2018华东师范大学计算机系机试题目代码
Problem A
给一个小学生都会算的1位数与1位数运算的代数式,请你求出这个表达式的值。
表达式仅含+-*/四种运算,题目保证0不为除数。
Sample Input 1:
1+1Sample Output 1:
2Sample Input 2:
3*4Sample OutPut2:
12C语言解答
#include Python解答
expr=input()
print(int(eval(expr)))
Problem B
现在小学生也在学习基本的编程,课程目标是让小学生能够有基本的算法思想,并不涉及复杂的数据和实现细节与原理。LOGO语言就非常适合小学生学习,它通过绘图的方式来直观的表现出如何用程序代码控制事物。例如控制台上初始给出一个点,使用语句FD 1/1 表示将控制台上的点Forward 1/1的距离,即,向当前方向移动1的距离,这样就画出一条线段。语句LT 60则表示当前朝向向左转60度,接着再使用语句FD 1/1就画出一条与之前的直线夹角为120度的一条线段,这时控制台上就有绘制出了一条折线段。
现在的任务是输出一段能绘制分形的LOGO语言的程序代码。
如果你还对分形不了解,下面我们先介绍一下分形:
分形(Fractal) 是一个几何形状可以分成数个部分,且每一部分都(至少近似地)是整体缩小后的形状,即具有自相似的性质。自然界中一定程度上具有分形的性质的事物有云朵、闪电、植物根系、雪花等等。著名的科赫曲线就是一种分形,它绘制的是形态类似雪花的图案。
以下是0阶到3阶的科赫曲线:
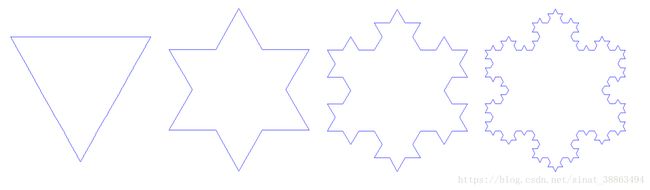
本题的任务只要求画出科赫曲线的一部分即可,具体要求为:
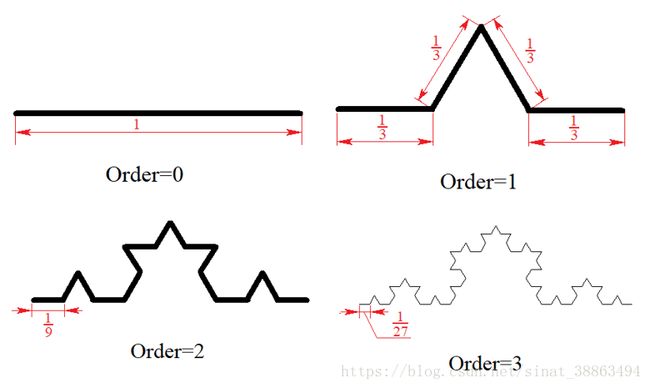
输入:
1行,1个数字n,表示图形的阶数 (0<n<10) ( 0 < n < 10 )
输出:
能绘制上述图形的LOGO程序代码
如果你有递归的思想,那么应该不难看出,这个问题就是一个递归的形式,我们应该先把题目描述转化成算法步骤:
绘制长为x的图形:
如果x已经不能再分成x/3,就画出长为x的直线。
先画长为x/3的图形,左转60度,画出长为x/3的图形,左转240度,画出长为x/3的图形,左转60度,画出长为x/3的图形,画完。
这样就有了程度的基本框架,再把相应的LOGO语言的指令填入,就是此题的答案了。
本题C++和python的程序代码不再赘述
C语言解答
#include Problem C
给出一个含有N (0 < N < 200000)个数字的数列,请你对它排序,每个数的范围均处于 [−1050,1050] [ − 10 50 , 10 50 ] 。负数前有负号‘-’,正数前没有+号,每个数字不含前导0,零用一个0表示。
输入:
2行,第1行有1个数字N,表示数列中数据的个数
第2行有N个数字,表示待排序的数列,数字间用空格分隔,题目保证每个数字在 [−1050,1050] [ − 10 50 , 10 50 ] 范围内。
输出:
1行,将N个数字从小到大排序后的结果,数字间用空格分隔。
Sample Input :
5
991 -31 -1 5 -10000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Sample Output:
-10000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 -31 -1 5 991
C语言解答
#include "%s",a[i].value);
a[i].digit=strlen(a[i].value);
if(a[i].value[0]=='-')
a[i].isPositive=0;
else
a[i].isPositive=1;
}
sort(a,N);
for(i=0;i"%s ",a[i].value);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
int myCompare(ElemType a,ElemType b)
{
if(a.isPositive && b.isPositive == 1){
//both of a and b are positive
if(a.digit!=b.digit)
return a.digitelse
return strcmp(a.value,b.value)<0;
}
else if(a.isPositive==0 && b.isPositive==0){
if(a.digit!=b.digit)
return a.digit>b.digit;
else
return strcmp(a.value+1,b.value+1)>0;
}
else
return a.isPositive==0;
}
void QuickSort(ElemType *a,int lwbd,int upbd)
{
int i=lwbd,j=upbd;
if(iwhile(iwhile(iif(iwhile(iif(i1);
QuickSort(a,i+1,upbd);
}
}
void sort(ElemType *a,int N)
{
QuickSort(a,0,N-1);
}
Cpp解答:用到STL库与运算符重载
#include else
return strcmp(value,b.value)<0;
}
else if( isPositive== false && b.isPositive==false)
