Dubbo学习之路(七):集群容错-Directory
上一篇文章说到服务调用流程,其中有几个很重要的名词,今天就主要说一下Directory
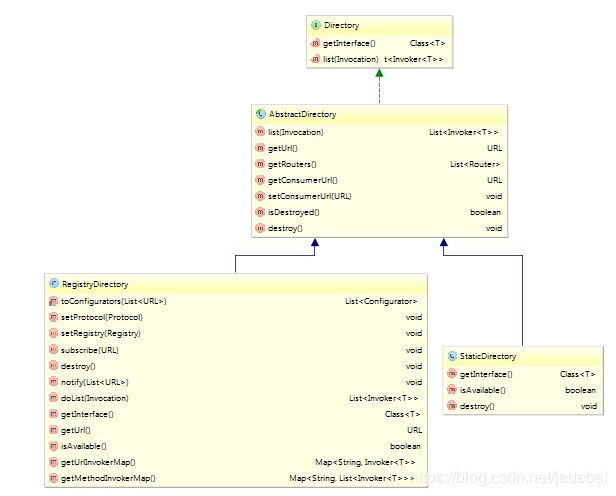
我们知道,主要是利用这个类,去获取到当前注册的所有的Invoker,我们先看一下这个接口的实现类和方法
这里一共有两个实现类:StaticDirectory(静态),RegistryDirectory(注册中心)
StaticDirectory(静态),这个我们使用的少,基本不使用,这里面的Invoker主要是通过构造方法来传入的,我们看一下源码
public StaticDirectory(List> invokers) {
this(null, invokers, null);
}
public StaticDirectory(List> invokers, List routers) {
this(null, invokers, routers);
}
public StaticDirectory(URL url, List> invokers) {
this(url, invokers, null);
}
public StaticDirectory(URL url, List> invokers, List routers) {
super(url == null && invokers != null && !invokers.isEmpty() ? invokers.get(0).getUrl() : url, routers);
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invokers == null");
this.invokers = invokers;
} 我们在使用过程中,主要使用的还是注册中心模式的(动态的)RegistryDirectory,这里如何做到动态的呢?我们接着往下看,看看一下这个类的继承关系图
我们看到这里,实现了NotifyListener这个接口,这个接口里面有一个notify方法,这里就是注册中心的回调方法(事件的监听方法),已达到动态变动的效果。
根据上面的介绍其实这篇我们主要看的就是一行代码:List
我们看一下RegistryDirectory的doList方法
public List> doList(Invocation invocation) {
if (forbidden) {
// 1. No service provider 2. Service providers are disabled
throw new RpcException(RpcException.FORBIDDEN_EXCEPTION,
"No provider available from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " for service " + getConsumerUrl().getServiceKey() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please check status of providers(disabled, not registered or in blacklist).");
}
List> invokers = null;
Map>> localMethodInvokerMap = this.methodInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localMethodInvokerMap != null && localMethodInvokerMap.size() > 0) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Object[] args = RpcUtils.getArguments(invocation);
if (args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
&& (args[0] instanceof String || args[0].getClass().isEnum())) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName + "." + args[0]); // The routing can be enumerated according to the first parameter
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName);
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(Constants.ANY_VALUE);
}
if (invokers == null) {
Iterator>> iterator = localMethodInvokerMap.values().iterator();
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
invokers = iterator.next();
}
}
}
return invokers == null ? new ArrayList>(0) : invokers;
} 其实这个代码很简单,就是在变量methodInvokerMap中获取invokers。那到底这个methodInvokerMap的值到底是哪里来的呢?
我们通过代码中可以看到是在refreshInvoker方法中进行赋值的,而往上追随我们发现,真正的入口是notify方法,我们看一下整体代码
@Override
public synchronized void notify(List urls) {
List invokerUrls = new ArrayList();
List routerUrls = new ArrayList();
List configuratorUrls = new ArrayList();
for (URL url : urls) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
String category = url.getParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CATEGORY);
if (Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY.equals(category)
|| Constants.ROUTE_PROTOCOL.equals(protocol)) {
routerUrls.add(url);
} else if (Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY.equals(category)
|| Constants.OVERRIDE_PROTOCOL.equals(protocol)) {
configuratorUrls.add(url);
} else if (Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY.equals(category)) {
invokerUrls.add(url);
} else {
logger.warn("Unsupported category " + category + " in notified url: " + url + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost());
}
}
// configurators
if (configuratorUrls != null && !configuratorUrls.isEmpty()) {
this.configurators = toConfigurators(configuratorUrls);
}
// routers
if (routerUrls != null && !routerUrls.isEmpty()) {
List routers = toRouters(routerUrls);
if (routers != null) { // null - do nothing
setRouters(routers);
}
}
List localConfigurators = this.configurators; // local reference
// merge override parameters
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = directoryUrl;
if (localConfigurators != null && !localConfigurators.isEmpty()) {
for (Configurator configurator : localConfigurators) {
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = configurator.configure(overrideDirectoryUrl);
}
}
// providers
refreshInvoker(invokerUrls);
}
private void refreshInvoker(List invokerUrls) {
if (invokerUrls != null && invokerUrls.size() == 1 && invokerUrls.get(0) != null
&& Constants.EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(invokerUrls.get(0).getProtocol())) {
this.forbidden = true; // Forbid to access
this.methodInvokerMap = null; // Set the method invoker map to null
destroyAllInvokers(); // Close all invokers
} else {
this.forbidden = false; // Allow to access
Map> oldUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty() && this.cachedInvokerUrls != null) {
invokerUrls.addAll(this.cachedInvokerUrls);
} else {
this.cachedInvokerUrls = new HashSet();
this.cachedInvokerUrls.addAll(invokerUrls);//Cached invoker urls, convenient for comparison
}
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Map> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls);// Translate url list to Invoker map
Map>> newMethodInvokerMap = toMethodInvokers(newUrlInvokerMap); // Change method name to map Invoker Map
// state change
// If the calculation is wrong, it is not processed.
if (newUrlInvokerMap == null || newUrlInvokerMap.size() == 0) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("urls to invokers error .invokerUrls.size :" + invokerUrls.size() + ", invoker.size :0. urls :" + invokerUrls.toString()));
return;
}
this.methodInvokerMap = multiGroup ? toMergeMethodInvokerMap(newMethodInvokerMap) : newMethodInvokerMap;
this.urlInvokerMap = newUrlInvokerMap;
try {
destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap); // Close the unused Invoker
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("destroyUnusedInvokers error. ", e);
}
}
}
private Map>> toMergeMethodInvokerMap(Map>> methodMap) {
Map>> result = new HashMap>>();
for (Map.Entry>> entry : methodMap.entrySet()) {
String method = entry.getKey();
List> invokers = entry.getValue();
Map>> groupMap = new HashMap>>();
for (Invoker invoker : invokers) {
String group = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.GROUP_KEY, "");
List> groupInvokers = groupMap.get(group);
if (groupInvokers == null) {
groupInvokers = new ArrayList>();
groupMap.put(group, groupInvokers);
}
groupInvokers.add(invoker);
}
if (groupMap.size() == 1) {
result.put(method, groupMap.values().iterator().next());
} else if (groupMap.size() > 1) {
List> groupInvokers = new ArrayList>();
for (List> groupList : groupMap.values()) {
groupInvokers.add(cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(groupList)));
}
result.put(method, groupInvokers);
} else {
result.put(method, invokers);
}
}
return result;
} 这里的代码其实在前面的章节已经介绍过(五),在消费者的发现和订阅时会订阅ZK的事件,然后调用notify方法,详细内容可以在文章(五)中查看。