【算法设计与分析】图:Djikstra算法
文章目录
- 算法介绍
- 算法过程
- Java实现
- 例题
算法介绍
Djikstra算法是单源最短路径算法:用于计算有向图中某个节点到其他节点的最短路径,当然无向图也可以。该算法要求图中不存在负权边。
bellman-ford算法也是单源最短路径算法,区别在于Djikstra算法要求图中不能有负权边,bellman-ford可以有负权边。
算法过程
求A到其他节点的最短路径:

维护三个东西,从A到其他节点的路径长度队列Queue,数组visited用于记录已保存最短路径的节点,数组res用于记录节点A到其他节点的最短路径。
开始时,Queue中只有A节点自己,三组数据如下:
Queue:[(A, 0)] 起始节点为A,A到A的距离为0
visited:[true, false,false,false,false] A节点是已经访问过的节点,是true,其他节点是false
res:[0,∞,∞,∞,∞] A到自己的距离是0,到其他节点的距离目前是∞
将以A为起点的路径加入到Queue中,2和4是节点D和B的路径权重:
Queue:[(D, 2), (B, 4)]
visited:[true, false,false,false,false]
res:[0,∞,∞,∞,∞]
在Queue中,路径最短的是D,取出D,更新三组数据:
Queue:[(B, 3), (C, 3), (E, 9)]
因为A-D-B的路径权重为3小于A-B的路径权重4,所以更新一下B的路径权重。
visited:[true,false,false,true,false]
res: [0,∞, ∞,2,∞]
取出B,更新三组数据:
Queue: [(C,3), (E, 9)]
visited: [true,true,false,true,false]
res: [0,3, ∞,2, ∞]
取出C,更新三组数据:
Queue:[(E, 6)]
visited: [true,true,true,true,false]
res: [0,3, 3,2, ∞]
取出E,更新三组数据:
Queue:[]
visited: [true,true,true,true,true]
res: [0,3, 3,2, 6]
至此,Queue队列空,计算过程结束。
Java实现
输入:
int[][] weights:二维数组,表示起点、终点及对应的路径权重,例如:
int[][] weights= {
{2,1,1},
{2,3,1},
{3,4,1}
};
表示下面这个图:
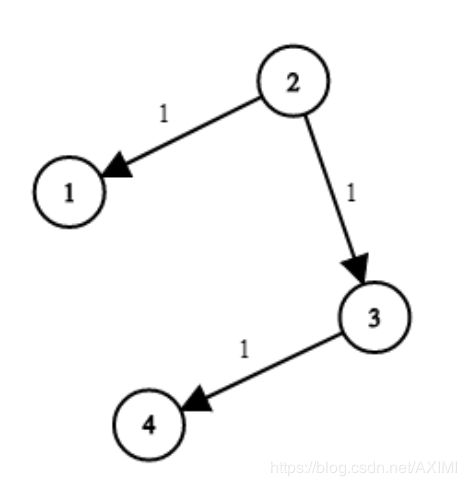
N:表示节点的个数,上面这个图的N为4
K:表示起点
输出:
int[] path:从节点K出发,到其他所有节点的最短路径数组。
例如对于上面的图来说,起点为节点2时,输出的path为:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
public int dij(int[][] weights, int N, int K) {
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> graph=new HashMap<>();
for(int[] w:weights) {
graph.putIfAbsent(t[0], new HashMap<Integer, Integer>());
graph.get(w[0]).put(w[1], w[2]);
}
Queue<int[]> path = new PriorityQueue<>((a ,b)->(a[1]-b[1]));
path.offer(new int[] {K, 0});
Boolean[] visited=new Boolean[N+1];
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
int[] res=new int[N+1];
while(path.size()>0) {
int[] curEdge=path.poll();
int node=curEdge[0];
int weight=curEdge[1];
if(visited[node]) continue;
visited[node]=true;
res[node]=weight;
N--;
if(graph.containsKey(node)) {
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> e: graph.get(node).entrySet()) {
if(visited[e.getKey()]) continue;
path.offer(new int[] {e.getKey(), weight+e.getValue()});
}
}
}
return res;
}
例题
leetcode743