ORACLE提供可以把PL/SQL程序存储在数据库中,并可以在任何地方运行他,这样就叫做存储过程或者函数,
意思就说白了,就是你之前写的select,什么update,这些东西存储起来,我想把这些操作存储起来,像表,
视图,结构式的,当然他不是对象,这里不叫对象,他也能够存储起来,像Function,这是系统提供的,你自己创建的,
之前写过,我们可以删掉他,这儿说明他确确实实存在,包括像这个触发器,这里没有,说明没有创建,当你创建一个
函数,存储过程的时候,那就能够保存下来,什么时候想调用,就调用就完了,触发器,当你想对某个表进行操作的时候,
也是类似于一个函数的东西,这个时候叫做触发器,自动的触发他,就是这样,它是可以被保存起来的,过程和函数的唯一
区别就是函数总是向调用者返回数据,而过程不返回数据,相当于一个有返回值,一个没有,函数是有的,过程是没有的

创建create or replace function,跟前面写的视图都一样,然后这个function的名,如果有参数的话,后边写上
他整个的参数类型,这相当于是一个小括号,function涉及到的形参一样,形参你写到这里边,先写一个参数名,再写参数类型,
这里就不需要指定一个参数的大小了,仅仅是几个类型就行,这个形参什么时候给你填进去,就是通过declare语句,我们上午讲了
declare,begin,在begin;里面调用这个函数的时候,参数是什么,return紧接着就是你返回函数的返回值类型,然后这个叫is,
is里面操作的你可以把它假象成,加上declare,函数在整个的使用当中,你需要定义一个变量,你就定义到这儿,再是你这个函数的
执行体,如果有异常的话,我给你写的这个结构,函数的结构

存储函数,这个结构怎么写,他就是create or replace function,取个function名,就写func_name,
括号写上你参数的类型,参数类型,id number类型的,逗号,name,你想查指定表当中的id,这个id,这个名字的
那个人,等等,或者你想查一下id这个人的工资,salary也是number类型的,往那放,这里又具体分,讲什么out,
一会说到这再说,这是定义这个函数,然后他return,返回值类型,假设你要返回,这里不写这个id,写dept_id,
我返回指定部门的,所有的工资,指定部门可能有很多人,这些所有人的工资,return也是工资,工资是number类型的,
你就返回number类型的,然后is,你在这个过程当中,是不是再涉及到你要定义一些变量,如果需要的话,你写在is这一块,
就是函数的使用过程中,需要声明的变量,或者叫记录类型,写在这,声明一个变量,记录类型,甚至还可以是游标,游标就
写在这,然后呢,begin,开始,这是函数的执行,函数的执行体,在这个过程当中,出现一个异常,考虑异常的处理,处理函数
处理过程中的异常,处理完了以后,就给他end,这是存储函数的一个过程,这里相当于declare,我们写一个PL/SQL的时候,
declare begin end,你就把他当成declare,就是在声明函数中调用到的变量,这是函数的一个形参,这样创建好以后,他就有
这个了,有这个function以后,大概形式就是这样
create or replace function func_name(dept_id number,salary number)
return number;
is
begin
exception
end;

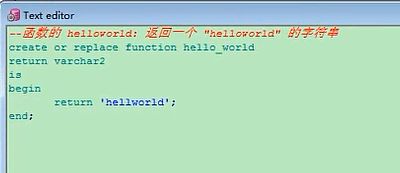
22.2 返回一个"helloworld: atguigu"的字符串,其中atguigu 由执行函数时输入。
--函数的声明(有参数的写在小括号里)
create or replace function hello_func(v_logo varchar2)
--返回值类型
return varchar2
is
--PL/SQL块变量的声明
begin
--函数体
return 'helloworld'|| v_logo;
end;
这就是这个函数的作用,函数的helloworld,调用这个函数就返回hellworld,看他怎么写,create or replace function,
叫hello_world,这个函数没有形参,返回helloworld这个字符串,return varchar2,不用写那个什么,不用写分号,也不用写大小,
is声明,也不用声明,直接begin,return,这是你函数的执行体,执行后的结果,因为你这个函数是需要有返回值的,我就在这里给你
返回,没有异常,没有就end,这是一个最简单的存储函数,创建了
create or replace function hello_world
is
begin
return "helloworld";
end;

创建以后我们在这看,这里就有一个hello_world
正常来写,declare什么什么,这里也不用declare,直接begin,dbms_output.put_line,调用你hello_world
这个函数,end,这就出来了
begin
dbms_output.put_line(hello_world);
end;

