SSLSocket加密通讯
以使用C#实现
SSL Socket通讯是对socket的扩展,增加Socket通讯的数据安全性,SSL认证分为单向和双向认证。单向认证只认证服务器端的合法性而不认证客户端的合法性。双向认证是同时认证服务端和客户端。下面我分别说说使用C#实现单向认证和双向认证的过程,并用代码实现。
一、 单向认证
第1步:准备一个数字证书,可以使用如下脚本生成
先进入到vs2005的命令行状态,即:
开始–>程序–>Microsoft Visual Studio 2005–>Visual Studio Tools–>Visual Studio 2005 命令提示
键入: makecert -r -pe -n “CN=TestServer” -ss Root -sky exchange
说明:上面的指令将在创建一个受信任的根证书,
或者
1、购买或申请证书,得到一系列证书文件、包含各中间层认证机构证书(一般证书供应商会提供)
2、运行MMC工具,添加证书管理单元、使用“计算机账户”,再将证书导入,保存到哪个证书目录下自己记住,以便下一步找证书
3、查出与域名对应的证书的Hash(也叫指纹,默认是中间含空格,可复制出来,删除空格)
4、用httpcfg工具进行绑定,注意使用:"0.0.0.0:端口号",端口号一般是443,也可改其他的
命令: httpcfg set ssl -i 0.0.0.0:443 -h 证书哈希值
或者: netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=证书哈希值 appid={00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}
5、如httpcfg出现1312错误(未能添加 SSL 证书,错误: 1312 指定的登录会话不存在。可能已被终止。),
多半是证书部署有问题,多尝试导入安装不同格式的证书
第2步创建服务器端程序,代码如下:
using System;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Text;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.IdentityModel.Tokens;
using System.IdentityModel.Selectors;
namespace ConsoleApp
{
public class Program
{
static X509Certificate serverCertificate = null;
public static void RunServer()
{
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(IPAddress.Parse("192.168.1.25"), 901);
listener.Start();
while (true)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for a client to connect...");
TcpClient client = listener.AcceptTcpClient();
ProcessClient(client);
}
catch
{
}
}
}
static void ProcessClient(TcpClient client)
{
SslStream sslStream = new SslStream(client.GetStream(), false);
try
{
sslStream.AuthenticateAsServer(serverCertificate, false, SslProtocols.Tls, true);
DisplaySecurityLevel(sslStream);
DisplaySecurityServices(sslStream);
DisplayCertificateInformation(sslStream);
DisplayStreamProperties(sslStream);
sslStream.ReadTimeout = 5000;
sslStream.WriteTimeout = 5000;
byte[] message = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello from the server.");
Console.WriteLine("Sending hello message.");
sslStream.Write(message);
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for client message...");
while (true)
{
string messageData = ReadMessage(sslStream);
Console.WriteLine("Received: {0}", messageData);
if (messageData.ToUpper() == "EXIT")
break;
}
}
catch (AuthenticationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception: {0}", e.Message);
if (e.InnerException != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Inner exception: {0}", e.InnerException.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("Authentication failed - closing the connection.");
sslStream.Close();
client.Close();
return;
}
finally
{
sslStream.Close();
client.Close();
}
}
static string ReadMessage(SslStream sslStream)
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
StringBuilder messageData = new StringBuilder();
int bytes = -1;
do
{
bytes = sslStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
Decoder decoder = Encoding.UTF8.GetDecoder();
char[] chars = new char[decoder.GetCharCount(buffer, 0, bytes)];
decoder.GetChars(buffer, 0, bytes, chars, 0);
messageData.Append(chars);
if (messageData.ToString().IndexOf("") != -1)
{
break;
}
}
while (bytes != 0);
return messageData.ToString();
}
static void DisplaySecurityLevel(SslStream stream)
{
Console.WriteLine("Cipher: {0} strength {1}", stream.CipherAlgorithm, stream.CipherStrength);
Console.WriteLine("Hash: {0} strength {1}", stream.HashAlgorithm, stream.HashStrength);
Console.WriteLine("Key exchange: {0} strength {1}", stream.KeyExchangeAlgorithm, stream.KeyExchangeStrength);
Console.WriteLine("Protocol: {0}", stream.SslProtocol);
}
static void DisplaySecurityServices(SslStream stream)
{
Console.WriteLine("Is authenticated: {0} as server? {1}", stream.IsAuthenticated, stream.IsServer);
Console.WriteLine("IsSigned: {0}", stream.IsSigned);
Console.WriteLine("Is Encrypted: {0}", stream.IsEncrypted);
}
static void DisplayStreamProperties(SslStream stream)
{
Console.WriteLine("Can read: {0}, write {1}", stream.CanRead, stream.CanWrite);
Console.WriteLine("Can timeout: {0}", stream.CanTimeout);
}
static void DisplayCertificateInformation(SslStream stream)
{
