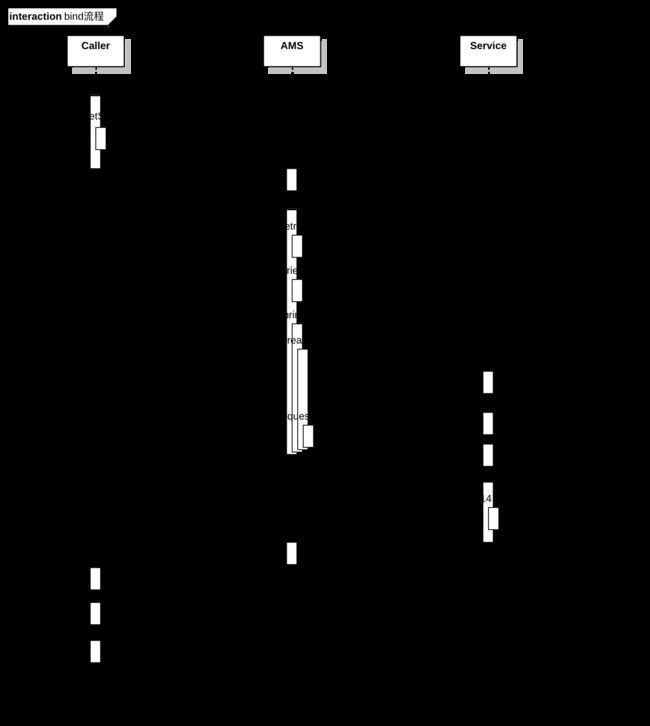
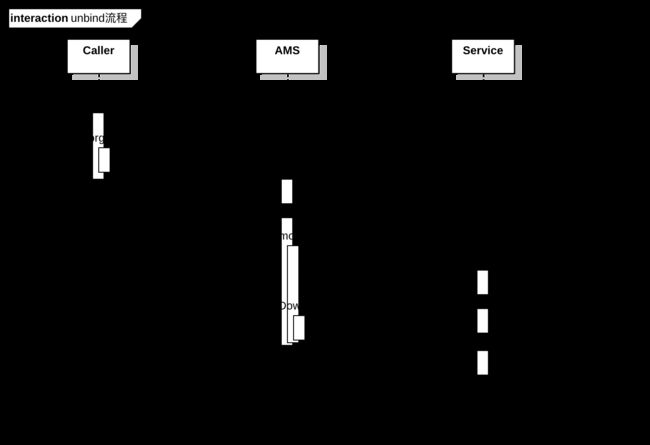
Service启动流程总结-bind和unbind
文章目录
- 回顾
- 概述
- 基本使用
- 源码探究
- bind过程
- Caller发起bind
- IServiceConnection说明
- AMS处理bind请求
- Service处理bind请求
- AMS发布Service
- Caller处理连接回调
- unbind过程
- 总结
回顾
Service启动系列总结:
《Service启动流程总结-start和stop service》
概述
在开发中我们使用Context#bindService和Context#unbindService来绑定和解绑Service,通过绑定来启动Service,可以方便的调用Service提供的API。Service的bind、unbind过程和start、stop过程类似,比较大的区别是多了Binder的传递过程。
基本使用
- 定义AIDL文件
// ISpeaker.aidl
package com.cdh.study;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface ISpeaker {
String sayHello();
}
- 定义Server端
public class SpeakerService extends Service {
// 创建由aidl文件自动生成的Stub实例
private final ISpeaker.Stub mSpeakerBinder = new ISpeaker.Stub() {
@Override
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException {
return "hello!";
}
};
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// 返回Stub实例
return mSpeakerBinder;
}
}
在Service的onBind回调中返回创建的ISpeaker.Stub实例,Stub继承Binder和ISpeaker。Client端在成功连接后便可通过其调用Server端的sayHello方法。
- 定义Client端
// Server端API接口,若Client和Server处于同一进程则返回的即是Server端binder实例,否则是Server端binder代理
private ISpeaker mISpeaker;
// 创建ServiceConnection实例,用作回调接口
private final ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// 连接回调,service即Server端onBind返回的IBinder
mISpeaker = ISpeaker.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// 断连回调
mISpeaker = null;
}
};
public void bind() {
// 绑定Server
mContext.bindService(new Intent(mContext, SpeakerService.class), mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
public void unbind() {
// 解绑Server,需要传入绑定时的ServiceConnection接口(内部以ServiceConnection作为key)
mContext.unbindService(mConnection);
}
- 调用Server端提供的API
public void requestHello() {
if (mISpeaker != null) {
try {
// 调用Service方法,会返回"hello!"