或者你在这使用select语句也行,select hello_world,from dual
select hello_world from dual;

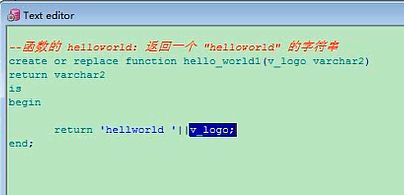
这就是具体调用这个函数了,这是这个例子,然后我把它写得复杂一点,给这个函数带上一个参数,hello_world1,
带个参数,什么参数,加上一个v_log,它是一个varchar2类型的,返回他这个varchar2,然后is是声明,声明写到这里也行,
变量的声明,这里不需要变量声明,这个变量已经有了不需要声明,begin,v_log他赋一个值,直接return,这里我定义了
一个形参,相当于,然后呢走到这,创建好了
create or replace function hello_world1(v_logo varchar2)
return varchar2
is
begin
return 'helloworld' || v_logo;
end;

然后这个调用,select就这么写,select hello_world1,这个参数,varchar型的,他,from他
select hello_world1('atguigu') from dual;
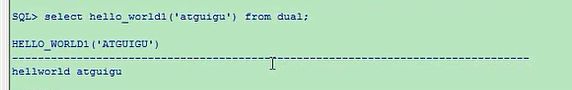
这是select,如果你想使用PL/SQL句型的话,那你就这样
begin
dbms_output.put_line(hello_world('atguigu'));
end;
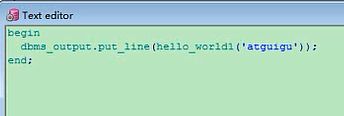

一种是使用PL/SQL程式的形式,一种是SELECT的形式,关键是你要会写这个,这个格式,创建一个函数,函数名,
函数是否需要参数,需要的话就需要写上一个参数,参数的话只要指明类型就行,函数一定是有返回值的,一定会
return一个东西,然后函数在使用过程中,是否需要声明一些变量,相当于在JAVA里边,方法里边,局部变量,起在
is和begin之间,你也可以把它理解成declare,我们之前写在declare和begin之间的东西可以写在这儿,begin,你这个
函数具体执行的函数体,结束,一定要记住这,那这儿你也可以加上一个输出语句,这里or replace相当于把它替换了
create or replace function hello_world1(v_logo varchar2)
return varchar2
is
begin
dbms_output.put_line('人家是函数啦,么么哒');
return 'helloworld' || v_logo;
end;
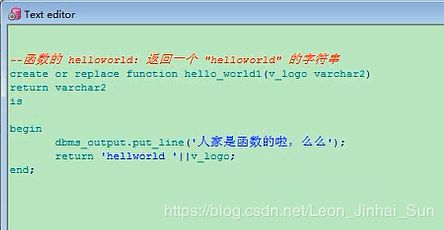

select hello_world1('atguigu1') from dual;

就相当于他执行这个函数体,你这个传入的就放到这儿了,跟你讲JAVA的情况一样,实际上你声明一个值,给我
传一个值,调用你传入的这个值,就是这个意思,这个你看返回的这个顺序,你看它是先输出的这个,再打印的这个,
因为它是有返回值的,他select先拿到你这个返回值,然后返回完了以后,你要这样写的话,或者说有两种执行方式,
另一种
begin
dbms_output.put_line(hello_world1('atguigu'));
end;


这个先输出的这个,是按照你的顺序,这个你了解一下就行,重点是你如何来定义这个函数,
这个函数就这样,然后我们看别的例题
22.3 创建一个存储函数,返回当前的系统时间
create or replace function func1
return date
is
--定义变量
v_date date;
begin
--函数体
--v_date := sysdate;
select sysdate into v_date from dual;
dbms_output.put_line('我是函数哦');
return v_date;
end;
执行法1:
select func1 from dual;
执行法2:
declare
v_date date;
begin
v_date := func1;
dbms_output.put_line(v_date);
end;
创建一个存储函数,返回当前的系统时间,这个就是函数的作用,create or replace function,get_sysdate,这是他的
函数名,return是一个date类型的,然后is需要声明变量吗,声明一个也行,声明一下就这样,date类型的,这个不需要指明大小,
begin,可以这样写,v_date := sysdate,然后呢,然后return date,没有异常,直接end,这样写
create or replace function get_sysdate
return date
is
v_date date;
begin
v_date := sysdate;
return v_date;
end;


