SpringBoot
Spring Boot
0.学习来源:https://www.imooc.com/t/4559066
1.简述
Spring boot是SpringMVC的进阶版
2.构建SpringBoot的demo项目
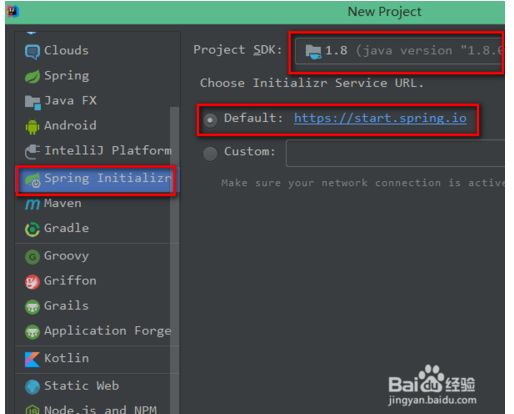
2.1 idea创建项目
- idea旗舰版:
- idea社区版:
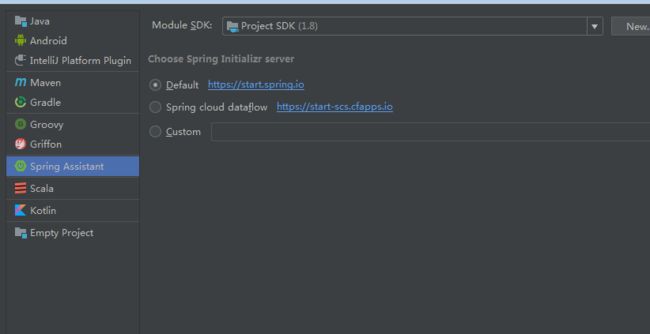
社区版没有Spring initializr选项,需要安装插件叫做 Spring Assistant
后面的步骤都是大同小异
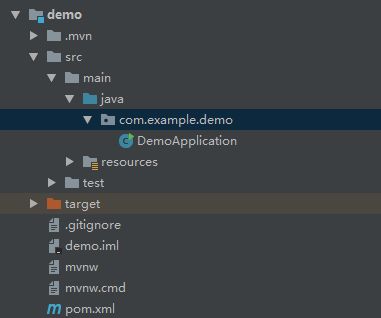
创建完项目以后是这样子的
说明:
- DemoApplication是自动生成的
- pom.xml里面是maven依赖
2.2 运行项目
2.2.1 直接运行
并没有下载配置过tomcat就可以运行,不知道是不是内部自带的。
2.2.2 增加一些内容以后再运行
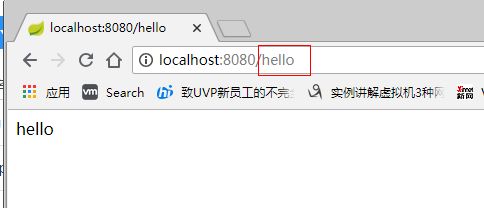
- 创建一个HelloController类:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(){
return "hello";
}
}
- 再运行
3.配置
3.1 application.properties
修改一些配置
//修改端口
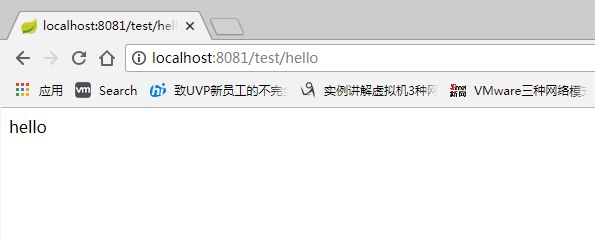
server.port = 8081
//老版更改路径
server.context-path =/test
//新版更改路径
server.servlet.context-path =/test
重新运行
3.2 application.yml(推荐使用)
这个也是配置文件,和application.propertices作用差不多,但是写法格式不一样。
server:
port: 8082
servlet.context-path: /test2
//注意冒号后面有空格
3.3 读取application.yml里面的其他数据
server:
port: 8080
servlet.context-path: /test
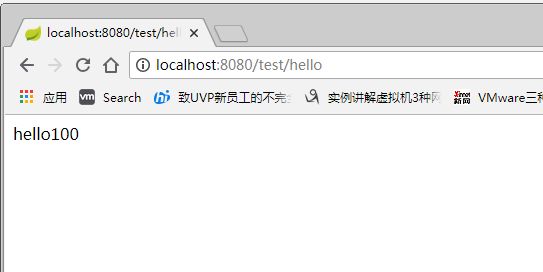
data: 100
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
//把application.yml里面的data数据注入到data变量里面
@Value("${data}")
private int data;
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(){
return "hello"+data;
}
}
server:
port: 8081
servlet.context-path: /test
data: 1000
age: 1000
content: "data: ${data},age: ${age}"
content2: "${data}"
content3: ${data}
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
//把application.yml里面的data数据注入到data变量里面
@Value("${data}")
private int data;
@Value("${content}")
private String content;
@Value("${content2}")
private String content2;
@Value("${content3}")
private int content3;
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(){
return "content:"+content+" content2:"+content2+" content3:"+content3;
}
}
3.5 读取yml文件到bean类
bean:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class personProperties {
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private String name;
}
application.yml
server:
port: 8081
servlet.context-path: /test
person:
age: 10
name: zhangsan
controller调用
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Resource(name = "personProperties")//或者Autowired
private personProperties personProperties;
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(){
return "age:"+personProperties.getAge()+" name:"+personProperties.getName();
}
}
运行结果
3.6 多个yml配置文件选择
比如说有两个yml配置文件,在开发环境时和真正使用时有些参数是不一样的,用两个yml配置文件把他们区分开,比如一个data在开发时使用的10,在项目使用时是20。这样子,在不同的环境下选择不同的yml配置文件
application-dev.propertices:
server:
port: 8080
servlet.context-path: /test
data: 10
application-prod.propertices:
server:
port: 8080
servlet.context-path: /test
data: 20
application.propertices:
spring:
profiles:
active: dev或者是prod可以选择
controller:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${data}")
private int data;
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(){
return "data:"+data;
}
}
4. 注解
4.1 RestControlle和@Controller+@ResponseBody
@RestControlle
等价于:@Controller+@ResponseBody
就是说:
这两种效果一样
4.2 @RequestMapping
4.2.1 匹配多个路径
表示http://localhost:8080/test/hi和http://localhost:8080/test/hello都可以访问到
@RequestMapping(value = {"/hello","/hi"},method = RequestMethod.GET)
4.2.2 在class前面加RequestMapping
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@Value("${data}")
private int data;
@RequestMapping(value = "/say",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(){
