SSM实现简单的CRUD之Web层
前言
本篇文章主要来讲解Web层,主要介绍前端交互设计、Restful:url满足Restful设计规范、Spring MVC、bootstrap+jquery这四个方面的开发。
Restful接口设计学习
CRUD API URL 设计
| 请求类型 | url | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| DELETE | /emp/{ids} | 删除某一个员工信息 |
| PUT | /emp/{empId} | 修改员工信息 |
| GET | /emp/{id} | 查询员工信息 |
| GET | checkuser | 用户名是否重复 |
| GET | /depts | 所有部门 |
| POST | /emp | 员工保存 |
| POST | /emp | 所有员工(所携带参数不一样) |
一定记得在web.xml文件中加入以下配置:
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
filter-mapping>接下来基于上述资源接口来开始我们对Spring MVC框架的使用。
整合配置Spring MVC框架
在这我不做说明可以到我的这篇文章看如何配置http://blog.csdn.net/qq_33524158/article/details/78360268
Controller开发
在开发Controller之前先注意一点 因为整个crud我们是全程基于ajax,所以先创建一个在cn.hfbin.crud包下创建dto包,用来存放放回的数据。新建一个Msg类,内容如下:
package cn.hfbin.crud.dto;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 通用的返回的类
*
* @author hfbin
*
*/
public class Msg {
//状态码 100-成功 200-失败
private int code;
//提示信息
private String msg;
//用户要返回给浏览器的数据
private Map extend = new HashMap();
public static Msg success(){
Msg result = new Msg();
result.setCode(100);
result.setMsg("处理成功!");
return result;
}
public static Msg fail(){
Msg result = new Msg();
result.setCode(200);
result.setMsg("处理失败!");
return result;
}
public Msg add(String key,Object value){
this.getExtend().put(key, value);
return this;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public Map getExtend() {
return extend;
}
public void setExtend(Map extend) {
this.extend = extend;
}
}
Controller中的每一个方法都对应我们系统中的一个资源URL,其设计应该遵循Restful接口的设计风格。在cn.hfbin.crud包下创建一个controller包用于放web层Controller开发的代码,在该包下创建一个EmployeeController.java,内容如下:
package cn.hfbin.crud.controller;
import cn.hfbin.crud.bean.Employee;
import cn.hfbin.crud.dto.Msg;
import cn.hfbin.crud.service.EmployeeService;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 处理员工CRUD请求
*/
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService;
/**
* 单个批量二合一
* 批量删除:1-2-3
* 单个删除:1
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{ids}",method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public Msg deleteEmp(@PathVariable("ids")String ids){
//批量删除
if(ids.contains("-")){
List del_ids = new ArrayList();
String[] str_ids = ids.split("-");
//组装id的集合
for (String string : str_ids) {
del_ids.add(Integer.parseInt(string));
}
employeeService.deleteBatch(del_ids);
}else{
Integer id = Integer.parseInt(ids);
employeeService.deleteEmp(id);
}
return Msg.success();
}
/**
* 如果直接发送ajax=PUT形式的请求
* 封装的数据
* Employee
* [empId=1014, empName=null, gender=null, email=null, dId=null]
*
* 问题:
* 请求体中有数据;
* 但是Employee对象封装不上;
* update tbl_emp where emp_id = 1014;
*
* 原因:
* Tomcat:
* 1、将请求体中的数据,封装一个map。
* 2、request.getParameter("empName")就会从这个map中取值。
* 3、SpringMVC封装POJO对象的时候。
* 会把POJO中每个属性的值,request.getParamter("email");
* AJAX发送PUT请求引发的血案:
* PUT请求,请求体中的数据,request.getParameter("empName")拿不到
* Tomcat一看是PUT不会封装请求体中的数据为map,只有POST形式的请求才封装请求体为map
* org.apache.catalina.connector.Request--parseParameters() (3111);
*
* protected String parseBodyMethods = "POST";
* if( !getConnector().isParseBodyMethod(getMethod()) ) {
success = true;
return;
}
*
*
* 解决方案;
* 我们要能支持直接发送PUT之类的请求还要封装请求体中的数据
* 1、配置上HttpPutFormContentFilter;
* 2、他的作用;将请求体中的数据解析包装成一个map。