Console.WriteLine("Certificate revocation list checked: {0}", stream.CheckCertRevocationStatus);
X509Certificate localCertificate = stream.LocalCertificate;
if (stream.LocalCertificate != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Local cert was issued to {0} and is valid from {1} until {2}.",
localCertificate.Subject,
localCertificate.GetEffectiveDateString(),
localCertificate.GetExpirationDateString());
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Local certificate is null.");
}
X509Certificate remoteCertificate = stream.RemoteCertificate;
if (stream.RemoteCertificate != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Remote cert was issued to {0} and is valid from {1} until {2}.",
remoteCertificate.Subject,
remoteCertificate.GetEffectiveDateString(),
remoteCertificate.GetExpirationDateString());
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Remote certificate is null.");
}
}
private static void DisplayUsage()
{
Console.WriteLine("To start the server specify:");
Console.WriteLine("serverSync certificateFile.cer");
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
X509Store store = new X509Store(StoreName.Root);
store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadWrite);
// 检索证书
X509Certificate2Collection certs = store.Certificates.Find(X509FindType.FindBySubjectName, "TestServer", false); // vaildOnly = true时搜索无结果。
if (certs.Count == 0) return;
serverCertificate = certs[0];
RunServer();
store.Close(); // 关闭存储区。
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}第3步,创建客户端代码
namespace ConsoleAppClient
{
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Text;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
namespace Examples.System.Net
{
public class SslTcpClient
{
private static Hashtable certificateErrors = new Hashtable();
// The following method is invoked by the RemoteCertificateValidationDelegate.
public static bool ValidateServerCertificate(
object sender,
X509Certificate certificate,
X509Chain chain,
SslPolicyErrors sslPolicyErrors)
{
if (sslPolicyErrors == SslPolicyErrors.None)
return true;
Console.WriteLine("Certificate error: {0}", sslPolicyErrors);
// Do not allow this client to communicate with unauthenticated servers.
return false;
}
public static void RunClient(string machineName)
{
// Create a TCP/IP client socket.
// machineName is the host running the server application.
TcpClient client = new TcpClient(machineName, 901);
Console.WriteLine("Client connected.");
// Create an SSL stream that will close the client's stream.
SslStream sslStream = new SslStream(client.GetStream(), false, new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(ValidateServerCertificate), null);
try
{
sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient("TestServer");
}
catch (AuthenticationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception: {0}", e.Message);
if (e.InnerException != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Inner exception: {0}", e.InnerException.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("Authentication failed - closing the connection.");
client.Close();
return;
}
// Encode a test message into a byte array.
// Signal the end of the message using the "".
byte[] messsage = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello from the client.");
// Send hello message to the server.
sslStream.Write(messsage);
sslStream.Flush();
// Read message from the server.
string serverMessage = ReadMessage(sslStream);
Console.WriteLine("Server says: {0}", serverMessage);
messsage = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("exit");
sslStream.Write(messsage);
sslStream.Flush();
// Close the client connection.
client.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Client closed.");
}
static string ReadMessage(SslStream sslStream)
{
// Read the message sent by the server.
// The end of the message is signaled using the
// "" marker.
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
StringBuilder messageData = new StringBuilder();
int bytes = -1;
do
{
bytes = sslStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
// Use Decoder class to convert from bytes to UTF8
// in case a character spans two buffers.
Decoder decoder = Encoding.UTF8.GetDecoder();
char[] chars = new char[decoder.GetCharCount(buffer, 0, bytes)];
decoder.GetChars(buffer, 0, bytes, chars, 0);
messageData.Append(chars);
// Check for EOF.
if (messageData.ToString().IndexOf("") != -1)
{
break;
}
} while (bytes != 0);
return messageData.ToString();
}
private static void DisplayUsage()
{
Console.WriteLine("To start the client specify:");
Console.WriteLine("clientSync machineName [serverName]");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string machineName = null;
machineName = "192.168.1.25";
try
{
RunClient(machineName);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
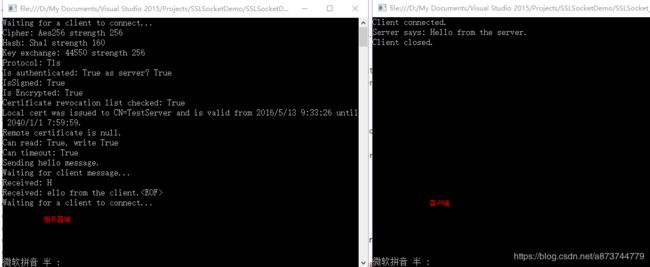
} 运行效果如下图:
导致通讯失败可能问题如下:
1)证书没有导入到受信任的根证书列表中;2)证书失效;3)客户端在使用AuthenticateAsClient注册时没有正确使用服务器端证书名称。
二、 双向认证
第1步:创建所需证书,服务器端所需证书同单向认证中的创建过程
先进入到vs2005的命令行状态,即:
开始–>程序–>Microsoft Visual Studio 2005–>Visual Studio Tools–>Visual Studio 2005 命令提示
键入:
makecert -r -pe -n “CN=TestClient” -ss Root -sky exchange
第2步:创建服务端程序
服务端的程序同单向认证的服务器端代码
第3步:创建客户端程序
namespace ConsoleAppClient
{
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Net.Security;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Text;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
namespace Examples.System.Net
{
public class SslTcpClient
{
private static Hashtable certificateErrors = new Hashtable();
// The following method is invoked by the RemoteCertificateValidationDelegate.
public static bool ValidateServerCertificate(
object sender,
X509Certificate certificate,
X509Chain chain,
SslPolicyErrors sslPolicyErrors)
{
if (sslPolicyErrors == SslPolicyErrors.None)
return true;
Console.WriteLine("Certificate error: {0}", sslPolicyErrors);
// Do not allow this client to communicate with unauthenticated servers.
return false;
}
public static void RunClient(string machineName)
{
// Create a TCP/IP client socket.
// machineName is the host running the server application.
TcpClient client = new TcpClient(machineName, 901);
Console.WriteLine("Client connected.");
// Create an SSL stream that will close the client's stream.
SslStream sslStream = new SslStream(client.GetStream(), false, new RemoteCertificateValidationCallback(ValidateServerCertificate), null);
// The server name must match the name on the server certificate.
X509Store store = new X509Store(StoreName.Root);
store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadWrite);
//// 检索证书
X509Certificate2Collection certs = store.Certificates.Find(X509FindType.FindBySubjectName, "TestClient", false);
try
{
sslStream.AuthenticateAsClient("TestServer", certs, SslProtocols.Tls, false);
}
catch (AuthenticationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception: {0}", e.Message);
if (e.InnerException != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Inner exception: {0}", e.InnerException.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("Authentication failed - closing the connection.");
client.Close();
return;
}
// Encode a test message into a byte array.
// Signal the end of the message using the "".
byte[] messsage = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello from the client.");
// Send hello message to the server.
sslStream.Write(messsage);
sslStream.Flush();
// Read message from the server.
string serverMessage = ReadMessage(sslStream);
Console.WriteLine("Server says: {0}", serverMessage);
messsage = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("exit");
sslStream.Write(messsage);
sslStream.Flush();
// Close the client connection.
client.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Client closed.");
}
static string ReadMessage(SslStream sslStream)
{
// Read the message sent by the server.
// The end of the message is signaled using the
// "" marker.
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
StringBuilder messageData = new StringBuilder();
int bytes = -1;
do
{
bytes = sslStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
// Use Decoder class to convert from bytes to UTF8
// in case a character spans two buffers.
Decoder decoder = Encoding.UTF8.GetDecoder();
char[] chars = new char[decoder.GetCharCount(buffer, 0, bytes)];
decoder.GetChars(buffer, 0, bytes, chars, 0);
messageData.Append(chars);
// Check for EOF.
if (messageData.ToString().IndexOf("") != -1)
{
break;
}
} while (bytes != 0);
return messageData.ToString();
}
private static void DisplayUsage()
{
Console.WriteLine("To start the client specify:");
Console.WriteLine("clientSync machineName [serverName]");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string machineName = null;
machineName = "192.168.1.25";
try
{
RunClient(machineName);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}