然后你在这执行一个
select get_sysdate from dual;

23. 定义带参数的函数: 两个数相加
create or replace function add_func(a number, b number)
return number
is
begin
return (a + b);
end;
执行函数
begin
dbms_output.put_line(add_func(12, 13));
end;
或者
select add_func(12,13) from dual;
定义带参数的函数,create or replace function,add,add相加的意思,两个参数相加,定义v_num1,number类型的,
v_num2,还是number类型,return返回number类型的,is需要再声明一个变量不,v_sum计算他们的和,number类型的,
指明10个,begin,v_sum等于v_num1加上v_num2,return v_sum
create or replace function add add_param(v_num1 number,v_num2 number)
return number
is
v_sum number(10);
begin
v_sum := v_num1 + v_num2;
return v_sum;
end;


创建好了,这个,运行一下
select add_param(2,4) from dual;

在这也行,这个就是使用PL/SQL块的形式
begin
dbms_output.put_line(add_param(3,4));
end;

24. 定义一个函数: 获取给定部门的工资总和, 要求:部门号定义为参数, 工资总额定义为返回值.
create or replace function sum_sal(dept_id number)
return number
is
cursor sal_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = dept_id;
v_sum_sal number(8) := 0;
begin
for c in sal_cursor loop
v_sum_sal := v_sum_sal + c.salary;
end loop;
--dbms_output.put_line('sum salary: ' || v_sum_sal);
return v_sum_sal;
end;
执行函数
begin
dbms_output.put_line(sum_sal(80));
end;
定义一个函数,获取给定部门的工资总和,要求部门号定义为参数,工资总和定义为返回值,返回总额肯定需要你把
一个人一个人的工资加起来,或者再准确点说,所有人都会把工资遍历一遍,使用游标吧,这就把刚才讲的给他结合起来了,
function get_sal,dept_id,number类型的,返回值类型,number的,is,需不需要声明一个变量,声明sum工资,是一个number
类型的,10,分号结束,然后begin,方法体怎么来写,我们现在这个时候再往下写,怎么求指定部门所有的和,使用一个游标,
游标是不是又得写在当时的declare里,那你这个就写这儿呗,指定这个人的部门的工资,cursor给他创建完以后,你就得open,
或者我用一个for更简单,让他加到这个里边,c.salary,这个你要先给他指定一个值,游标都不用关了,返回
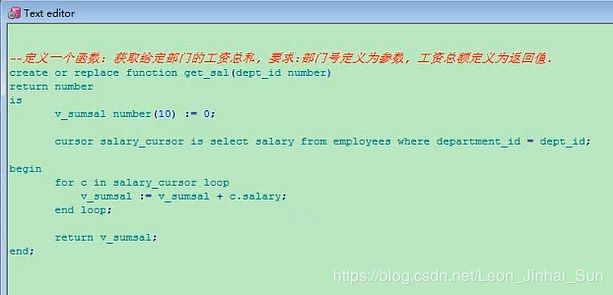
create or replace function get_sal(dept_id number)
return number
is
v_sumsal number(10) := 0;
cursor salary_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = dept_id;
begin
for c in salary_cursor loop
v_sumsal := v_sumsal + c.salary;
end loop;
return v_sumsal;
end;

get_sal,select,get_sal,80号部门的
select get_sal(80) from dual;

你要在这用declare也行,begin,dbms
declare
v_deptid number(4) := 80;
begin
dbms_output.put_line(get_sal(v_deptid));
end;