* 3、request被重新包装,request.getParameter()被重写,就会从自己封装的map中取数据
* 员工更新方法
* @param employee
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{empId}",method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public Msg saveEmp(Employee employee,HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("请求体中的值:"+request.getParameter("gender"));
System.out.println("将要更新的员工数据:"+employee);
employeeService.updateEmp(employee);
return Msg.success();
}
/**
* 根据id查询员工
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Msg getEmp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmp(id);
return Msg.success().add("emp", employee);
}
/**
* 检查用户名是否可用
* @param empName
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/checkuser")
public Msg checkuser(@RequestParam("empName")String empName){
//先判断用户名是否是合法的表达式;
String regx = "(^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{6,16}$)|(^[\u2E80-\u9FFF]{2,5})";
if(!empName.matches(regx)){
return Msg.fail().add("va_msg", "用户名必须是6-16位数字和字母的组合或者2-5位中文");
}
//数据库用户名重复校验
boolean b = employeeService.checkUser(empName);
if(b){
return Msg.success();
}else{
return Msg.fail().add("va_msg", "用户名不可用");
}
}
/**
* 员工保存
* 1、支持JSR303校验
* 2、导入Hibernate-Validator
*
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/emp",method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public Msg saveEmp(@Valid Employee employee,BindingResult result){
if(result.hasErrors()){
//校验失败,应该返回失败,在模态框中显示校验失败的错误信息
Map map = new HashMap();
List errors = result.getFieldErrors();
for (FieldError fieldError : errors) {
System.out.println("错误的字段名:"+fieldError.getField());
System.out.println("错误信息:"+fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
map.put(fieldError.getField(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}
return Msg.fail().add("errorFields", map);
}else{
employeeService.saveEmp(employee);
return Msg.success();
}
}
/**
* 导入jackson包。
* @param pn
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/emps")
@ResponseBody
public Msg getEmpsWithJson(
@RequestParam(value = "pn", defaultValue = "1") Integer pn) {
// 这不是一个分页查询
// 引入PageHelper分页插件
// 在查询之前只需要调用,传入页码,以及每页的大小
PageHelper.startPage(pn, 10);
// startPage后面紧跟的这个查询就是一个分页查询
List emps = employeeService.getAll();
// 使用pageInfo包装查询后的结果,只需要将pageInfo交给页面就行了。
// 封装了详细的分页信息,包括有我们查询出来的数据,传入连续显示的页数
PageInfo page = new PageInfo(emps, 5);
return Msg.success().add("pageInfo", page);
}
}
在这不做过多的说明每一行代码都有注释
下面说明一下这三个注解代表什么
@ResponseBody 返回json数据
@RequestMapping(“”) 请求路径
@RequestParam 请求参数
DepartmentController.java 这个Controller就做一个部门查询很简单,代码如下:
package cn.hfbin.crud.service;
import cn.hfbin.crud.bean.Department;
import cn.hfbin.crud.dao.DepartmentMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class DepartmentService {
@Autowired
private DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
//获取所有部门
public List getDepts() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
List list = departmentMapper.selectByExample(null);
return list;
}
}
到此,Controller的开发任务完成,接下来进行我们的页面开发。
页面开发
页面由前端工程师完成,这里直接拷贝我github上源代码中jsp的代码(webapp包下的所有资源)即可。
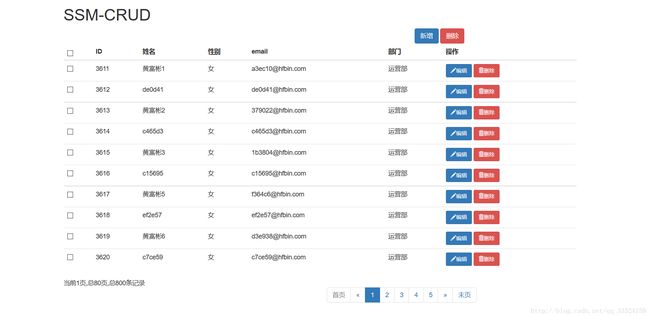
然后运行Tomcat服务器,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/emps,即可访问我们的秒杀列表页面:
在这附上js的逻辑代码: