Go基本概念
- 编码
- 声明变量
- 常量
- 变量类型
- iota enumerate
- 潜规则
- 数组,切片,映射
-
- 数组
- 切片
- 映射
- make, new
-
- 控制语句
-
- if
- goto
- for
- switch
- function
- pass by pointers
- defer
- main and init functions
- import
- struct
-
编码
- Go默认支持UTF-8编码
声明变量
var vname1, vname2, vname3 typevar vname1, vname2, vname3 type = v1, v2, v3var vname1, vname2, vname3 = v1, v2, v3vname1, vname2, vname3 := v1, v2, v3var c complex64 = 5+5i
常量
const Pi float32 = 3.1415926const MaxThread = 10const prefix = "astaxie_"
变量类型
- boolean
bool - Numerical
rune, int8, int16, int32, int64, byte, uint8, uint16, uint32, uint64
rune == int32, byte == uint8
float32, float64
complex64 - String
s := "hello"
m := `hello
world`注:string是不能直接修改的,若想修改可以这样
s := "hello"
c := []byte(s) // convert string to []byte type
c[0] = 'c'
s2 := string(c) // convert back to string type
fmt.Printf("%s\n", s2)- Error
err := errors.New("dfsdsfs sdlfk")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}iota enumerate
这个是为了生成 enum 值,起始于0,按1递增
const (
x = iota // x == 0
y = iota // y == 1
z = iota // z == 2
w // w == 3
)
const v = iota // v == 0潜规则
Go 里没有 public private 关键字,首字母大写的变量、方法、常量都可以被被外部引用,否则就小写
数组,切片,映射
数组
var arr [n]type
var arr [10]int
a := [3]int{1, 2, 3}
c := [...]int{4, 5, 6}
doubleArray := [2][4]int{[4]int{1,2,3,4}, [4]{5,6,7,8}}
easyArray := [2][4]int{{1,2,3,4},{5,6,7,8}}
切片
切片和数组的区别是切片长度可变,也就是不指定数组长度。事实上,切片是引用类型。
var fslice []int
slice := []byte{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}
切片有 length(len) 和 capability(cap) 两个概念,一个是切片长度,一个是切片总容量
注:
* append操作将改变原先的 slice,所以其他指向该数组的 slices 都会被影响。
* 但是,如果原先的 slice没有空间了(cap-len==0),那么append将返回一个新的数组,指向原先数组的slices将不被影响。
映射
映射就类似Python里的字典,定义方式是: map[keyType] valueType
var numbers map[string] int
numbers := make(map[string]int)
numbers["one"] = 1
rating := map[string]float32 {"C": 5, "Go": 4.5, "Python": 4.5}
csharpRating, ok := rating["C#"]
delete(rating, "C")映射是无序的,它也是引用类型,没有固定长度。
make, new
make 是为slice,map,channel这三个类型分配内存空间的,返回的也是对应的类型。此外make也会进行初始化,所以它返回的肯定不是空值。
new也是用来分配空间的,但是返回的是指针。new不仅针对slice,map,channel这三个类型。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var s1 = make([]int, 0)
var s2 []int
fmt.Println(s1 == nil) // false
fmt.Println(s2 == nil) // true
}控制语句
if
if integer == 3 {
fmt.Println("The integer is equal to 3")
} else if integer < 3 {
fmt.Println("The integer is less than 3")
} else {
fmt.Println("The integer is greater than 3")
}goto
func myFunc() {
i := 0
Here: // label ends with ":"
fmt.Println(i)
i++
goto Here // jump to label "Here"
}for
func main(){
sum := 0;
for index:=0; index < 10 ; index++ {
sum += index
}
fmt.Println("sum is equal to ", sum)
}sum := 1
for sum < 1000 {
sum += sum
}for 也有 break,continue这样的关键字
for k,v := range map {
fmt.Println("map's key:",k)
fmt.Println("map's val:",v)
}switch
i := 10
switch i {
case 1:
fmt.Println("i is equal to 1")
