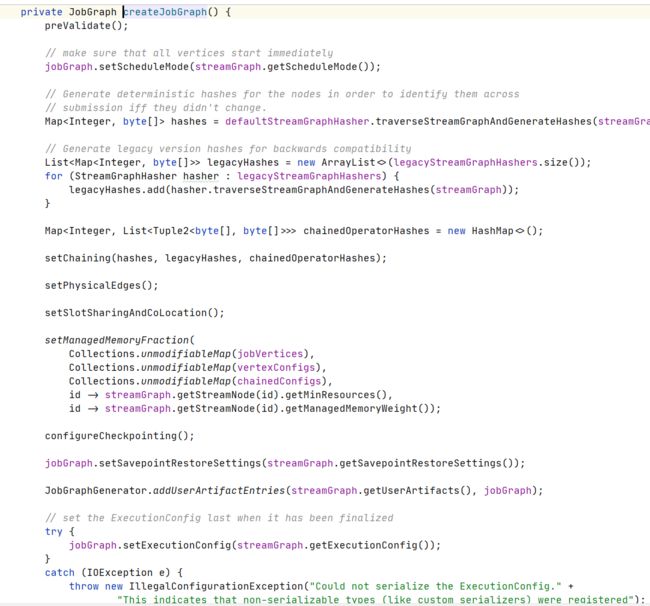
生成JobGraph
执行
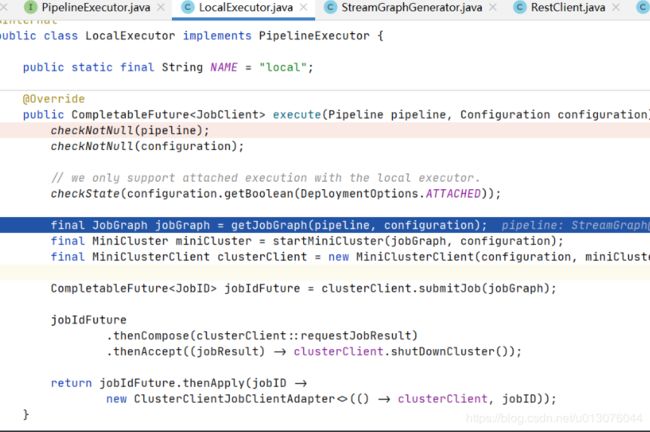
PipelinExecutor
execute 执行
生成jobGraph
- 使用PipeLineTranslator生成JobGraph
Job Graph生成逻辑
生成结果
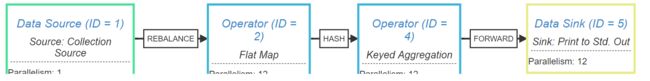
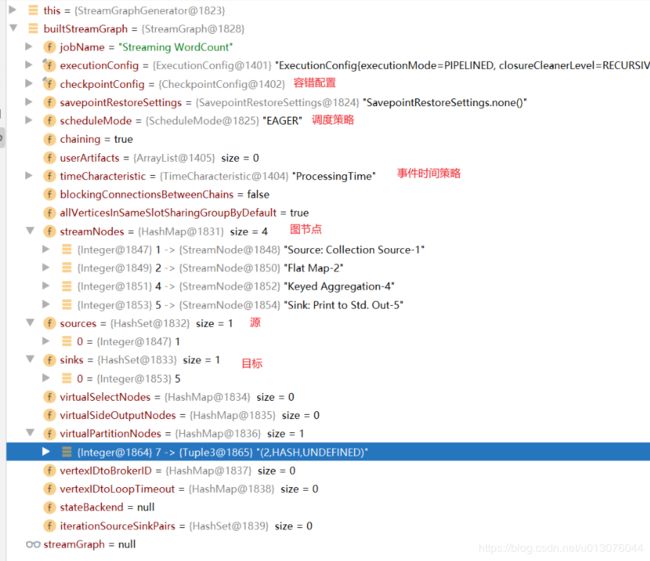
可以看到上面 key-aggregate-sink合并为了一个chain。
JobGraph 对象结构如上图所示,taskVertices 中只存在三个 TaskVertex,Sink operator 被嵌到 Keyed operator 中去了。
提交作业
这里相当于把本地作业提交到集群上面。就是一个作业元数据上传的过程。底层的RestClient使用的是Netty。
ClientUtils#submitJob
public static JobExecutionResult submitJob(
ClusterClient client,
JobGraph jobGraph) throws ProgramInvocationException {
checkNotNull(client);
checkNotNull(jobGraph);
try {
return client
.submitJob(jobGraph)
.thenApply(DetachedJobExecutionResult::new)
.get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
ExceptionUtils.checkInterrupted(e);
throw new ProgramInvocationException("Could not run job in detached mode.", jobGraph.getJobID(), e);
}
}
通过 RestClusterClient 提交到集群上
public CompletableFuture submitJob(@Nonnull JobGraph jobGraph) {
// 生成二进制包,用于作业恢复
CompletableFuture jobGraphFileFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
final java.nio.file.Path jobGraphFile = Files.createTempFile("flink-jobgraph", ".bin");
try (ObjectOutputStream objectOut = new ObjectOutputStream(Files.newOutputStream(jobGraphFile))) {
objectOut.writeObject(jobGraph);
}
return jobGraphFile;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new CompletionException(new FlinkException("Failed to serialize JobGraph.", e));
}
}, executorService);
// 查询所有需要上传的包
CompletableFuture>> requestFuture = jobGraphFileFuture.thenApply(jobGraphFile -> {
