JAVA编程中常用函数总结
输入
格式1:Scanner sc = new Scanner (new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
格式2:Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);
在读入数据量大的情况下,格式1的速度会快些。
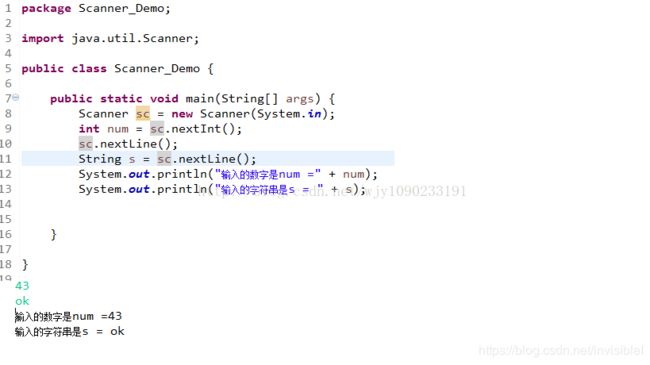
读一个整数: int n = sc.nextInt(); 相当于 scanf("%d", &n); 或 cin >> n;
读一个字符串:String s = sc.next(); 相当于 scanf("%s", s); 或 cin >> s;
读一个浮点数:double t = sc.nextDouble(); 相当于 scanf("%lf", &t); 或 cin >> t;
读一整行: String s = sc.nextLine(); 相当于 gets(s); 或 cin.getline(…);
判断是否有下一个输入可以用sc.hasNext()或sc.hasNextInt()或sc.hasNextDouble()或sc.hasNextLine()
举例:
(1)输入整数:
Input 输入数据有多组,每组占一行,由一个整数组成。
Sample Input
56
67
100
123
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){ //判断是否结束
int score = sc.nextInt();//读入整数
System.out.println(score);//。。。。
}
}
}
(2)输入浮点数:
输入数据有多组,每组占2行,第一行为一个整数N,指示第二行包含N个实数。
Sample Input
4
56.9 67.7 90.5 12.8
5
56.9 67.7 90.5 12.8
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
double a = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println(a);//。。。。。。
}
}
System.out.println("in the end");
}
}
(3)输入字符串:
输入数据有多行,第一行是一个整数n,表示测试实例的个数,后面跟着n行,每行包括一个由字母和数字组成的字符串。
Sample Input
2
asdfasdf123123asdfasdf
asdf111111111asdfasdfasdf
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String str = sc.next();
System.out.println(str);//。。。。。。
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String str = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(str);//。。。。。。
}
}
}
(4)nextInt()后使用nextLine()存在的问题

首先,Scanner是一个扫描器,它扫描数据都是去内存中一块缓冲区中进行扫描并读入数据的,而我们在控制台中输入的数据也都是被先存入缓冲区中等待扫描器的扫描读取。这个扫描器在扫描过程中判断停止的依据就是“空白符”,空格啊,回车啊什么的都算做是空白符。
nextInt()方法在扫描到空白符的时候会将前面的数据读取走,但会丢下空白符“\r”在缓冲区中,但是,nextLine()方法在扫描的时候会将扫描到的空白符一同清理掉。
了解了这两个方法特性和区别,就知道了上边的代码究竟是怎么回事,以及知道了解决的方法。像是上边的代码nextInt()方法之后在缓冲区中留下了“\r”,然后nextLine()方法再去缓冲区找数据的时候首先看到了“\r”,然后就把这个“\r”扫描接收进来,并在缓冲区内清除掉。其实,nextLine()方法是执行过的,并没有不执行。
输出
System.out.print();
System.out.println();
System.out.format();
System.out.printf();
例题:
(1)System.out.println();
首行输入自然数n,代表测试数量;
其后,每行输入一个操作符(+ - * /)和两个正整数
输出:结果
Sample Input
4
+ 1 2
- 1 2
* 1 2
/ 1 2
Sample Output
3
-1
2
0.50
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String op = sc.next();
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
if(op.charAt(0)=='+'){
System.out.println(a+b);
}else if(op.charAt(0)=='-'){
System.out.println(a-b);
}else if(op.charAt(0)=='*'){
System.out.println(a*b);
}else if(op.charAt(0)=='/'){
if(a % b == 0)
System.out.println(a / b);
else System.out.format("%.2f", (a / (1.0*b))).println();
}
}
}
}
注意:Java里对于两个整型数据直接做除法运算,最终只能得到一个整数结果,小数部分被舍弃。
(2)规格化的输出
DecimalFormat的使用
0 数字 是 阿拉伯数字
# 数字 是 阿拉伯数字如果不存在就显示为空
. 数字 是 小数分隔符或货币小数分隔符
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//经典案例
double pi = 3.1415927;//圆周率
//取一位整数
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("0").format(pi));//3