mISpeaker.sayHello();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Client端首先进行绑定Service,成功绑定后会回调ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected方法,在这里获取Server端binder实例或binder代理,之后便可通过binder来调用Server端API。
以上是一个bind service的简单例子,接下来跟踪源码调用看看bind service的整体流程。
源码探究
文中源码基于 Android 10.0
bind过程
Caller发起bind
Caller指调用方,发起bind service,将会调用ContextImpl的bindService方法:
[ContextImpl#bindService]
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
// 传入意图、ServiceConnection实例、BIND_AUTO_CREATE(表示目标Service未启动时自动创建)和主线程Handler和当前用户具柄
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, null, mMainThread.getHandler(), null,
getUser());
}
[ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon]
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
String instanceName, Handler handler, Executor executor, UserHandle user) {
// Keep this in sync with DevicePolicyManager.bindDeviceAdminServiceAsUser.
// binder通信接口,用于AMS向Caller进程通信
IServiceConnection sd;
// ···
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
if (executor != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), executor, flags);
} else {
// 此时executor是null,执行这个case获取IServiceConnection
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
// 省略显示意图校验 ···
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
// ···
// 请求AMS进行bind流程
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindIsolatedService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, instanceName, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
该方法中先获取IServiceConnection,然后调用AMS的bindIsolatedService方法。
IServiceConnection说明
在前面的基本使用例子中,Client端通过ServiceConnection接口回调获取Server端binder。但ServiceConnection只是一个普通接口,不支持跨进程通信。因此这里利用IServiceConnection进行AMS向Caller进程调用时的binder通信接口。
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
上文通过这个方法获取IServiceConnection,mPackageInfo是LoadedApk,进入方法看看。
[LoadedApk#getServiceDispatcher]
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
return getServiceDispatcherCommon(c, context, handler, null, flags);
}
[LoadedApk#getServiceDispatcherCommon]
private IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcherCommon(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, Executor executor, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
// ···
if (sd == null) {
if (executor != null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, executor, flags);
} else {
// 创建ServiceDispatcher
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
}
// ···
} else {
// ···
}
// 返回其中的mIServiceConnection成员
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
这里省略了判断缓存的部分,若没有缓存,则新建ServiceDispatcher包装传入的参数。
接着看ServiceDispatcher构造方法:
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mActivityExecutor = null;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
ServiceDispatcher会持有InnerConnection和ServiceConnection。
InnerConnection继承IServiceConnection.Stub,它实现了IServiceConnection的connected方法:
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
// 利用弱引用持有ServiceDispatcher
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
// 连接回调转发给ServiceDispatcher
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
InnerConnection持有ServiceDispatcher,当绑定Server端成功时,AMS会调用其connected方法,在该方法中将参数转发给ServiceDispatcher。
AMS处理bind请求
回到ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon方法中,再获取到IServiceConnection后,便调用AMS#bindIsolatedService方法:
[ActivityManagerService#bindIsolatedService]
public int bindIsolatedService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String instanceName,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// ···
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, instanceName, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
调用ActiveServices的bindServiceLocked方法:
[ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked]
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String instanceName, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// ···
// 用于保存发起方Activity和Service的连接信息
ActivityServiceConnectionsHolder<ConnectionRecord> activity = null;
if (token != null) {
// 将token强转为Token,然后获取它内部通过弱引用持有的ActivityRecord,最后创建ActivityServiceConnectionsHolder保存ActivityRecord返回
activity = mAm.mAtmInternal.getServiceConnectionsHolder(token);
if (activity == null) {
// 如果查找ActivityRecord失败,则bind失败
Slog.w(TAG, "Binding with unknown activity: " + token);
return 0;
}
}
// ···
final boolean callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND;
final boolean isBindExternal = (flags & Context.BIND_EXTERNAL_SERVICE) != 0;
final boolean allowInstant = (flags & Context.BIND_ALLOW_INSTANT) != 0;
// 从查找或新建可用ServiceRecord
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, instanceName, resolvedType, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true,