25. 关于 OUT 型的参数: 因为函数只能有一个返回值, PL/SQL 程序可以通过 OUT 型的参数实现有多个返回值
要求: 定义一个函数: 获取给定部门的工资总和 和 该部门的员工总数(定义为 OUT 类型的参数).
要求: 部门号定义为参数, 工资总额定义为返回值.
create or replace function sum_sal(dept_id number, total_count out number)
return number
is
cursor sal_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = dept_id;
v_sum_sal number(8) := 0;
begin
total_count := 0;
for c in sal_cursor loop
v_sum_sal := v_sum_sal + c.salary;
total_count := total_count + 1;
end loop;
--dbms_output.put_line('sum salary: ' || v_sum_sal);
return v_sum_sal;
end;
执行函数:
delare
v_total number(3) := 0;
begin
dbms_output.put_line(sum_sal(80, v_total));
dbms_output.put_line(v_total);
end;
我们说函数,自变量可以有多个,但是函数返回值永远只有一个,这样才叫函数,这里为什么要定义一个out型的参数,
因为我们知道return永远是return一个,但是我又想存储过程当中,除了要返回工资总额之外,我还想让你返回点别的,
比如说这个,除了要你返回给定部门的工资总额之外,我还想看看这个部门有多少员工,那你这个一个函数,相当于两个
返回值,一个是指定部门的工资总和,一个是该部门的员工总数,你要是变成两个function,那变成一个里面怎么去做,
这个就要使用一个out型的参数,这个参数怎么用,我们就以他举例说一下,在这个里边也有一些说明,in默认不写的话
他就是in,比如in,标记表示传递给函数的值,在该函数执行过程中不改变,你像我们80号部门的80,就是你在执行的过程当中,
只要你用到这个变量了,他都是80,out标记表示一个值在函数中进行计算并通过该参数传递给调用语句,这个变量需要你在
函数执行之前,来定义一下,而这个值是可以被改变的,我们就写一个这个例子,定义一个函数,获取给定部门的工资总额,
和该部门的员工总数,把这个定义成一个out型的参数,部门号定义为参数,工资总额定义为返回值,那我们这个怎么写,定义一个函数,
给定部门的工资总额和他,除了把它当做一个参数之外,还得给一个总人数,total_count,也是一个number类型的,然后为了表明他
不是一个参数,你要这样写的话,那你调用这个函数,需要指定两个参数,不是一个参数,这个也是一个返回值,但是不是return出来的,
加一个out,get_sal1,这个number是工资总和,is,工资总和为0,然后呢,cursor还是指向他,需要指明total_count还是一个值,
一开始没有,所以他的值可以改变,赋值为0,这个是把它工资给累加起来,同时让他累加,还是返回工资总和,这个变量,就是在
你计算工资总和的过程当中,不知不觉的把这个值给他,记录了一下,那么这个值就相当于记录到了,然后给他end结束,执行完了,
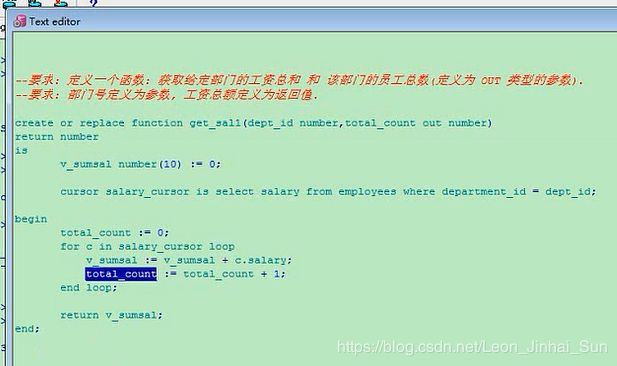
create or replace function get_sal1(dept_id number,total_count out number)
return number
is
v_sumsal number(10) := 0;
cursor salary_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = dept_id;
begin
total_count := 0;
for c in salary_cursor loop
v_sumsal := v_sumsal + c.salary;
total_count := total_count + 1;
end loop;
return v_sumsal;
end;

怎么用这个,多了一个,declare,我定义一个变量,number吧,我在这dbms,调用这个函数,前面是80号部门的,
我让他去记录,这个先给他赋一个值先,这个打印的结果就是你这个的返回值,80号部门的工资,但是他把我这个值
给记录下来了,那我这个时候打印我这个值先,这个是工资总和,这个是公司的人数
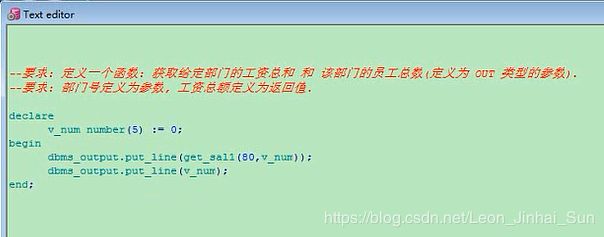
declare
v_num number(5) := 0;
begin
dbms_output.put_line(get_sal(80,v_sum));
dbms_output.put_line(v_num);
end;

