su命令,sudo命令,限制root远程登录
su命令
用来切换用户
su - username 切换用户,root和普通用户之间可互相切换
加 - 是为了彻底切换,包括用户家目录一起切换
su - -c "command /folder/filename" username 不切换用户,且指定以某用户的身份去执行命令
ls -la /etc/skel/系统默认的模板目录
cp /etc/skel/.bash* /home/user5
chown -R user5:user5 /home/user5/ 更改属主属组
例:
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]#
su AA
只切换用户,未切换家目录
[AA
@localhost
root
]$ whoami
AA
[AA@localhost root]$
su - AA
切换用户,并切换家目录
密码:
上一次登录:三 4月 4 01:57:30 CST 2018pts/1 上
[AA
@localhost
~
]$ whoami
AA
[AA@localhost ~]$
su - BB
彻底切换用户BB
密码:
-bash-4.2$
ls /home
用户bash信息错误,排查解决
AA CC DD FF
发现缺失BB用户家目录
-bash-4.2$ su - root
密码:
上一次登录:三 4月 4 02:16:14 CST 2018pts/1 上
[root@localhost ~]#
mkdir /home/BB
创建用户BB家目录
[root@localhost ~]#
su - BB
彻底切换BB用户
上一次登录:三 4月 4 02:16:49 CST 2018pts/1 上
-bash-4.2$ ls /home
用户bash信息依然错误,继续排查
AA BB CC DD FF
-bash-4.2$ ls -la /home/BB
查看BB用户家目录,发现目录下缺失以 .bash开头的配置文件
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 4月 4 02:18 .
drwxr-xr-x. 7 root root 56 4月 4 02:18 ..
-bash-4.2$ su - root
密码:
上一次登录:三 4月 4 02:37:16 CST 2018从 192.168.30.1pts/1 上
[root@localhost ~]# cp /etc/skel/.bash* /home/BB
拷贝系统默认模板里以 .bash开头的配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# chown -R BB:BB /home/BB
更改BB用户家目录及下层文件的属主属组信息
[root@localhost ~]# su - BB
上一次登录:三 4月 4 02:37:33 CST 2018pts/1 上
[
BB@localhost ~
]$
bash信息正常,问题已排查解决
例:指定以root用户的身份创建文件1.txt
[BB@localhost ~
]$
su - -c "touch 1.txt /root" root
密码:
[BB@localhost ~]$ su - root
密码:
上一次登录:三 4月 4 02:55:14 CST 2018pts/1 上
[root@localhost ~
]# ls
1.txt
anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@localhost ~]#
sudo命令
以指定用户的身份临时执行命令(通常给普通用户临时授予root用户身份)
用法:用visudo命令去编辑sudo命令配置文件sudoers的临时文件 /etc/sudoers.tmp,并在修改后保存。替换掉sudo命令配置文件 /etc/sudoers。
由于此文件非常重要用visudo命令可以检测语法错误。
1、给普通用户在使用sudo命令时临时授予root身份,并设置使用的命令范围并寻找:
Allow root to run any commands anywhere这行,然后在
root ALL=(ALL) ALL 这行下面增加用户或用户组,并赋权:
root 用户 ALL=(ALL) 表示 ALL 表示命令
例如
username ALL=(ALL) ALL或/usr/bin/ls, /usr/bin/mv, /usr/bin/cat
当指定用户使用ls, mv, cat, 权限时临时赋予其root身份,且验证指定用户自己的密码(非root用户密码)
username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ls, /usr/bin/mv, /usr/bincat
当指定用户使用ls, mv, cat, 权限时临时赋予其root身份,且无需输入密码
2、给指定用户组,在执行指定命令时,临时授予root用户身份,用法同用户一样,同时命令组可用alias定义。
例:
[root@bogon ~]# visudo
## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as
## the root user, without needing the root password.
##
## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections
## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular
## users or groups.
##
## This file must be edited with the 'visudo' command.
## Host Aliases
## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhaps using
## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead.
# Host_Alias FILESERVERS = fs1, fs2
# Host_Alias MAILSERVERS = smtp, smtp2
## User Aliases
## These aren't often necessary, as you can use regular groups
## (ie, from files, LDAP, NIS, etc) in this file - just use %groupname
## rather than USERALIAS
# User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikem
User_Alias ANDY = CC, DD
给CC,DD用户指定别名为 ANDY
## Command Aliases
## These are groups of related commands...
## Networking
# Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/route, /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping, /sbin/dhclient, /usr/bin/net, /sbin/iptables, /usr/bin/rfcomm, /usr/bin/wvdial, /sbin/iwconfig, /sbin/mii-tool
Cmnd_Alias
ANDY_CMD = /usr/bin/mv, /usr/bin/cat
给mv、cat命令指定别
名为ANDY_
CMD
## Installation and management of software
# Cmnd_Alias SOFTWARE = /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/up2date, /usr/bin/yum
## Services
## Updating the locate database
# Cmnd_Alias LOCATE = /usr/bin/updatedb
## Storage
# Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /sbin/fdisk, /sbin/sfdisk, /sbin/parted, /sbin/partprobe, /bin/mount, /bin/umount
## Delegating permissions
# Cmnd_Alias DELEGATING = /usr/sbin/visudo, /bin/chown, /bin/chmod, /bin/chgrp
## Processes
# Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall
## Drivers
# Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modprobe
# Defaults specification
#
# Refuse to run if unable to disable echo on the tty.
#
Defaults !visiblepw
#
# Preserving HOME has security implications since many programs
# use it when searching for configuration files. Note that HOME
# is already set when the the env_reset option is enabled, so
# this option is only effective for configurations where either
# env_reset is disabled or HOME is present in the env_keep list.
#
Defaults always_set_home
Defaults match_group_by_gid
Defaults env_reset
Defaults env_keep = "COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE KDEDIR LS_COLORS"
Defaults env_keep += "MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE"
Defaults env_keep += "LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES"
Defaults env_keep += "LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE"
