Android 自定义View(一)
最近项目里涉及到自定义View的东西还是挺多的,所以打算在自定义View上多花点时间,也顺便分享给大家。
先总结下自定义View的步骤:
1、自定义View的属性
2、在View的构造方法中获得我们自定义的属性
[3、重写onMeasure]
4、重写onDraw
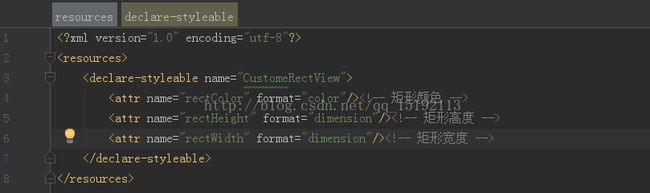
1.首先在我们的res/values/目录下建立一个attrs.xml文件,然后在里面声明我们我们需要的自定义属性
我们定义了矩形的颜色,矩形的高度,矩形的宽度3个属性,format是指该属性的取值类型:
一共有:string,color,demension,integer,enum,reference,float,boolean,fraction,flag;
不太明白的可以google一下
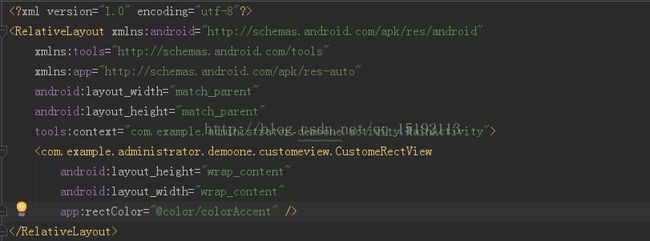
然后在布局中声明我们的自定义View
需要引入xmls:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"这样就会自动查找我们的自定义属性,也可以采用另外一种引入方式,xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.administrator.demoone.customeview.CustomeRectView"
我们的命名空间,后面的包路径指的是项目的package
2.在View的构造方法里获取我们的自定义属性
public class CustomeRectView extends View { private Paint mPiant;//定义画笔对象 private int rectColor;//矩形的颜色 private int rectHeight;//矩形的高度 private int rectWidth;//矩形的宽度 public CustomeRectView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public CustomeRectView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public CustomeRectView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); /** * 获取我们自定义的属性 */ TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomeRectView, defStyleAttr, 0); int arrayCount = array.getIndexCount(); for (int i = 0; i < arrayCount; i++) { int index = array.getIndex(i); switch (index) { case R.styleable.CustomeRectView_rectColor: //getColor(int index,int defaultValue) rectColor=array.getColor(R.styleable.CustomeRectView_rectColor, Color.BLACK); break; case R.styleable.CustomeRectView_rectHeight: /** * 获取dimension值得时候会有3个不同的方法getDimension()、getDimensionPixelSize()和getDimenPixelOffset() * 结果值都是将资源文件中定义的dip值乘以屏幕密度,即rectHeight*屏幕密度,只是getDimension()返回的是float, * 其余两个返回的是int, 其中getDimensionPixelSize()返回的是实际数值的四舍五入, * 而getDimensionPixelOffset返回的是实际数值去掉后面的小数点; */ rectHeight=array.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.CustomeRectView_rectHeight,200); break; case R.styleable.CustomeRectView_rectWidth: rectWidth=array.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.CustomeRectView_rectWidth,200); break; } } array.recycle(); } }
我们重写了3个构造方法,默认的布局文件调用的是两个参数的构造方法,所以记得让所有的构造调用我们的三个参数的构造,我们在三个参数的构造中获得自定义属性。
3.重写OnDraw,调用系统的onMeasure
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPiant=new Paint(); mPiant.setColor(rectColor);//设置画笔的颜色 mPiant.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);//设置画笔的样式 mPiant.setAntiAlias(true);//去除锯齿 /** * Draw the specified Rect using the specified paint. The rectangle will * be filled or framed based on the Style in the paint. * * @param left The left side of the rectangle to be drawn * @param top The top side of the rectangle to be drawn * @param right The right side of the rectangle to be drawn * @param bottom The bottom side of the rectangle to be drawn * @param paint The paint used to draw the rect */ canvas.drawRect(0,0,getWidth(),getHeight(),mPiant); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); }
此时的效果是:
但是此时如果我们把布局文件的宽和高写成wrap_content,去掉我们自定义的宽高属性
运行效果如下
系统帮我们测量的高度和宽度都是MATCH_PARNET,当我们设置明确的宽度和高度时,系统帮我们测量的结果就是我们设置的结果,当我们设置为WRAP_CONTENT,或者MATCH_PARENT系统帮我们测量的结果就是MATCH_PARENT的长度。
所以,当设置了WRAP_CONTENT时,我们需要自己进行测量,即重写onMesure方法”:
重写之前先了解MeasureSpec的specMode,一共三种类型:
EXACTLY:一般是设置了明确的值或者是MATCH_PARENT
AT_MOST:表示子布局限制在一个最大值内,一般为WARP_CONTENT
UNSPECIFIED:表示子布局想要多大就多大,很少使用
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int widthMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int width; int height; //如果设置了明确的大小 if(widthMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){ width=widthSize; }else{ //设置宽 width=dpToPx(getContext(),200); } if(heightMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){ height=heightSize; }else{ //设置高 height=dpToPx(getContext(),200); } setMeasuredDimension(width,height); } /** * 根据手机的分辨率从 dp 的单位 转成为 px(像素) */ public int dpToPx(Context context, float dpValue){ final float scale=context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int)(dpValue*scale+0.5f); }
此时的效果如下,就和我们在布局文件里设置的一样了
好了,后续还会陆续更新。各位路过顶个呗~