这个就是讲out变量怎么用,正常我们讲一个函数就一个返回值,这里同样也是一个,我就想在运算当中
再给我算一个值,其实相当于在看一个因变量,是直接让你返回的,然后被记录下来了,我可以通过这种方式,
让你在计算总工资的时候,把这个值给改变了,再后边就是存储过程,大家先把我讲的存储函数的给看一看,
过程没有返回值,刚才我们讲的都是存储函数,函数是有返回值的,你把这个格式给记住一下,这是函数的格式,
函数的格式有了,你再往里套,过程没有返回值了,这不叫function了,这个是面向过程
26*. 定义一个存储过程: 获取给定部门的工资总和(通过 out 参数), 要求:部门号和工资总额定义为参数
create or replace procedure sum_sal_procedure(dept_id number, v_sum_sal out number)
is
cursor sal_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = dept_id;
begin
v_sum_sal := 0;
for c in sal_cursor loop
--dbms_output.put_line(c.salary);
v_sum_sal := v_sum_sal + c.salary;
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line('sum salary: ' || v_sum_sal);
end;
[执行]
declare
v_sum_sal number(10) := 0;
begin
sum_sal_procedure(80,v_sum_sal);
end;
获取给定部门的工资总和,然后部门号和工资总额定义为参数,那我写的时候把工资总额当成返回值了,是吧,他定义为参数,
对应的用存储过程写,没有返回值,所以你只能用out,用out来写,set serveroutput on

这是刚才写的存储函数,然后现在让你写一个存储过程,给定部门的工资总额,然后create or replace,
然后get_sal2,部门号这是作为一个参数,工资总额sumsal,out型的,也是number类型,没有return,is
就不用再定义了,sumsal赋个值,添加进去以后,for循环完了以后,sumsal,end结束
create or replace procedure get_sal2(dept_id number,sumsal out number)
is
cursor salary_cursor is select salary from employees where department_id = dept_id;
begin
sumsal := 0;
for c in salary_cursor loop
sumsal := sumsal + c.salary;
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line(sumsal);
end;


创建好以后调用一下,你不是要传一个变量吗,80号部门,你要写一个变量,那你还得在PL/SQL写,
declare,v_sal,number类型的,冒号等于,给一个初始化值,begin,80号部门的,把他放进去,end结束
declare
v_sal number(10) := 0;
begin
get_sal2(80,v_sal);
end;


因为他没有返回值了,就像我们JAVA里面的函数,这就打印80号部门的工资总和,这个就是一个存储过程,
你要是函数搞清楚了,存储过程,是比较简单的,把这个改一改,没有return,这里边也不要有return,一般里边都会
有一个输出语句,或者你也不一定是输出了,也有可能是增删改,因为增删改是不需要返回的,增删改不需要返回,
所以把增删改定义成一个存储过程
27*. 自定义一个存储过程完成以下操作:
对给定部门(作为输入参数)的员工进行加薪操作, 若其到公司的时间在 (? , 95) 期间, 为其加薪 %5
[95 , 98) %3
[98, ?) %1
得到以下返回结果: 为此次加薪公司每月需要额外付出多少成本(定义一个 OUT 型的输出参数).
create or replace procedure add_sal_procedure(dept_id number, temp out number)
is
cursor sal_cursor is select employee_id id, hire_date hd, salary sal from employees where department_id = dept_id;
a number(4, 2) := 0;
begin
temp := 0;
for c in sal_cursor loop
a := 0;
if c.hd < to_date('1995-1-1', 'yyyy-mm-dd') then
a := 0.05;
elsif c.hd < to_date('1998-1-1', 'yyyy-mm-dd') then
a := 0.03;
else
a := 0.01;
end if;
temp := temp + c.sal * a;
update employees set salary = salary * (1 + a) where employee_id = c.id;
end loop;
end;
对于给定部门,把它作为一个参数,相当于对指定部门进行操作,进行加薪,既然没有返回值,如果你需要一些返回的情况,
必须使用OUT来声明一下,他这里也确实需要,需要判断这个部门一个月额外付出多少成本,对每个人都加薪,额外输出多少钱,
create or replace,procedure,加薪,add_sal,使用这个,add_sal加薪,需要在里面给定部门,dept_id,number类型的,逗号,
他需要判断额外需要多少钱,这个作为一个out型的参数,他也是number类型的,没有return了,is,额外的要定义一个变量,
一个部门有很多人,就定义一个cursor,cursor,让他去遍历一下,cursor sal_cursor is select,你到底需要查什么,employees,
where department_id = dept_id,这都需要查什么,看你都需要什么,一般也是需要的,额外需要付出多少,一般employee_id也用,不对的
话再改,employee_id,salary,然后再加上hire_date,我先取这三个变量,从这三个表当中,这是加薪,这是加的一个东西,多定义一个变量,
一个是0.03,一个是0.01,比如我再定义一个变量,v_i吧,number类型的,两位小数,就是用来记录这个东西,差不多,然后直接begin,
用for,省得你open,fetch,close,循环,然后呢,判断一下hire_date,不同的hire_date所赋的值是不一样的,如果c的hire_date是在这个
时间段的,这个怎么写啊,让这个hire_date小于一个时间,字符串和date的一个转换,那我就这样一下吧,to_char,是一个date型的,
如果这个是小于1995,按说字符串是不可以比大小的,但是如果你字符串是纯数字的话,他有一个隐式转换,隐式转换纯数字,纯数字的
字符串可以隐式转换,如果是这样的话,then,为其加百分之五,v_i记录一下,加薪的幅度,elsif,1998,0.03,其余的else,直接then了,
然后if就是end if,end if完了,还是得更新一下他的工资,下面操作,1更新工资,2付出的成本,先看这个,一开始他的成本在这儿呢,
在这给他赋值,temp冒号等于0,付出的成本,temp = temp + c.salary*v_i,这就是额外多的,更新工资,update,update employees,
set salary = salary(1+v_i),where employee_id = c.employee_id,然后给他这样操作了,操作完以后,end loop,end
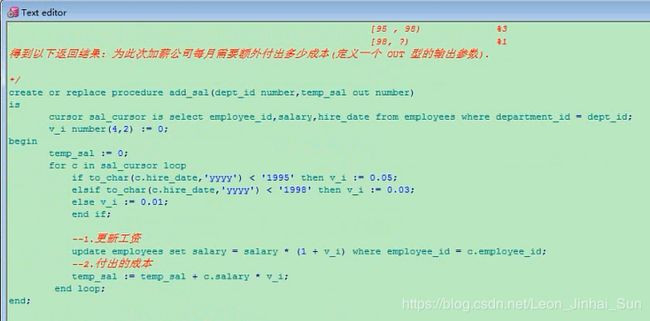
create or replace procedure add_sal(dept_id number,temp_sal out number)
is
cursor sal_cursor is select employee_id,salary,hire_date from employees where department_id = dept_id;
v_i number(4,2) := 0;
begin
temp_sal := 0;
for c in sal_cursor loop
if to_char(c.hire_date,'yyyy') < '1995' then v_i := 0.05;
elsif to_char(c.hire_date,'yyyy') < '1998' then v_i := 0.03;
else v_i := 0.01;
end if;
update employees set salary = salary*(1+v_i) where employee_id = c.employee_id;
temp_sal := temp_sal + c.salary*v_i;
end loop;
end;

创建好以后,然后呢,执行,这里你定义一个变量,declare定义一个变量,定义一下到底要花多少钱,
number,10个单位,冒号等于0,begin,add_sal,80号部门的,然后呢v_temp,我把你要花的给你输出一下
create or replace procedure add_sal(dept_id number,temp_sal out number)
is
cursor sal_cursor is select employee_id,salary,hire_date from employees where department_id = dept_id;
v_i number(4,2) := 0;
begin
temp_sal := 0;
for c in sal_cursor loop
if to_char(c.hire_date,'yyyy') < '1995' then v_i := 0.05;
elsif to_char(c.hire_date,'yyyy') < '1998' then v_i := 0.03;
else v_i := 0.01;
end if;
update employees set salary = salary*(1+v_i) where employee_id = c.employee_id;
temp sal := temp_sal + c.salary*v_i;
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line(temp_sal);
end;
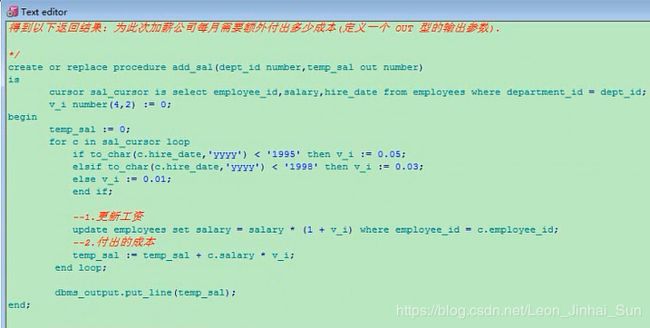
declare
v_temp number(10) := 10;
begin
add_sal(80,_v_temp);
end;

这就叫存储过程,我觉得存储过程比存储函数要简单,你把存储函数理解理解,这个改一改就了事了,
这就是存储过程,存储过程就搞定了














