List jarFileNames = new ArrayList<>(8);
List artifactFileNames = new ArrayList<>(8);
Collection filesToUpload = new ArrayList<>(8);
filesToUpload.add(new FileUpload(jobGraphFile, RestConstants.CONTENT_TYPE_BINARY));
for (Path jar : jobGraph.getUserJars()) {
jarFileNames.add(jar.getName());
filesToUpload.add(new FileUpload(Paths.get(jar.toUri()), RestConstants.CONTENT_TYPE_JAR));
}
for (Map.Entry artifacts : jobGraph.getUserArtifacts().entrySet()) {
final Path artifactFilePath = new Path(artifacts.getValue().filePath);
try {
// Only local artifacts need to be uploaded.
if (!artifactFilePath.getFileSystem().isDistributedFS()) {
artifactFileNames.add(new JobSubmitRequestBody.DistributedCacheFile(artifacts.getKey(), artifactFilePath.getName()));
filesToUpload.add(new FileUpload(Paths.get(artifacts.getValue().filePath), RestConstants.CONTENT_TYPE_BINARY));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new CompletionException(
new FlinkException("Failed to get the FileSystem of artifact " + artifactFilePath + ".", e));
}
}
final JobSubmitRequestBody requestBody = new JobSubmitRequestBody(
jobGraphFile.getFileName().toString(),
jarFileNames,
artifactFileNames);
return Tuple2.of(requestBody, Collections.unmodifiableCollection(filesToUpload));
});
// 上传jar包,提交作业
final CompletableFuture submissionFuture = requestFuture.thenCompose(
requestAndFileUploads -> sendRetriableRequest(
JobSubmitHeaders.getInstance(),
EmptyMessageParameters.getInstance(),
requestAndFileUploads.f0,
requestAndFileUploads.f1,
isConnectionProblemOrServiceUnavailable())
);
// 删除生成的jobGraph文件
submissionFuture
.thenCombine(jobGraphFileFuture, (ignored, jobGraphFile) -> jobGraphFile)