case 2, 3, 4:
fmt.Println("i is equal to 2, 3 or 4")
case 10:
fmt.Println("i is equal to 10")
default:
fmt.Println("All I know is that i is an integer")
}integer := 6
switch integer {
case 4:
fmt.Println("integer <= 4")
fallthrough
case 5:
fmt.Println("integer <= 5")
fallthrough
case 6:
fmt.Println("integer <= 6")
fallthrough
case 7:
fmt.Println("integer <= 7")
fallthrough
case 8:
fmt.Println("integer <= 8")
fallthrough
default:
fmt.Println("default case")
}fallthrough会使得switch在按顺序查到匹配的case后,继续匹配下去
function
func SumAndProduct(A, B int) (int, int) {
return A + B, A * B
}func SumAndProduct(A, B int) (add int, multiplied int) {
add = A+B
multiplied = A*B
return
}variadic functions
func myfunc(arg ...int) {
for _, n := range arg {
fmt.Println(n)
}
}pass by pointers
package main
import "fmt"
// simple function to add 1 to a
func add1(a *int) int {
*a = *a + 1 // we changed value of a
return *a // return new value of a
}
func main() {
x := 3
fmt.Println("x = ", x) // should print "x = 3"
x1 := add1(&x) // call add1(&x) pass memory address of x
fmt.Println("x+1 = ", x1) // should print "x+1 = 4"
fmt.Println("x = ", x) // should print "x = 4"
}defer
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
defer fmt.Printf("%d ", i)
}panic and recover
func throwsPanic(f func()) (b bool) {
defer func() {
if x := recover(); x != nil {
b = true
}
}()
f() // if f causes panic, it will recover
return
}main and init functions
main 只能有一个,init可以有多个,但也只推荐一个package一个init
这俩方法都会被自动调用.
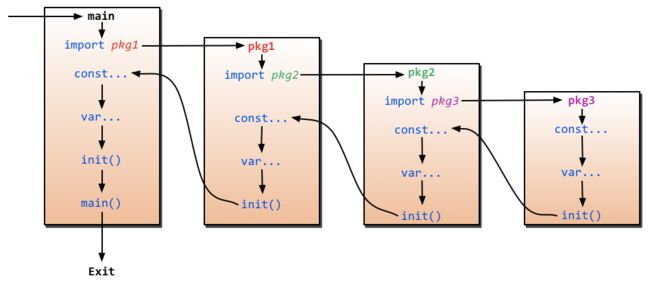
import
- Dot operator
import (
. "fmt"
)这样可以省略包名,直接调用里面的函数:
fmt.Println(“…”) => Println(“…”)
2. alias operation
import (
f "fmt"
)fmt.Println(“…”) => f.Println(“…”)
3. _ operator
import (
_ "github.com/zzz"
)只执行 zzz 里的init函数,不引入该包中的其他变量或函数
struct
1、 simple struct
type person struct {
name string
age int
}
P := person{"Tom", 25} // 顺序要和定义的一致
Q := person{age: 24, name: "Bob"} // 可以无序
R := struct{name string; age int}{"Amy", 18} // 匿名struct2、 embedded fields in struct
package main
import "fmt"
type Human struct {
name string
age int
weight int
}
type Student struct {
Human // embedded field, it means Student struct includes all fields that Human has.
specialty string
}
func main() {
// instantiate and initialize a student
mark := Student{Human{"Mark", 25, 120}, "Computer Science"}
// access fields
fmt.Println("His name is ", mark.name)
fmt.Println("His age is ", mark.age)
fmt.Println("His weight is ", mark.weight)
fmt.Println("His specialty is ", mark.specialty)
// modify mark's specialty
mark.specialty = "AI"
fmt.Println("Mark changed his specialty")
fmt.Println("His specialty is ", mark.specialty)
fmt.Println("Mark become old. He is not an athlete anymore")
mark.age = 46
mark.weight += 60
fmt.Println("His age is", mark.age)
fmt.Println("His weight is", mark.weight)
}