Android笔记之使用CMake进行JNI开发(Android Studio)
不知道有多少朋友像我一样,被Android NDK开发的环境配置折腾到吐,然后放弃。从事Android工作几年了,也不太愿意接触NDK开发。不过福利终于来了,新的AS中开始使用CMake开发jni,开发c跟开发java一样简单,你只需单纯的执着于业务目标,跟折腾环境说拜拜。那我们现在就开始吧!
环境需求
方式一、在工程创建的时候添加
首先使用AS(3.0)新建一个JniTest工程
在创建工程的过程中就有是否支持jni调用的选项

当你把这个选项勾选上后,你会发现项目的App模块下自动就把cmake相关的内容配置好了,我们来看看与无jni调用的工程有什么不同。
首先,app目录下多了CMakeLists.txt文件,内容如下:
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
# 配置so库信息
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
# 生成的so库名称,此处生成的so文件名称是libnative-lib.so
native-lib
# Sets the library as a shared library.
# STATIC:静态库,是目标文件的归档文件,在链接其它目标的时候使用
# SHARED:动态库,会被动态链接,在运行时被加载
# MODULE:模块库,是不会被链接到其它目标中的插件,但是可能会在运行时使用dlopen-系列的函数动态链接
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
# 资源文件,可以多个,
# 资源路径是相对路径,相对于本CMakeLists.txt所在目录
src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp )
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
# 从系统查找依赖库
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
# android系统每个类型的库会存放一个特定的位置,而log库存放在log-lib中
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
# android系统在c环境下打log到logcat的库
log )
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
# 配置库的链接(依赖关系)
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
# 目标库
native-lib
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
# 依赖于
${log-lib} )代码已经添加比较清晰的注释,使用的时候只需要拷贝到模块目录下,上方代码删除注释后一目了然,无需发愁!再看看app/build.gradle下又有什么变化:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 26
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.test.jnitest2"
minSdkVersion 15
targetSdkVersion 26
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
cppFlags ""
}
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "CMakeLists.txt"
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
}主要的多了关于CMake的两项配置:
// android下
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "CMakeLists.txt" // cmake配置文件路径
}
}// defaultConfig下
cmake {
cppFlags ""
// 生成多个版本的so文件
abiFilters 'arm64-v8a', 'armeabi-v7a', 'x86', 'x86_64'
}具体的更多配置,请详查官方文档,根据需要修改。ok,配置就这么多,是不是很简单。接着我们看看资源目录:
![]()
我们发现系统已经帮我们把native-lib.cpp源文件写好了,根据函数名可以知道,函数的native申明是在MainActivity中。我们再看看MainActivity文件,与以前的jni调用方式完成一样:
// Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
static {
// 加载库
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Example of a call to a native method
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
tv.setText(stringFromJNI()); // 发生jni调用
}
/**
* A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library,
* which is packaged with this application.
*/
public native String stringFromJNI(); // native申明上面的过程包括了库的加载、native方法申明、jni方法调用三个过程。跟以往不同的是,你可以按住ctrl键鼠标左键点击native方法,也能像java一样跳转到方法的定义了,即native-lib.cpp文件中的Java_com_test_jnitest2_MainActivity_stringFromJNI方法。
现在我们在MainActivity中再声明一个方法:
public native String getStr(String s);自动就出现了创建jni方法的选项,确定后你会在native-lib.cpp中发现函数定义框架已经写好:

方式二、在项目开发过程中添加
有时候,我们的项目已经在进行中或者维护中了,突然需要使用jni调用怎么办呢?AS已经提供了相对便捷的方法。首先在要使用jni调用的工程模块下新建一个CMakeLists.txt:

代码:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.6)
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
xjni
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/jni/XJni.c )
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
xjni
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib} )
CMakeLists.txt具体配置上面已经说过了,这个地方是去掉了注释了的。需要注意的是,如果我们不在c源代码文件中输出日志到logcat,那么我们是不需要依赖log库的,也就是说find_library、target_link_libraries不是必须的。
接着配置模块支持jni调用,对项目模块右键:

在弹出的提示框中选择刚新建配置的CMakeLists.txt文件:

我们看看app/build.gradle有什么变化:

编译完成,编译器会报找不到XJni.c文件错误。ok,那我们新建一个/app/src/main/jni/XJni.c:
#include 只有一行代码,ok,再编译,没问题!接下来新建jni调用java文件XJni.java:
package com.test.jnitest4;
public class XJni {
static {
System.loadLibrary("xjni");
}
public native String getStr(String s);
}getStr方法显示错误红色,不用着急,我们选中函数名,按快捷键alt+enter:
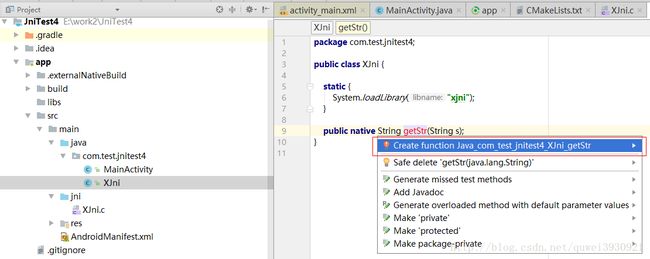
选择create function后,函数就自动在XJni.c文件中生成了
#include 需要注意的是,你最好让.java文件名与.c文件名同名,否则你可能快捷键不会出现create function选项。修改.c文件名的时候记得对应将CMakeLists.txt中修改。
总之,JNI入门难度大大降低,AS在这方面还有很多适用的功能提供,例如debug、在c代码中输入日志到logcat等,只需简单操作就可完成,非常人性。


