记录:spring data jpa简单使用
网课记录,很基础,没什么技术含量
JPA是个规范,而Hibernate是这个规范的一个实现,spring data jpa则是在Hibernate的基础上再进行的一次封装。
项目依赖(单独引入JPA,实际上在springboot工程当中引入JPA的依赖比这个要简单一些):
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.11version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.38version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>4.3.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>4.3.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.datagroupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-jpaartifactId>
<version>1.8.0.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernategroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanagerartifactId>
<version>4.3.6.Finalversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
JPA相关配置(使用了java config,原课程里还在用xml配置,我觉得太麻烦了,还是用java config顺手一些。实际上在springboot工程里配置这个也就是application.yml里几句话的事儿,不用下面代码中这么麻烦):
import com.wmx.util.JDBCUtil;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.wmx")
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.wmx", entityManagerFactoryRef = "entityManager",
transactionManagerRef = "transactionManager")
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DriverManagerDataSource getDriverManagerDataSource(){
InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName(properties.getProperty("jdbc.driverClass"));
driverManagerDataSource.setUrl(properties.getProperty("jdbc.url"));
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername(properties.getProperty("jdbc.user"));
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword(properties.getProperty("jdbc.password"));
return driverManagerDataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(getDriverManagerDataSource());
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean(name = "entityManager")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean getEntityManager(){
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean manager = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
manager.setDataSource(getDriverManagerDataSource());
manager.setJpaVendorAdapter(new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter());
manager.setJpaProperties(getJPAProperties());
manager.setPackagesToScan("com.wmx");
return manager;
}
@Bean
public Properties getJPAProperties() {
InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jpa.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return properties;
}
@Bean(name = "transactionManager")
public JpaTransactionManager getTransactionManager(){
JpaTransactionManager jpaTransactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
jpaTransactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(getEntityManager().getObject());
return jpaTransactionManager;
}
}
JPA配置主要就两部分:
一是entityManager的配置,里面包含数据源,JPA属性等一些配置
二是事务管理器transactionManager的配置,具体代码看上面的就行。
db.properties的内容我就不贴了,这里贴出jpa.properties的内容:
hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
#显示sql
hibernate.show_sql = true
#格式化sql
hibernate.format_sql = true
#自动创建表
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto = update
如何加载java config的上下文:
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DataSourceConfig.class);
下面用这个context去getBean就可以了。
spring data jpa的核心就是repository接口:
public interface Repository<T, ID extends Serializable> {
}
T是表实体类,ID则是主键的数据类型,比如:
public interface EmployeeRepository extends Repository<Employee, Integer> {
}
这就是一个表的repository接口。
repository接口是一个空接口,是标记接口(eg:序列化接口也是标记接口)
继承这个接口,就会被spring容器所管理
除了继承repository接口,还有一种实现方式,是@RepositoryDefinition注解:
@RepositoryDefinition(domainClass = AccountEntity.class, idClass = Integer.class)
public interface AccountEntityRepository {
AccountEntity findByName(String name);
}
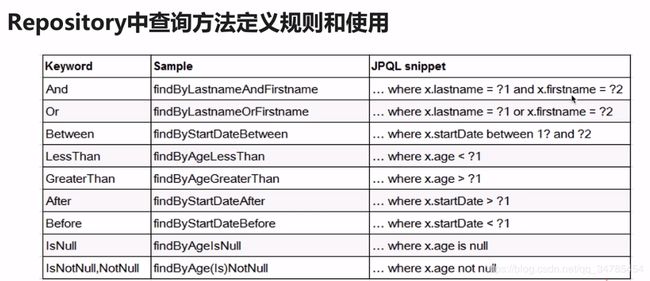
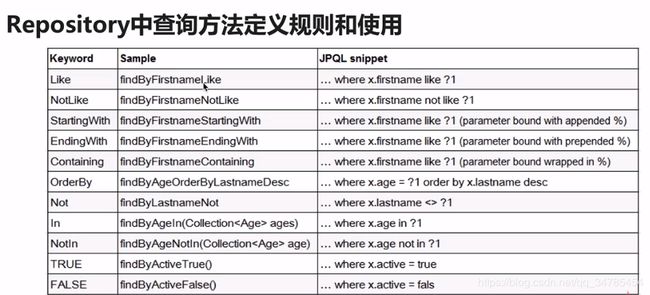
repository查询方法定义规则和使用:
Employee findByName(String name);
//where name like ?% and age < ?
List<Employee> findByNameStartingWithAndAgeLessThan(String name, Integer age);
//where name like %? and age < ?