.thenAccept(jobGraphFile -> {
try {
Files.delete(jobGraphFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Could not delete temporary file {}.", jobGraphFile, e);
}
});
// 返回jobId
return submissionFuture
.thenApply(ignore -> jobGraph.getJobID())
.exceptionally(
(Throwable throwable) -> {
throw new CompletionException(new JobSubmissionException(jobGraph.getJobID(), "Failed to submit JobGraph.", ExceptionUtils.stripCompletionException(throwable)));
});
}
// 提交到集群
private , U extends MessageParameters, R extends RequestBody, P extends ResponseBody> CompletableFuture
sendRetriableRequest(M messageHeaders, U messageParameters, R request, Collection filesToUpload, Predicate retryPredicate) {
return retry(() -> getWebMonitorBaseUrl().thenCompose(webMonitorBaseUrl -> {
try {
return restClient.sendRequest(webMonitorBaseUrl.getHost(), webMonitorBaseUrl.getPort(), messageHeaders, messageParameters, request, filesToUpload);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new CompletionException(e);
}
}), retryPredicate);
}
FlinkCluster Server
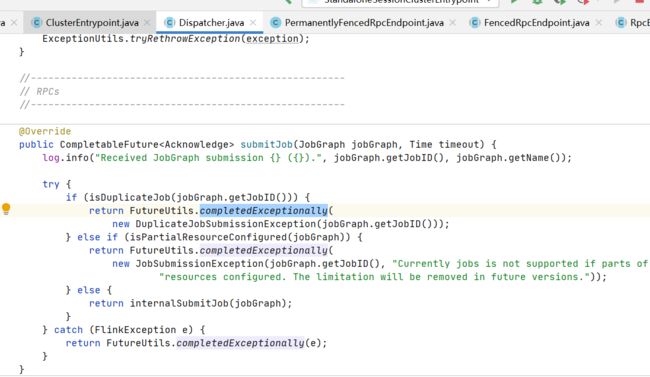
Dispatcher 接收请求
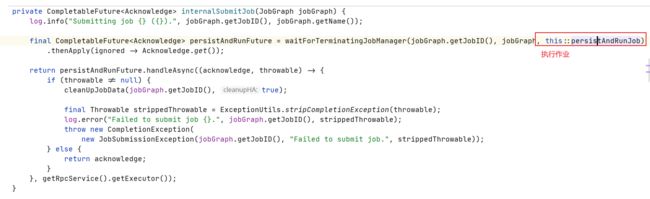
内部执行
持久化和启动作业
持久化作业
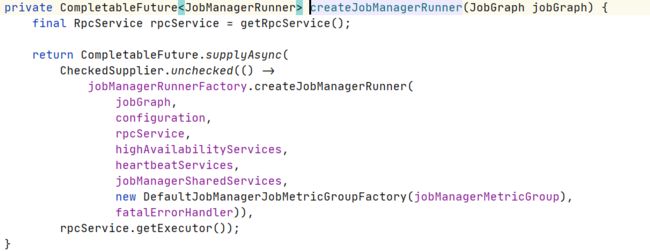
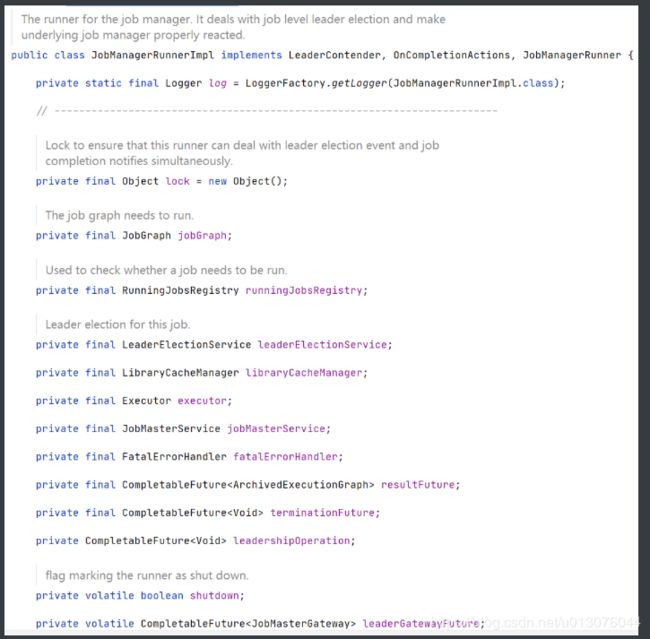
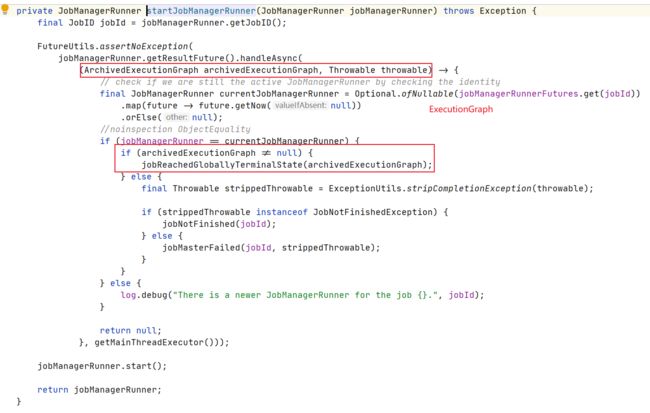
创建JobManagerRunner(JobManagerRunnerImpl)
属性
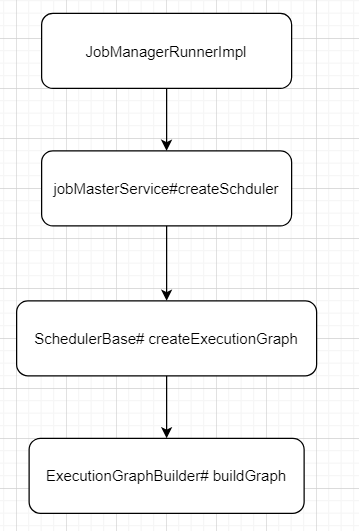
翻译JobGraph => ExecutionGraph
ExecutionGraphBuilder# buildGraph逻辑
-
create a new execution graph, if none exists so far
-
set the basic properties
-
initialize the vertices that have a master initialization hook
-
file output formats create directories here, input formats create splits
-
topologically sort the job vertices and attach the graph to the existing one
- 将 JobGraph 里面的 jobVertex 从 Source 节点开始排序。
- 在 executionGraph.attachJobGraph(sortedTopology)方法里面,根据 JobVertex 生成 ExecutionJobVertex,在 ExecutionJobVertex 构造方法里面,根据 jobVertex 的 IntermediateDataSet 构建 IntermediateResult,根据 jobVertex 并发构建 ExecutionVertex,ExecutionVertex 构建的时候,构建 IntermediateResultPartition(每一个 Execution 构建 IntermediateResult 数个IntermediateResultPartition );将创建的 ExecutionJobVertex 与前置的 IntermediateResult 连接起来。
- 构建 ExecutionEdge ,连接到前面的 IntermediateResultPartition,最终从 ExecutionGraph 到物理执行计划。
-
configure the state checkpointing
-
create all the metrics for the Execution Graph
实际启动作业
执行作业
JobMaster
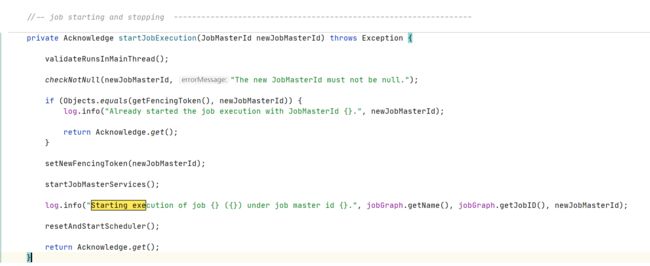
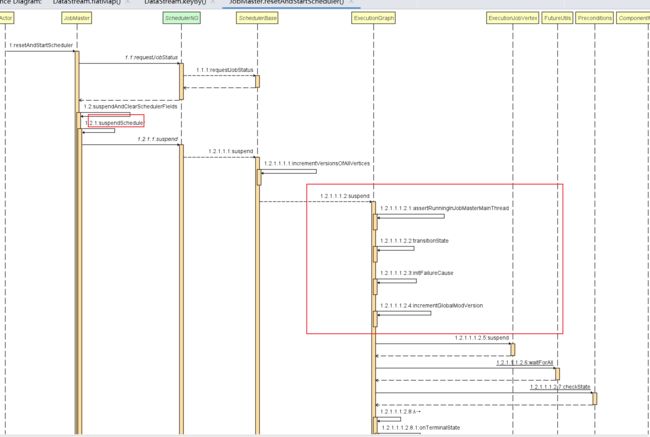
调度器执行
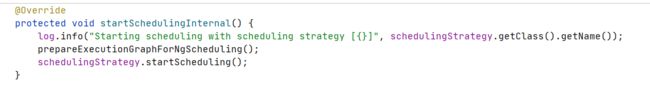
resetAndStartScheduler =》
总结
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jC5iQsH7-1592732400299)(images/image-20200621172505926.png)]
- 第一层 StreamGraph 从 Source 节点开始,每一次 transform 生成一个 StreamNode,两个 StreamNode 通过 StreamEdge 连接在一起,形成 StreamNode 和 StreamEdge 构成的DAG。
- 第二层 JobGraph,依旧从 Source 节点开始,然后去遍历寻找能够嵌到一起的 operator,如果能够嵌到一起则嵌到一起,不能嵌到一起的单独生成 jobVertex,通过 JobEdge 链接上下游 JobVertex,最终形成 JobVertex 层面的 DAG。
- JobVertex DAG 提交到任务以后,从 Source 节点开始排序,根据 JobVertex 生成ExecutionJobVertex,根据 jobVertex的IntermediateDataSet 构建IntermediateResult,然后 IntermediateResult 构建上下游的依赖关系,形成 ExecutionJobVertex 层面的 DAG 即 ExecutionGraph。
- 最后通过 ExecutionGraph 层到物理执行层。
参考资料
https://ververica.cn/developers/advanced-tutorial-2-flink-job-execution-depth-analysis/ Flink 作业执行深度解析