Defaults env_keep += "LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY"
#
# Adding HOME to env_keep may enable a user to run unrestricted
# commands via sudo.
#
# Defaults env_keep += "HOME"
Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
## Next comes the main part: which users can run what software on
## which machines (the sudoers file can be shared between multiple
## systems).
## Syntax:
##
## user MACHINE=COMMANDS
##
## The COMMANDS section may have other options added to it.
##
## Allow root to run any commands anywhere
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
在这一行下方增加内用,命令语法要一致,否则会报错
AA ALL=(ALL) /usr/bin/ls, /usr/bin/mv, /usr/bin/cat
给AA用户在使用sudo ls,sudo mv,sudo cat三条命令时临时赋予其root身份
,命令要使用绝对路径,且,号后有空格
BB ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ls
给BB用户在使用sudo ls命令时,临时赋予root身份,且不用输入密码
ANDY ALL=(ALL) ANDY_CMD
给别名为 ANDY的用户在执行别名为 ANDY_CMD命令时临时赋予其root身份
ELON ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/su
给ELON用户在执行sudo su命令时临时授予root用户身份,且不用输密码
## Allows members of the 'sys' group to run networking, software,
## service management apps and more.
# %sys ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS
## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
## Same thing without a password
# %wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
## Allows members of the users group to mount and unmount the
## cdrom as root
# %users ALL=/sbin/mount /mnt/cdrom, /sbin/umount /mnt/cdrom
## Allows members of the users group to shutdown this system
# %users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now
## Read drop-in files from /etc/sudoers.d (the # here does not mean a comment)
#includedir /etc/sudoers.d
~
~
-- INSERT --
在非插入模式下,输入:set nu 可以在编辑器里显示行号,在提示有语法错误时,方便查找
:wq 保存退出
验证结果
[root@bogon ~]#
su - AA
切换用户AA
上一次登录:四 4月 5 02:14:33 CST 2018pts/1 上
[AA@bogon ~]$
ls /root
直接运行ls命令提示权限不够
ls: 无法打开目录/root:
权限不够
[AA@bogon ~]$
sudo ls /root
sudo ls命令 可以查看
我们信任您已经从系统管理员那里了解了日常注意事项。
总结起来无外乎这三点:
#1) 尊重别人的隐私。
#2) 输入前要先考虑(后果和风险)。
#3) 权力越大,责任越大。
[sudo] AA 的密码:
提示需要输入AA用户的密码,而不是root用户
1.txt 2.txt anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg
查看成功
[AA@bogon ~]$
cat /root/1.txt
直接运行cat命令提示权限不够
cat: /root/1.txt:
权限不够