List<Employee> findByNameEndingWithAndAgeLessThan(String name, Integer age);
//where name in (?,?,...) or age < ?
List<Employee> findByNameInOrAgeLessThan(List<String> names, Integer age);
通过单测,全部好用。
这种写法的问题:1、方法名太长了,稍微复杂一点的查询,方法名就会起飞。2、本身这种写法对复杂查询的支持也不太好。
为了解决这个问题,于是有了@Query注解查询:
方法名不需要遵循查询方法运行规则
支持命名参数和索引参数的使用(例子会有这两种写法,直接上代码)
支持本地查询(即使用数据库标准语法)
@Query注解示例:
@Query("select o from Employee o where id = (select max(id) from Employee)")
Employee getEmployeeByMaxId();
@Query("select d from Employee d where d.name = ?1 and d.age = ?2")
List<Employee> getByParams1(String name, Integer age);
@Query("select d from Employee d where d.name = :name and d.age = :age")
List<Employee> getByParams2(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") Integer age);
@Query("select d from Employee d where d.name like %:name%")
List<Employee> getByParams3(@Param("name") String name);
//本地查询,使用的是数据库标准语法,而不是面向对象的HQL
@Query(nativeQuery = true, value = "select count(1) from employee")
int getByNativeQuery();
需要注意的是,在不使用nativeQuery = true的情况下,@Query注解中的sql语句是面向对象的HQL语法,不是标准的sql语法。
更新与删除:
需要使用@Modifying注解
事务使用@Transactional注解(在service层使用,而不是DAO层)
示例:
@Modifying
@Query("update Employee d set d.age = ?2 where d.id = ?1")
void updateAgeById(Integer id, Integer age);
repository子接口:
1、CrudRepository:实现基本的crud方法(比如save方法,findOne方法等)
2、PagingAndSortingRepository:在crud基础上实现了分页和排序相关的方法
3、JpaRepository,在分页基础上,实现JPA规范相关方法
分页及排序:继承PagingAndSortingRepository接口:
public interface EmployeePageSortRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}
使用方法(注意注释):
//页号是从0开始计算的,所以本方法查询的是
//第二页的信息,每页3条记录,按id降序进行排序
@Test
public void page1() {
Sort.Order order = new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id");
Sort sort = new Sort(order);
EmployeePageSortRepository er = SpringUtil.getApplicationContext().getBean(EmployeePageSortRepository.class);
Pageable p = new PageRequest(1,3, sort);
Page<Employee> pg = er.findAll(p);
System.out.println("总页数:"+pg.getTotalPages());
System.out.println("总条数:"+pg.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("当前页元素:"+pg.getContent());
System.out.println("每页条数:"+pg.getSize());
System.out.println("当前页:"+pg.getNumber());
System.out.println(er);
}
不过使用这种方法也有一个问题,就是这分页查询是不带条件的,实用性不太高。
为了给分页查询带上条件,于是又有一个接口:JpaSpecificationExecutor
JpaSpecificationExecutor:
public interface EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutorRepository
extends JpaSpecificationExecutor<Employee>, JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}
这里同时继承两个接口,这样既能有查询条件,又能使用分页。
示例代码:
@Test
public void page2() {
Sort.Order order = new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id");
Sort sort = new Sort(order);
Pageable p = new PageRequest(0,3, sort);
EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutorRepository er =
SpringUtil.getApplicationContext().getBean(EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutorRepository.class);
Specification specification = new Specification() {
//查询年龄大于45
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root root, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder) {
Path path = root.get("age");
return criteriaBuilder.gt(path, 45);
}
};
Specification specification1 = new Specification() {
//查询年龄大于45,并且id小于3
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root root, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder) {
Path path = root.get("age");
Path path2 = root.get("id");
criteriaQuery.where(criteriaBuilder.gt(path, 45), criteriaBuilder.lt(path2, 3));
return null;
}
};
Page<Employee> pg = er.findAll(specification1, p);
System.out.println("总页数:"+pg.getTotalPages());
System.out.println("总条数:"+pg.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("当前页元素:"+pg.getContent());
System.out.println("每页条数:"+pg.getSize());
System.out.println("当前页:"+pg.getNumber());
System.out.println(er);
}
该接口的其余用法见这篇博客,这篇总结了一些,包括多表关联的写法:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/659e9715d01d
其实感觉这玩意儿已经有点背离初衷了,我用你封装的框架,主要还是为了少写代码,不过现在发现写个多条件的查询,代码量也不比写原生sql少啊。
感觉这东西除了切数据库很方便,不用改代码之外,其余地方不如mybatis。
对我来说,还是直接写原生sql比较简单粗暴一些。。。