//取一位整数和两位小数
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("0.00").format(pi));//3.14
//取两位整数和三位小数,整数不足部分以0填补。
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("00.000").format(pi));// 03.142
//取所有整数部分
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#").format(pi));//3
//以百分比方式计数,并取两位小数
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.##%").format(pi));//314.16%
//扩展
NumberFormat formatter = new DecimalFormat( "000000");
String s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -001235
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "##");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -1235
System.out.println(s);
s = formatter.format(0); // 0
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "##00");
s = formatter.format(0); // 00
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( ".00");
s = formatter.format(-.567); // -.57
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "0.00");
s = formatter.format(-.567); // -0.57
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "#.#");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -1234.6
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "#.######");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -1234.567
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( ".######");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -1234.567
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "#.000000");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -1234.567000
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "#,###,###");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -1,235
System.out.println(s);
s = formatter.format(-1234567.890); // -1,234,568
System.out.println(s);
// The ; symbol is used to specify an alternate pattern for negative values
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "#;(#) ");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // (1235)
System.out.println(s);
// The ' symbol is used to quote literal symbols
formatter = new DecimalFormat( " '# '# ");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // -#1235
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( " 'abc '# ");
s = formatter.format(-1234.567); // - abc 1235
System.out.println(s);
formatter = new DecimalFormat( "#.##%");
s = formatter.format(-12.5678987);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
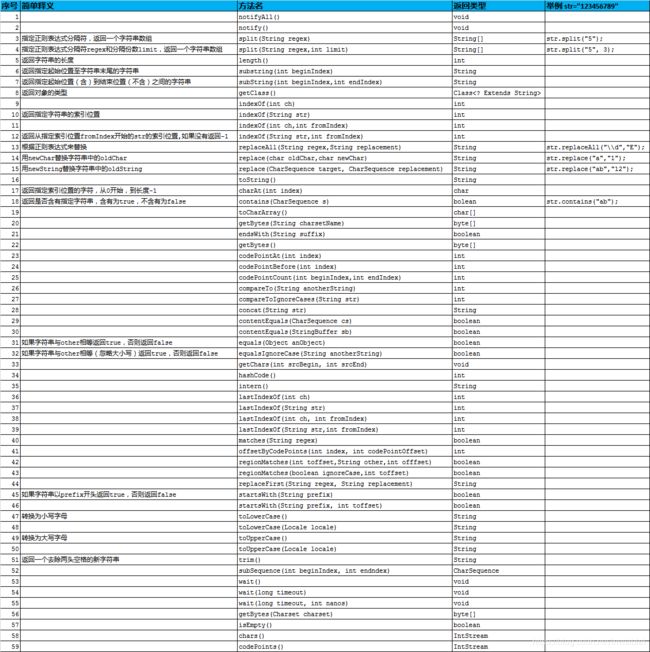
字符串函数
(1)取出某位charAt(n)
String 类用来存储字符串,可以用charAt方法来取出其中某一字节,计数从0开始:
String a = "Hello"; // a.charAt(1) = 'e'
(2)取出子串substring(n,m)
用substring方法可得到子串,如上例
System.out.println(a.substring(0, 4)) // output "Hell"
注意:第2个参数位置上的字符不包括进来。这样做使得 s.substring(a, b) 总是有 b-a个字符。
(3)字符串连接可以直接用 + 号
String a = "Hello";
String b = "world";
System.out.println(a + ", " + b + "!"); // output "Hello, world!"
