一、SpringData入门
在上次学SpringBoot的时候,那时候的教程就已经涉及到了一点SpringData JPA的知识了。当时还是第一次见,觉得也没什么大不了,就是封装了Hibernate的API而已。
然后在慕课网上又看到了SpringData的教程了。于是就进去学习了一番。
教程地址:https://www.imooc.com/learn/821
源码下载地址:https://img.mukewang.com/down/58e60b910001594b00000000.zip
在教程中是以原始JDBC和Spring JDBC Template来进行引入SpringData的。
由于原始的JDBC和Spring JDBC Template需要书写的代码量还是比较多的,于是我们就有了SpringData这么一个框架了。
1.1SpringDataJPA入门
SpringData JPA只是SpringData中的一个子模块
JPA是一套标准接口,而Hibernate是JPA的实现
SpringData JPA 底层默认实现是使用Hibernate
SpringDataJPA 的首个接口就是Repository,它是一个标记接口。只要我们的接口实现这个接口,那么我们就相当于在使用SpringDataJPA了。
只要我们实现了这个接口,我们就可以使用"按照方法命名规则"来进行查询。我第一次见到他的时候觉得他贼神奇。
1.2项目配置
- 在pom.xml中添加相关依赖
- 在yml或者properties文件种配置对应的属性
- 创建实体和Repository测试
参考资源:
- http://blog.csdn.net/pdw2009/article/details/51115044
- http://blog.csdn.net/w_x_z_/article/details/53174308
例子:
比如:定义下面这么一个方法,就可以在外界使用了。
Employee findByName(String name);
也就是说,上面的方法会被解析成SQL语句:select * from Employee where name = ?
是不是觉得很方便!!!!
如果是简单的操作的话,直接定义这么一个方法,就能够使用了。确确实实很好。
简直比Mytais不知道好到哪里去了。Mybatis还要去写映射文件,专门写一个sql语句。
同时,创建了实体就能够自动帮我们创建数据库表了,修改了实体字段也能够将数据表一起修改。顿时就觉得很好用了。
/**
* 雇员: 先开发实体类===>自动生成数据表
*/
@Entity
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@GeneratedValue
@Id
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(length = 20)
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
当然了,上面根据方法名来使用是有弊端的:
- 1)方法名会比较长: 约定大于配置
- 2)对于一些复杂的查询,是很难实现
比如:
// where name like ?% and age findByNameStartingWithAndAgeLessThan(String name, Integer age);
// where name like %? and age findByNameEndingWithAndAgeLessThan(String name, Integer age);
// where name in (?,?....) or age findByNameInOrAgeLessThan(List names, Integer age);
// where name in (?,?....) and age findByNameInAndAgeLessThan(List names, Integer age);
因此,对于这种情况下还是要写SQL语句简单得多。
@Query("select o from Employee o where id=(select max(id) from Employee t1)")
public Employee getEmployeeByMaxId();
@Query("select o from Employee o where o.name=?1 and o.age=?2")
public List queryParams1(String name, Integer age);
@Query("select o from Employee o where o.name=:name and o.age=:age")
public List queryParams2(@Param("name")String name, @Param("age")Integer age);
@Query("select o from Employee o where o.name like %?1%")
public List queryLike1(String name);
