Ubuntu16.04下,用kdevelop搭建视觉里程计VO框架以及特征提取和匹配
kdevelop搭建视觉里程计VO
- 一、搭建VO框架
- 相关.pp和.h文件代码
- 二、在kDevelop导入相关工程
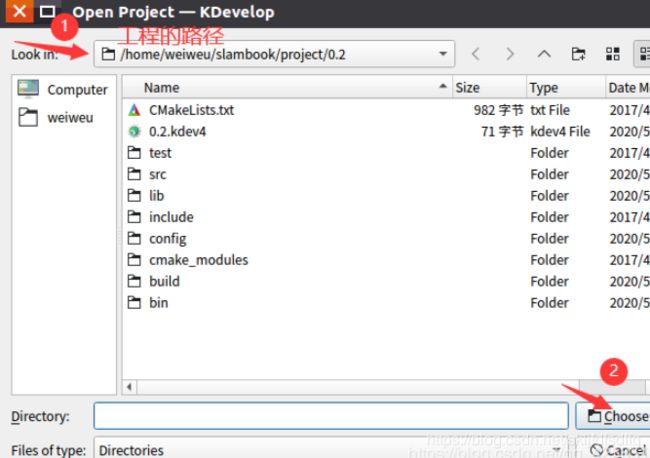
- 1、打开kDevelop并导入工程
- 3、添加运行参数文件
- 4、编译
- 5、运行程序
一、搭建VO框架
首先,我们来了解一下 Linux 程序的组织方式。在编写一个小规模的库时,我们通常
会建立一些文件夹,把源代码、头文件、文档、测试数据、配置文件、日志等等分类存放,这样会显得很有条理。如果一个库内容很多,我们还会把代码分解各个独立的小模块,以便测试。读者可以参照 OpenCV 或 g2o 的组织方式,看看一个大中型库是如何组织的。例如,OpenCV 有 core、imgproc、features2d 等模块,每个模块分别负责不同的任务。g2o则有 core、solvers、types 等若干种。不过在小型程序里,我们也可以把所有的东西揉在一起,称为 SLAM 库。现在我们要写的 SLAM 库是一个小型库,目标是帮读者将本书用到的各种算法融会贯通,书写自己的 SLAM 程序。挑选一个工程目录,在它下面建立这些文件夹来组织代码文件。
相关.pp和.h文件代码
①Camera
Camera 类存储相机的内参和外参,并完成相机坐标系、像素坐标系、和世界坐标系
之间的坐标变换。当然,在世界坐标系中你需要一个相机的(变动的)外参,我们以参数的形式传入。
slambook/project/0.2/include/myslam/camera.h
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
namespace myslam
{
// Pinhole RGBD camera model
class Camera
{
public:
typedef std::shared_ptr Ptr;
float fx_, fy_, cx_, cy_, depth_scale_; // Camera intrinsics
Camera();
Camera ( float fx, float fy, float cx, float cy, float depth_scale=0 ) :
fx_ ( fx ), fy_ ( fy ), cx_ ( cx ), cy_ ( cy ), depth_scale_ ( depth_scale )
{}
// coordinate transform: world, camera, pixel
Vector3d world2camera( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w );
Vector3d camera2world( const Vector3d& p_c, const SE3& T_c_w );
Vector2d camera2pixel( const Vector3d& p_c );
Vector3d pixel2camera( const Vector2d& p_p, double depth=1 );
Vector3d pixel2world ( const Vector2d& p_p, const SE3& T_c_w, double depth=1 );
Vector2d world2pixel ( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w );
};
}
#endif // CAMERA_H
slambook/project/0.2/src/camera.cpp
#include "myslam/camera.h"
#include "myslam/config.h"
namespace myslam
{
Camera::Camera()
{
fx_ = Config::get("camera.fx");
fy_ = Config::get("camera.fy");
cx_ = Config::get("camera.cx");
cy_ = Config::get("camera.cy");
depth_scale_ = Config::get("camera.depth_scale");
}
Vector3d Camera::world2camera ( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w )
{
return T_c_w*p_w;
}
Vector3d Camera::camera2world ( const Vector3d& p_c, const SE3& T_c_w )
{
return T_c_w.inverse() *p_c;
}
Vector2d Camera::camera2pixel ( const Vector3d& p_c )
{
return Vector2d (
fx_ * p_c ( 0,0 ) / p_c ( 2,0 ) + cx_,
fy_ * p_c ( 1,0 ) / p_c ( 2,0 ) + cy_
);
}
Vector3d Camera::pixel2camera ( const Vector2d& p_p, double depth )
{
return Vector3d (
( p_p ( 0,0 )-cx_ ) *depth/fx_,
( p_p ( 1,0 )-cy_ ) *depth/fy_,
depth
);
}
Vector2d Camera::world2pixel ( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w )
{
return camera2pixel ( world2camera ( p_w, T_c_w ) );
}
Vector3d Camera::pixel2world ( const Vector2d& p_p, const SE3& T_c_w, double depth )
{
return camera2world ( pixel2camera ( p_p, depth ), T_c_w );
}
}
②Frame
Frame 类是基本数据单元,只提供基本的数据存储和接口
slambook/project/0.1/include/myslam/frame.h
/*
*
* Copyright (C) 2016
*
* This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program. If not, see 二、在kDevelop导入相关工程
1、打开kDevelop并导入工程
3、添加运行参数文件
4、编译
5、运行程序
点击run->Current Launch Configuration选择要编译的可执行程序
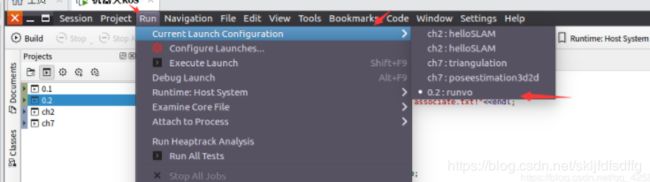
点击Execute运行程序

出现结果;