return "data:"+data;
}
}
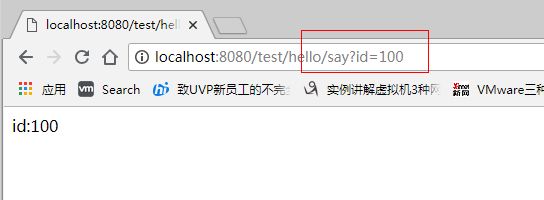
4.3 @PathVariable获取参数
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
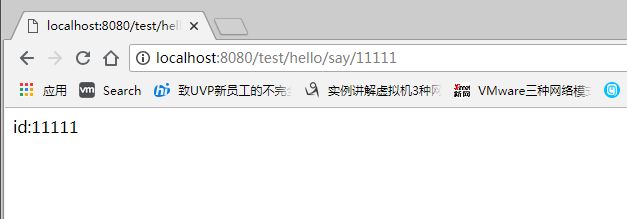
@RequestMapping(value = "/say/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return "id:"+id;
}
}
或者还可以调整id的位置
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}/say",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return "id:"+id;
}
}
4.4 @RequestParam
这个也是获取参数
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/say",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String say(@RequestParam(value = "id",required = false,defaultValue = "0") Integer id){
return "id:"+id;
}
}
4.5 @GetMapping(value = "/say")和@PostMapping(value = "/say")
@GetMapping(value = "/say") 等价于 @RequestMapping(value = "/say",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@PostMapping(value = "/say") 等价于 @RequestMapping(value = "/say",method = RequestMethod.POST)
5.SpringBoot+jpa+hibernate数据库的简单操作
5.1插入一条数据
先创建一个数据库,不需要创建表
添加依赖(jpa和mysql的)
4.0.0
com.example
demo
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
jar
demo
Demo project for Spring Boot
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.0.4.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
配置yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dbgirl
username: root
password: 123456
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
写一个bean类,注意注解Entity
package com.example.demo;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
//注解表示这个类对应数据库里面的一个表
@Entity
public class Girl {
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCupSize() {
return cupSize;
}
public void setCupSize(String cupSize) {
this.cupSize = cupSize;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
//注解表示这个id是主键,而且自增
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
private String cupSize;
private Integer age;
}
写一个接口
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface GirlRepository extends JpaRepository {
}
在Controller中:
@Autowired
private GirlRepository girlRepository;
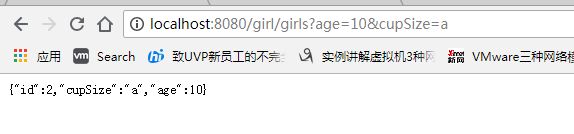
@RequestMapping(value = "girls",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Girl insert(@RequestParam("age") Integer age, @RequestParam("cupSize") String cupSize){
Girl girl = new Girl();
girl.setAge(age);
girl.setCupSize(cupSize);
System.out.println(age+cupSize);
return girlRepository.save(girl);
}
浏览器中:
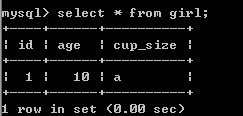
数据库中数据被插入
5.2 数据库事物
//Transactional注解给这个方法添加事物
@Transactional
@RequestMapping(value = "girls2",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void insertTwo(){
Girl girl = new Girl();
girl.setAge(1);
girl.setCupSize("a");
Girl girl2 = new Girl();
girl2.setAge(2);
girl2.setCupSize("b");
girlRepository.save(girl);
girlRepository.save(girl2);
}
以上都是简单的使用,更复杂的使用还需继续学习
6表单验证
还是上面的代码,整理一下包结构
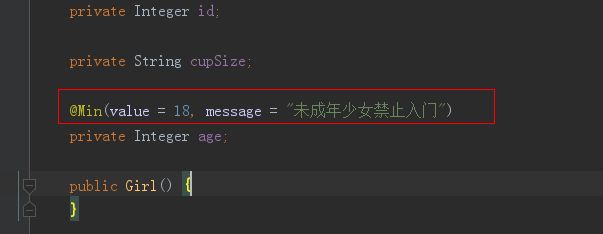
功能需求:插入一条新的数据的时候,该数据的某个值必须满足一定要求,比如age>18
给Girl的字段添加限制条件:
表示这个age数据的最小值是18,当插入的值小于18的时候,是插入不进去的。
@PostMapping(value = "/girls")
public Girl girlAdd(@Valid Girl girl, BindingResult bindingResult) {
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()){
//可以把message里面的值拿出来
System.out.println(bindingResult.getFieldError().getDefaultMessage());
return null;
}
girl.setCupSize(girl.getCupSize());
girl.setAge(girl.getAge());
return girlRepository.save(girl);
}
这个@Valid暂时不清楚有什么作用