callerFg, isBindExternal, allowInstant);
if (res == null) {
return 0;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return -1;
}
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
// ···
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// ···
// AppBindRecord记录一个绑定了Server的Caller信息
// 保存ServiceRecord(在运行的Service信息)、IntentBindRecord(绑定意图信息)、ProcessRecord(发起方进程信息)
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
// ConnectionRecord记录一个Caller和Service绑定的连接信息,保存绑定相关参数
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent,
callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName, callingPackage);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
// 保存连接信息
s.addConnection(binder, c);
b.connections.add(c);
if (activity != null) {
activity.addConnection(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
c.startAssociationIfNeeded();
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT) != 0) {
b.client.hasAboveClient = true;
}
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ALLOW_WHITELIST_MANAGEMENT) != 0) {
s.whitelistManager = true;
}
if ((flags & Context.BIND_ALLOW_BACKGROUND_ACTIVITY_STARTS) != 0) {
s.setHasBindingWhitelistingBgActivityStarts(true);
}
if (s.app != null) {
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(s.app, c, true);
}
// mServiceConnections中存储着所有ConnectionRecord
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
// 添加本次绑定连接信息
clist.add(c);
// 发起bind时通常会设置BIND_AUTO_CREATE
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// bringUpServiceLocked中会判断是否已启动Service,若未启动会先启动,遇到错误会返回描述原因字符串
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
// 省略更新Service所在进程优先级和oom_adj部分 ···
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
try {
// Service已经启动,则回调Caller端connected
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + s.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
// If this is the first app connected back to this binding,
// and the service had previously asked to be told when
// rebound, then do so.
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
// 若之前unbind过且返回true,则再次bind时会执行Service的onRebind回调
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
// 若前面bringUpServiceLocked方法中没有执行bind,则这里再次尝试执行Service的onBind回调
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
// ···
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return 1;
}
该方法中会检查Caller是否是有效的Activity,然后从缓存查找或新建ServiceRecord,然后利用ActivityServiceConnectionsHolder、AppBindRecord、ConnectionRecord、mServiceConnections保存本次绑定连接Service的相关参数信息。接着调用bringUpServiceLocked方法(flags设置了BIND_AUTO_CREATE)进行启动Service(若未启动)和绑定流程。
bringUpServiceLocked方法的主要逻辑在《Service启动流程总结-start和stop service》中简单总结过,其中又会调用realStartServiceLocked方法,这里看和bind相关的部分:
[ActiveServices#realStartServiceLocked]
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
// ···
try {
// ···
// 启动Service
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackage(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.getReportedProcState());
// ···
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application dead when creating service " + r);
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
// ···
}
// ···
// 进一步执行bind流程
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
// ···
// 内部会判断pendingStarts集合中元素个数,通过start启动Service时会触发onStartCommand回调,bind流程可忽略。
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
// ···
}
进入requestServiceBindingsLocked方法:
[ActiveServices#requestServiceBindingsLocked]
private final void requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
for (int i=r.bindings.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
// 依次取出ServiceRecord中保存的IntentBindRecord
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
// 进一步执行bind流程,若bind失败会返回false
if (!requestServiceBindingLocked(r, ibr, execInFg, false)) {
break;
}
}
}
看requestServiceBindingLocked方法:
[ActiveServices#requestServiceBindingLocked]
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// ···
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
// 调度Service执行bind回调
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.getReportedProcState());
if (!rebind) {
// 将requested成员置为true,那么在ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked方法结尾不会再执行requestServiceBindingLocked
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// 省略异常处理部分 ···
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// 省略异常处理部分 ···
}
}
return true;
}
该方法中通过IApplicationThread调度Service所在进程执行bind操作。
Service处理bind请求
接下来便来到Service所在进程,ActivityThread会发送BIND_SERVICE消息至主线程,执行handleBindService方法,直接看这个方法:
[ActivityThread#handleBindService]
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