{
if(digit!=b.digit)
return digit>b.digit;
else
return strcmp(value,b.value)>0;
}
else
return b.isPositive;
}
};
int main(void)
{
int i,N;
scanf("%d",&N);
numNode *s=new numNode [N];
for(i=0;iscanf("%s",s[i].value);
s[i].digit=strlen(s[i].value);
if(s[i].value[0]=='-')
s[i].isPositive=false;
else
s[i].isPositive=true;
}
sort(s,s+N);
for (i=0;iprintf("%s ",s[i].value);
printf("\n");
delete [] s;
return 0;
}
Problem D
有一个研究团队,团队分成许多研究小组,每个小组的一部分成员可能再分成小组。小组的成员只知道自己的组长是谁,而在同一个组长领导下的成员之间却相互不认识。现在这个团队希望有一个程序能统计一下各组长带领小组的规模,即对每一个成员想知道自己及自己带领下的小组有多少人。
输入:
2行,第1行有1个数字N (0<N<2×105) ( 0 < N < 2 × 10 5 ) ,代表小组的人数
第2行有N个数 a1,a2,...,ai,...,aN a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a i , . . . , a N ,表示第i个人的领导是 ai a i 。团队的领导用0表示,说明没有人做他的组长。数据保证没有环路。单独的一个成员视为1个人的小组。
输出:
1行,N个数字,表示第i名成员的团队的规模
Sample Input:
0 1 2 1 2 2Sample Output:
6 4 1 1 1 1C语言:
待续
Problem E
所谓“螺旋矩阵”,是指从左上角第1个格子开始,按顺时针螺旋方向从外圈向内逐个填充。给出一个数字N,将1至N^2填入一个N行N列的螺旋矩阵。
例如当N=4时,螺旋矩阵为
1 2 3 4
12 13 14 5
11 16 15 6
10 9 8 7当N=5时,螺旋矩阵为
1 2 3 4 5
16 17 18 19 6
15 24 25 20 7
14 23 22 21 8
13 12 11 10 9我现在想知道每一行的蛇形矩阵的和,希望你能通过编写程序求解。
输入:
1行,1个数字N (1<N<2×105) ( 1 < N < 2 × 10 5 )
输出:
N行,第i行表示蛇矩阵第i行的总和。
直接法:列出矩阵进行加和
不能通过所有测试,只能得出小数据的结果
#include =0 && yreturn 1;
else
return 0;
}
typedef long long resType;
resType accumulate(resType *a)
{
int i;
resType s=0;
for (i=0;ireturn s;
}
int main(void)
{
int i,k,x,y;
resType a[MAXN][MAXN];
for(x=0;xfor(y=0;y0;
scanf("%d",&N);
int dir[4][2]={{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
a[0][0]=1;
k=0;x=0;y=0;
for(i=2;i<=N*N;i++)
{
while(!(valid(x+dir[k][0],y+dir[k][1]) && a[x+dir[k][0]][y+dir[k][1]]==0))
k=(k+1)%4;
x=x+dir[k][0];
y=y+dir[k][1];
a[x][y]=i;
}
#if DEBUG
// output the matrix
for(x=0;xfor(y=0;yprintf("%4d",a[x][y]);
printf("\n");
}
#endif
for(i=0;iprintf("%d\n",accumulate(a[i]));
return 0;
}
找到数学规律可覆盖所有范围,C++解答
#include 2)
{
spl+=currD*i;
printf("%lld\n", spl);
currD-=deepD;
}
}
else
{
for(i=2;i2)
{
spl+=currD*i;
printf("%lld\n", spl);
currD-=deepD;
}
}
return 0;
}
python解答
N=int(input())
spl=int(N*(N+1)/2) #sum per line
currD=4*(N-1)-1 #current distance
deepD=8 #2_order distance
print(spl) #sum of the 1st line
for i in range(N-1,0,-2):
spl+=currD*i+1
print(spl)
currD-=deepD
currD=currD+deepD-10
if(N%2==1):
for i in range(1,N,2):
spl+=currD*i
print(spl)
currD-=deepD
else:
for i in range(2,N,2):
spl+=currD*i
print(spl)
currD-=deepD