@Query("select o from Employee o where o.name like %:name%")
public List queryLike2(@Param("name")String name);
@Query(nativeQuery = true, value = "select count(1) from employee")
public long getCount();
学过Hibernate的都知道上面的不是原生的SQL语句,是HQL/JPQL语句。不过他用起来还是比Mybatis简洁很多。
对于修改数据,需要增加Modify注解、并且一定要在事务的管理下才能修改数据
@Modifying
@Query("update Employee o set o.age = :age where o.id = :id")
public void update(@Param("id")Integer id, @Param("age")Integer age);
1.3Repository子类接口
CURDRepository接口的实现方法:
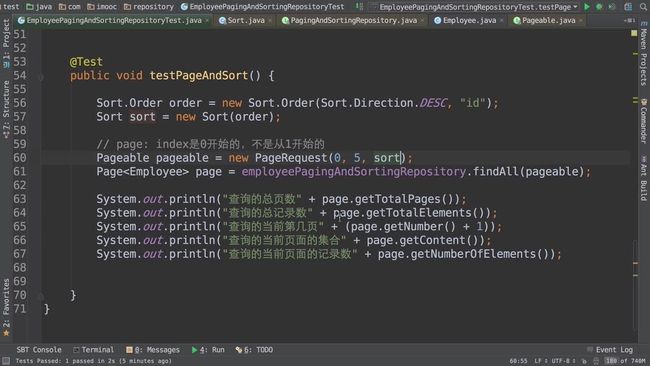
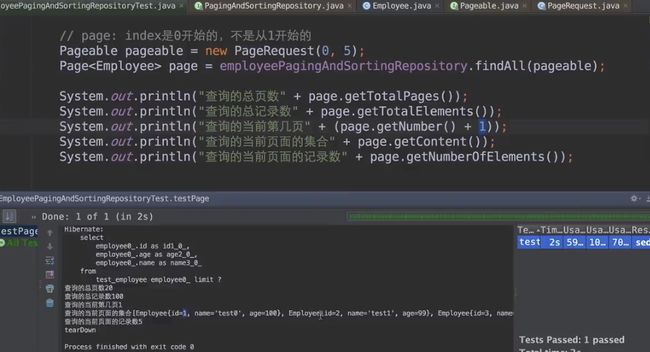
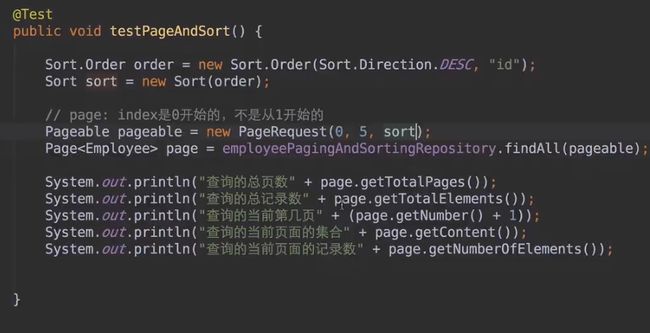
排序、分页接口:
增加过滤条件的接口:
JPA接口:
JpaRepository继承PagingAndSortingRepository,PagingAndSortingRepository又继承CrudRepository,也就是说我们平时自定义的接口只要继承JpaRepository,就相当于拥有了增删查改,分页,等等功能。
二、JPQL基础
原来JPQL是JPA的一种查询语言,之前我是认为它和HQL是一样的。其实是两个概念。不过它们用起来还真是差不多。
无非就是:JPA对应JPQL,而Hibernate对应HQL而已。都是面向对象的查询语言。
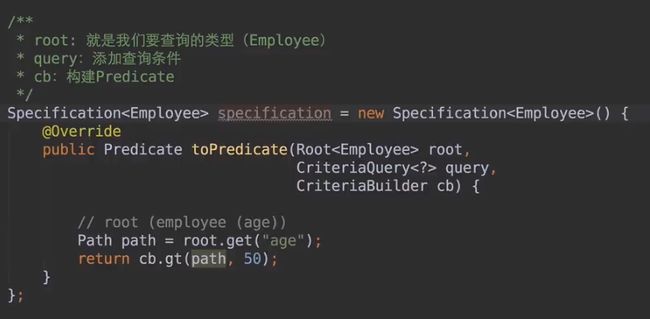
2.1 Criteria查询
这里就涵盖了很多的条件了。
2.2 Specification接口使用
其实这个接口的API就和Criteria是一样的,看懂了Criteria API,这个接口就会用了。
2.3 nameQuery注解
2.4query注解
2.5 小总结
https://www.zhihu.com/question/53706909
引入知乎的一段回答:
基本的增删改查和调用存储过程通过Spring Data JPA Repository来解决
稍微复杂的查询或是批量操作使用QueryDSL或Spring Data Specification的API来解决
特别特别复杂的查询操作可以使用Spring Data JPA Repository的注解定义native sql来解决
三、需要注意的地方
3.1 注解写在get方法上
刚开始用的时候我以为注解是写在属性上,但是遇到了很多的bug,在网上的解决方案又是很少。
遇到了一个Bug,在国内的论坛几乎都找不到答案:
org.hibernate.property.access.spi.PropertyAccessBuildingException: Could not locate field nor getter method for property named [cn.itheima.web.domain.Customer#cust_user_id]
搞得头都大了都没有找到合适的方法,不知道是哪里错了。
后来去看了JPA的一对多、多对一的博文去参考了一下,感觉我还是没有错。
最后才发现大多数的博文都是在get方法上写注解的,而我就在属性上直接写注解了。
在Get方法上写注解的原因是不用破坏我们的封装性,我直接在属性上写注解,而属性是private来进行修饰的。这也导致了我出现这个错误的原因。
3.2级联 .ALL慎用
在保存数据的时候,我以为直接使用casecade.ALL是最方便的,但是还出现了Bug。后来找到了答案:http://blog.csdn.net/csujiangyu/article/details/48223641
3.3@OneToOne的注解
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public@interfaceOneToOne {
Class targetEntity() default void.class;
CascadeType[]cascade()default();
FetchType fetch() default EAGER;
boolean optional() default true;
String mappedBy() default "";
}
1,targetEntity 属性表示默认关联的实体类型,默认为当前标注的实体类。
2,cascade属性表示与此实体一对一关联的实体的级联样式类型。
3,fetch属性是该实体的加载方式,默认为即时加载EAGER
4,optional属性表示关联的该实体是否能够存在null值,默认为ture,如果设置为false,则该实体不能为null,
5, mapperBy属性:指关系被维护端
3.4@JoinColumn注解
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public@interfaceJoinColumn {
String name() default "";
String referencedColumnName() default "";
boolean unique() default false;
boolean nullable() default true;
boolean insertable() default true;
booleanupdatabledefaulttrue;
String columnDefinition() default "";
String table() default "";
}
1,@JoinColumn注释是保存表与表之间关系的字段
2,如果不设置name,默认name = 关联表的名称+”-“+关联表主键的字段名,在上面实例3,中,默认为“address_id” **
默认情况下,关联实体的主键一般是用来做外键的,但如果此时不想用主键作为外键,则需要设置referencedColumnName属性,如:**
create table address (
id int(20) not null auto_increament,
ref_id int(20) notn ull,
province varchar(50),
city varchar(50),
postcode varchar(50),
detail varchar(50),
primary key(id)
)
@OneToOne@JoinColumn(name="address_id", referencedColumnName="ref_id")
private AddressEO address;
四、扩展阅读
后来我使用了SpringData JPA用于一个简单的项目,从中也遇到了不少的问题和相关的没有接触到的知识点。下面我会给出当时搜索到的资料和遇到的问题以及解决方案
4.1遇到的问题以及解决资料
SpringData JPA遇到的问题有:
参考资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/sevenlin/p/sevenlin_sprindatajpa20150725.html
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_35797610/article/details/78737211
-
CascadeType jpa spring 理解:最好在开始的使用只使用REFRESH,当遇到问题的时候再添加MERGER等等,不然一开始会很乱
- http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9c2cda810101jw4a.html
-
一对多,多对一的配置问题。注解写在GETTER方法上,不要写在属性上。这样会避免很多不必要的错误
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/0a2163273b3e
- http://blog.csdn.net/ABAP_Brave/article/details/52845986
- http://blog.csdn.net/lyg_2012/article/details/70195062
- http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_76c4136a0102y70d.html
- http://blog.csdn.net/mendeliangyang/article/details/52366799/
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/5c416a780b3e
-
异常处理:
- detached entity passed to persist异常:
- http://blog.csdn.net/csujiangyu/article/details/48223641
- JPA一堆多循环引用错误 HttpMessageNotWritableException:
- http://blog.csdn.net/wangping1223/article/details/78062881
- detached entity passed to persist异常:
五、总结
总的来说,如果是单表操作的话,那么SpringData JPA是十分方便的,如果是比较复杂的业务的话,那么使用SpringData JPA就有点麻烦了,因为它返回的是Object[],返回的结果还要手动进行封装,不太方便。灵活性很低...
如果文章有错的地方欢迎指正,大家互相交流。习惯在微信看技术文章,想要获取更多的Java资源的同学,可以关注微信公众号:Java3y