// 获取缓存的Service实例(启动时会将创建的Service保存在mServices中)
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
// 触发Service的onBind回调
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
// 通知AMS发布Service,并传送IBinder
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
// 触发Service的onRebind回调
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
**这里从mServices取出之前启动创建时保存的Service实例,然后调用它的onBind生命周期回调方法。**在开头例子中,返回了Server端binder实例ISpeaker.Stub。
接下来便请求ActivityManagerService,将binder传送给Caller端。
AMS发布Service
Server端在执行完Service的onBind后,需要将创建的binder传给Caller,以便Caller通过binder调用Service提供的API,因此需要通过publishService方法通知AMS。
接下来看ActivityManagerService的publishService方法,在该方法中又调用了ActiveServices的publishServiceLocked方法:
[ActiveServices#publishServiceLocked]
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// 省略DEBUG信息 ···
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> connections = r.getConnections();
for (int conni = connections.size() - 1; conni >= 0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
// 依次取出bind目标Service的Caller连接信息
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
// 省略DEBUG信息 ···
continue;
}
// 省略DEBUG信息 ···
try {
// conn是Caller发起bind时传过来的IServiceConnection
c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 省略DEBUG信息 ···
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
该方法中,会依次取出bind目标Service的等待中的Caller的ConnectionRecord,通过ConnectionRecord保存的IServiceConnection的connected方法调度到Caller进程。
Caller处理连接回调
AMS在处理publishService时,又会通过IServiceConnection调度Caller端,将会执行InnerConnection的connected方法,该方法中又会调用ServiceDispatcher的connected方法:
[ServiceDispatcher#connected]
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
if (mActivityExecutor != null) {
// mActivityExecutor默认为null
mActivityExecutor.execute(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else if (mActivityThread != null) {
// mActivityThread是构造时传入的主线程handler
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else {
doConnected(name, service, dead);
}
}
该方法中通过主线程handler切换到主线程执行connect回调。
RunConnection#run中会执行doConnected方法:
[ServiceDispatcher#doConnected]
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
// 缓存的旧的连接信息
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
// 新的连接信息
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
// 已经执行unbind
return;
}
// mActiveConnections中缓存已经完成连接的ConnectionInfo
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
// 已经连接过一样的Service
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
// ConnectionInfo保存连接信息
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
// 设置Service死亡监听
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
// 添加mActiveConnections集合保存
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
// 取消旧连接信息设置的死亡监听
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is now disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
if (dead) {
mConnection.onBindingDied(name);
}
// If there is a new viable service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
// 执行ServiceConnection接口的onServiceConnected回调
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
} else {
// The binding machinery worked, but the remote returned null from onBind().
mConnection.onNullBinding(name);
}
}
在该方法中,会执行mConnection的onServiceConnected回调,mConnection即我们创建的ServiceConnection接口实例。在onServiceConnected回调中保存Service->AMS->Caller传来的IBinder,若Caller与Service属于同一进程则保存的是Server端binder实例,否则是binder代理。
至此便完成了Caller向Service的绑定过程,也拿到了Service提供的binder接口,后续就可以提供binder很方便地调用Service提供的API。
unbind过程
当Caller发起绑定时的Activtiy退出或者主动调用unbindService方法时,会开始解绑流程。
进入ContextImpl的unbindService方法:
[ContextImpl#unbindService]
public void unbindService(ServiceConnection conn) {
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
// 获取缓存的IServiceConnection
IServiceConnection sd = mPackageInfo.forgetServiceDispatcher(
getOuterContext(), conn);
try {
// 请求AMS进行解绑
ActivityManager.getService().unbindService(sd);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
}
该方法中首先从LoadedApk获取缓存的IServiceConnection,然后请求AMS调度解绑。
forgetServiceDispatcher方法中从mServices集合中移除当前context和ServiceConnection对应的ServiceDispatcher,然后转存到mUnboundServices集合中,最后返回ServiceDispatcher持有的InnerConnection实例。
接着来到AMS侧,在ActivityManagerService#unbindService方法中又调用ActiveServices#unbindServiceLocked方法:
[ActiveServices#unbindServiceLocked]
boolean unbindServiceLocked(IServiceConnection connection) {
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
// ···
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// clist中保存着IServiceConnection对应的所有连接信息
while (clist.size() > 0) {
// 依次取出ConnectionRecord
ConnectionRecord r = clist.get(0);
// 移除连接相关信息和解绑操作
removeConnectionLocked(r, null, null);
if (clist.size() > 0 && clist.get(0) == r) {
// In case it didn't get removed above, do it now.
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Connection " + r + " not removed for binder " + binder);
// 未移除的话,这里立即移除
clist.remove(0);
}
// ···
}
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(OomAdjuster.OOM_ADJ_REASON_UNBIND_SERVICE);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return true;
}
该方法中取出缓存的ConnectionRecord,然后进一步执行解绑操作。
进入removeConnectionLocked方法:
[ActiveServices#removeConnectionLocked]
void removeConnectionLocked(ConnectionRecord c, ProcessRecord skipApp,
ActivityServiceConnectionsHolder skipAct) {
IBinder binder = c.conn.asBinder();
// 开始清理相关信息
AppBindRecord b = c.binding;
ServiceRecord s = b.service;
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.getConnections().get(binder);
if (clist != null) {
clist.remove(c);
if (clist.size() == 0) {
s.removeConnection(binder);
}
}
b.connections.remove(c);
c.stopAssociation();
if (c.activity != null && c.activity != skipAct) {
c.activity.removeConnection(c);
}
if (b.client != skipApp) {
b.client.connections.remove(c);
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT) != 0) {
b.client.updateHasAboveClientLocked();
}
// If this connection requested whitelist management, see if we should
// now clear that state.
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ALLOW_WHITELIST_MANAGEMENT) != 0) {
s.updateWhitelistManager();
if (!s.whitelistManager && s.app != null) {
updateWhitelistManagerLocked(s.app);
}
}
// And do the same for bg activity starts whitelisting.
if ((c.flags & Context.BIND_ALLOW_BACKGROUND_ACTIVITY_STARTS) != 0) {
s.updateHasBindingWhitelistingBgActivityStarts();
}
if (s.app != null) {
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(s.app, c, true);
}
}
clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist != null) {
clist.remove(c);
if (clist.size() == 0) {
mServiceConnections.remove(binder);
}
}
mAm.stopAssociationLocked(b.client.uid, b.client.processName, s.appInfo.uid,
s.appInfo.longVersionCode, s.instanceName, s.processName);
if (b.connections.size() == 0) {
b.intent.apps.remove(b.client);
}
if (!c.serviceDead) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Disconnecting binding " + b.intent
+ ": shouldUnbind=" + b.intent.hasBound);
if (s.app != null && s.app.thread != null && b.intent.apps.size() == 0
&& b.intent.hasBound) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(s, false, "unbind");
if (b.client != s.app && (c.flags&Context.BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY) == 0
&& s.app.setProcState <= ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_HEAVY_WEIGHT) {
// If this service's process is not already in the cached list,
// then update it in the LRU list here because this may be causing
// it to go down there and we want it to start out near the top.
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(s.app, false, null);
}
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(s.app, true,
OomAdjuster.OOM_ADJ_REASON_UNBIND_SERVICE);
b.intent.hasBound = false;
// Assume the client doesn't want to know about a rebind;
// we will deal with that later if it asks for one.
b.intent.doRebind = false;
// 调用Service端执行unbind
s.app.thread.scheduleUnbindService(s, b.intent.intent.getIntent());
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when unbinding service " + s.shortInstanceName, e);
serviceProcessGoneLocked(s);
}
}
// If unbound while waiting to start, remove the pending service
mPendingServices.remove(s);
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
boolean hasAutoCreate = s.hasAutoCreateConnections();
if (!hasAutoCreate) {
if (s.tracker != null) {
s.tracker.setBound(false, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
}
}
// 该方法中会判断unbind后是否执行销毁Service
bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked(s, true, hasAutoCreate);
}
}
}
该方法中会清理之前缓存的绑定相关的连接信息,然后调度Service端执行scheduleUnbindService触发onUnbind回调。
在ActivityThread的scheduleUnbindService方法中通过发送UNBIND_SERVICE消息至主线程,执行handleUnbindService方法:
[ActivityThread#handleUnbindService]
private void handleUnbindService(BindServiceData data) {
// 取出缓存的Service实例
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
// 执行Service的onUnbind回调方法
boolean doRebind = s.onUnbind(data.intent);
try {
// 判断onUnbind返回的结果,默认为false
if (doRebind) {
// 请求AMS支持reBind
ActivityManager.getService().unbindFinished(
data.token, data.intent, doRebind);
} else {
// 通知unbind完成
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// ···
}
}
}
该方法中取出缓存的Service实例,调用它的onUnbind生命周期回调方法,最后再通知AMS。
至此解绑流程便已完成。注意,可以看到解绑流程中没有调用ServiceConnection的onServiceDisconnected回调,onServiceDisconnected的回调时机是在绑定时判断旧连接时触发和Caller通过binder死亡监听监听到Service端进程死亡时触发。