[AA@bogon ~]$
sudo cat /root/1.txt
sudo cat命令 可以查看
123456 --
[AA@bogon ~]$
mv /root/2.txt /root/3.txt
直接运行mv命令提示权限不够
mv: 无法获取"/root/2.txt" 的文件状态(stat):
权限不够
[AA@bogon ~]$
sudo mv /root/2.txt /root/3.txt
sudo mv命令 可以更改文件名
[AA@bogon ~]$
[AA@bogon ~]$
su - BB
切换BB用户
密码:
上一次登录:四 4月 5 02:14:43 CST 2018pts/1 上
[BB@bogon ~]$
ls /root
直接运行ls命令提示权限不够
ls: 无法打开目录/root:
权限不够
[BB@bogon ~]$
sudo ls /root
sudo ls命令
1.txt 3.txt anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg
可以查看且未输入密码
[BB@bogon ~]$
[BB@bogon ~]$
su - CC
切换CC用户
密码:
上一次登录:四 4月 5 02:14:51 CST 2018pts/1 上
[CC@bogon ~]$
cat /root/1.txt
直接运行cat命令提示权限不够
cat: /root/1.txt:
权限不够
[CC@bogon ~]$
sudo cat /root/1.txt
sudo cat命令
我们信任您已经从系统管理员那里了解了日常注意事项。
总结起来无外乎这三点:
#1) 尊重别人的隐私。
#2) 输入前要先考虑(后果和风险)。
#3) 权力越大,责任越大。
[sudo] CC 的密码:
可以查看,且需要输入CC用户的密码,而不是root用户密码
123456 --
[CC@bogon ~]$
su - DD
切换DD用户
密码:
上一次登录:四 4月 5 02:15:01 CST 2018pts/1 上
[DD@bogon ~]$
mv /root/3.txt /root/2.txt
直接运行mv命令提示权限不够
mv: failed to access "/root/2.txt":
权限不够
[DD@bogon ~]$
sudo mv /root/3.txt /root/2.txt
sudo mv命令
我们信任您已经从系统管理员那里了解了日常注意事项。
总结起来无外乎这三点:
#1) 尊重别人的隐私。
#2) 输入前要先考虑(后果和风险)。
#3) 权力越大,责任越大。
[sudo] DD 的密码:
可以更改文件名,且需要输入DD用户密码,而不是root用户密码
[DD@bogon ~]$
su - root
密码:
上一次登录:四 4月 5 02:15:08 CST 2018pts/1 上
[root@bogon ~]#
ls
1.txt
2.txt
anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg
文件名修改成功
[root@bogon ~]#
[root@bogon ~]#
限制root远程登录
方法:
禁止root用户远程登录,且允许指定普通用户远程登录,并给指定用户使用sudo命令的列表里添加su命令(权限太大,仅限管理员使用)
1、配置远程登录配置文件 /etc/ssh/sshd_config
搜索/ root
修改 “ #PermitRootLogin yes ” 去掉#,yes改为no 保存
重启sshd服务 systemctl restart sshd.service
例:
[root@bogon ~]#
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
编辑ssh的配置文件
[root@bogon ~]#
~
~
# Authentication:
~
~
#LoginGraceTime 2m
PermitRootLogin no
找出这段并修改 “ #PermitRootLogin yes ” 去掉#,yes改为no
#StrictModes yes
#MaxAuthTries 6
#MaxSessions 10
~
~
[root@bogon ~]#
[root@bogon ~]#
systemctl restart sshd.service
重启ssh服务
[root@bogon ~]#
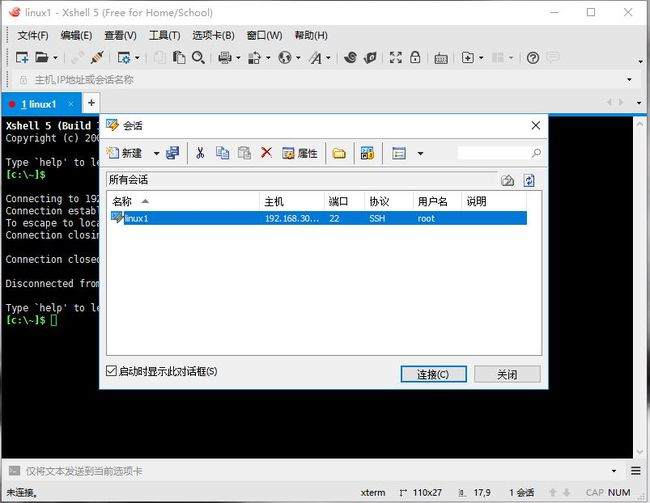
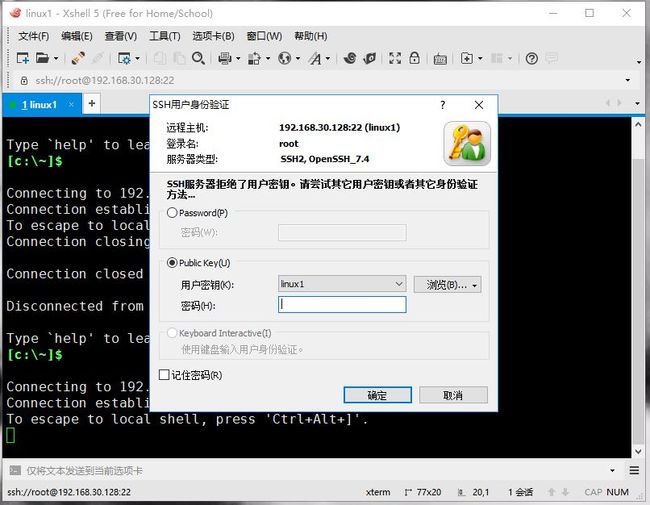
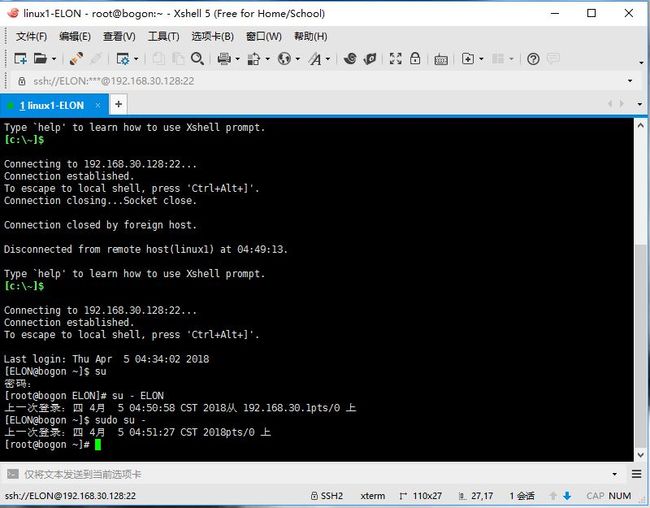
测试:
退出xshell重新登录
被服务器拒绝
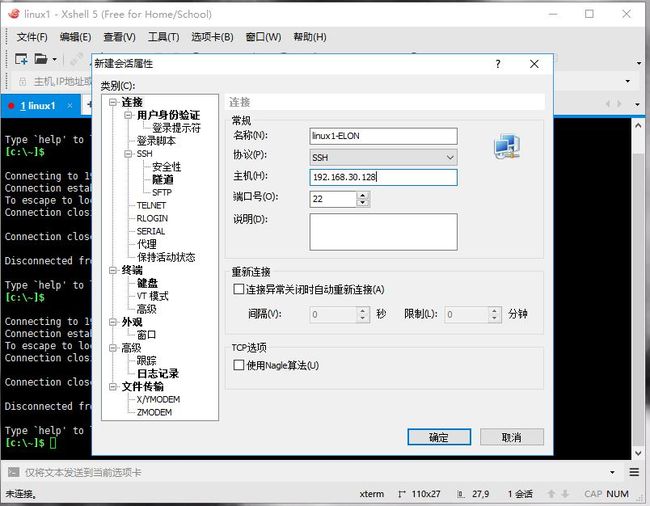
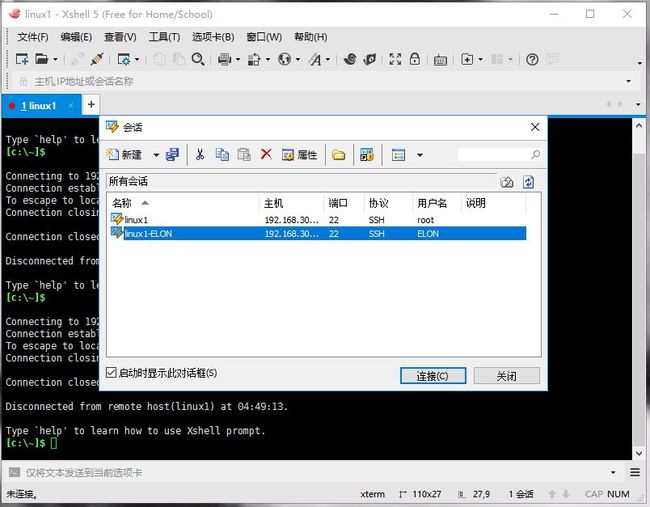
给ELON用户建立远程连接
已经可以登录,并且可以利用sudo su命令切换进root用户,且不用验证密码