(4)长度获取length()
String a = "hello";
int n = a.length();
System.out.print(n);
(5)判断是否字符串一样equals()
String a = "hello";
String b = "hello1";
boolean n = a.equals(b);
System.out.print(n);
该方法和equals方法相似,不同的地方在于,equalsIgnoreCase方法将忽略字母大小写的区别.
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
(6)replace和replaceAll()
public String replace(char oldChar,char newChar)
//该方法用字符newChar替换当前字符串中所有的字符oldChar,并返回一个新的字符串.
public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
//该方法用字符串replacement的内容替换当前字符串中遇到的第一个
//和字符串regex相一致的子串,并将产生的新字符串返回.
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)
//该方法用字符串replacement的内容替换当前字符串中遇到的所有和字符串regex相一致的子串
//并将产生的新字符串返回
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "hello";
String a1 = a.replace("l","o");
System.out.print(a1);//heooo
String a2 = a.replaceFirst("l","o");
System.out.print(a2);//heolo
String a3 = a.replaceAll("l","o");
System.out.print(a3);//heooo
}
}
(7)获取定位indexOf()
public int indexOf(int ch)
//该方法用于查找当前字符串中某一个特定字符ch出现的位置.该方法从头向后查找,
//如果在字符串中找到字符ch,则返回字符ch在字符串中第一次出现的位置;
//如果在整个字符串中没有找到字符ch,则返回-1.
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
//该方法和第一种方法类似,不同的地方在于,该方法从fromIndex位置向后查找,
//返回的仍然是字符ch在字符串第一次出现的位置.
public int lastIndexOf(int ch) //该方法和第一种方法类似,不同的地方在于,
//该方法从字符串的末尾位置向前查找,返回的仍然是字符ch在字符串第一次出现的位置.
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
//该方法和第二种方法类似,不同的地方在于,该方法从fromIndex位置向前查找,
//返回的仍然是字符ch在字符串第一次出现的位置.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "he1l2l2o342";
int a1 = a.indexOf('e');
int a2 = a.indexOf('2');
System.out.print(a1 + "/" + a2);//1/4
int a3 = a.indexOf('2',5);
System.out.print(a3);//6
}
}
(8)字符串分割split(" ")
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "he1l2l2o342";
String[] str2 = a.split("2");
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str2[i]);
}
}
}
输出:
he1l
l
o34
还可以限制个数split(" ",n):
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "he1l2l2o342";
String[] str2 = a.split("2",2);
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str2[i]);
//he1l
//l2o342
}
}
}
数字和字符串之间的转换
(1)String–>int
//转整型
int a;
String b = "1";
a= Integer.valueOf(b);
System.out.println(a);
(2)int/double–>String
//转字符串
double d=12.25;
int a = 1;
String str=String.valueOf(d);
String str1=String.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
int a=1234;
String str=a+"";
(3)String–>double
//字符串转换为浮点型数字
double a=0.0;
String str="111.11";
a=Double.valueOf(str); //字符串转换为double类型
System.out.println(a);
(4)double–>int
int a = (int)(new Double(2.0));
数组排序
(1)Arrays.sort()
默认为由小到大排序
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner (new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = cin.nextInt();
int a[] = new int [n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = cin.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
输入:
5
2
6
3
63
5
输出:
2 3 5 6 63
逆序sort()排序
class com<T> implements Comparator<T> {//对abcdefg进行比较大小,排序
public int compare(T o1, T o2) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(o1));
int j = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(o2));
if (i > j) return -1;
if (i < j) return 1;
return 0;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "2,5,7,9,111,68,0";
String[] strArr = s.split(",");
Arrays.sort(strArr, new com());//排序
for(String str : strArr){
System.out.print(str+",");
}
}
}
Math中的常用函数
(1)max
Math.max(a,b);
(2)log
Math.log(4);//默认情况下是以e为底
例如:如果对于log(2)8=3 //以2为底的情况
利用换底公式:
log(2)8 = log(8)/log(2)
Math.log(8)/Math.log(2);