Apache2.2.x 安装与配置详解
Apache2.2.x 安装
使用RPM包安装
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y httpd程序环境如下
配置文件
- 主配置文件路径
- /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- 其它配置文件路径
- /etc/httpd/conf.d/*.conf
服务脚本
- /etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd
- 配置文件:/etc/sysconfig/httpd
主程序文件
- /usr/sbin/httpd
- /usr/sbin/httpd.worker
- /usr/sbin/httpd.event
日志文件目录
- /var/log/httpd
- access_log:访问日志
- error_log:错误日志
站点文档目录
- /var/www/html
模块文件路径
- /usr/lib64/httpd/modules
使用源码包安装
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/apache2/ --sysconfdir=/usr/local/apache2/etc/ --with-included-apr --enable-so --enable-deflate=shared --enable-expires=shared --enable-rewrite=shared配置文件
- 主配置文件路径
- /usr/local/apache2/conf/httpd.conf
- 其它配置文件路径
- /usr/local/apache2/conf/extra/*.conf
站点文档目录
- /usr/local/apache2/htdocs/
Apache2.2.x 配置
配置文件的组成
[root@localhost ~]# grep "Section" /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
### Section 1: Global Environment # 全局配置部分
### Section 2: 'Main' server configuration # ‘主’服务配置部分
### Section 3: Virtual Hosts # 虚拟主机部分
常用配置
全局配置部分
持久连接
KeepAlive 为持久连接的选项,表示客户端与服务器连接建立后,每个资源(css,js,image)获取完成后不会断开连接,而是继续等待其它的请求完成;
# ...
KeepAlive Off
# On为开启,Off为关闭
# 下列选项 则是在 KeepAlive 状态为 On 的情况下 生效
# ...
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
# 数量限制,单个用户持久连接最大数量
# ...
KeepAliveTimeout 15
# 时间限制,持久连接超时时间存在的副作用:对并发访问量较大的服务器,持久连接功能会使用有些请求得不到响应;
折中方案:使用较短的持久连接时间
MPM
MPM 全称 Multipath Process Module:多道处理模块。有三个模块可供选择,分别为 prefork、worker、event,在编译时必须选择也只能选定一个
rpm安装的包提供三个二进制程序文件,分别用于实现对不同MPM机制的支持
rpm包 默认为/usr/sbin/httpd, 其使用prefork
[root@localhost ~]# ls /usr/sbin/httpd*
/usr/sbin/httpd /usr/sbin/httpd.event /usr/sbin/httpd.worker如何确认当前是何种工作方式?
# ps aux | grep httpd
# 查看
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | grep httpd如何更换使用的工作方式?
# vim /etc/sysconfig/httpd
# 启用 HTTPD 项,并进行更改
# HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker
# 重启 httpd 服务生效这里提及下如何查看编译到httpd的模块列表,也可以确认当前工作方式
查看静态编译的模块
[root@localhost /]# httpd -l
Compiled in modules:
core.c
prefork.c
http_core.c
mod_so.c发现 mod_so.c,表示可以动态加载模块
查看静态编译及动态装载的模块
[root@localhost /]# httpd -M
配置文件中MPM部分各项参数
# prefork MPM
# ...
StartServers 8 # 服务启动时启动的进程数
MinSpareServers 5 # 最小空闲进程数
MaxSpareServers 20 # 最大空闲进程数
ServerLimit 256 # 服务器生命周期内MaxClients的最大值
MaxClients 256 # 允许启动的最大服务器进程数
MaxRequestsPerChild 4000 # 单个进程提供的最大请求数
# worker MPM
# ...
StartServers 4 # 服务启动时启动的进程数
MaxClients 300 # 客户端同时最大连接数(并发)
MinSpareThreads 25 # 最小空闲工作线程数
MaxSpareThreads 75 # 最大空闲工作线程数
ThreadsPerChild 25 # 单个进程中的常量工作线程数
MaxRequestsPerChild 0 # 单个进程提供的最大请求数(0为无限制)
监听IP和Port
Listen项用于设置监听的IP和端口,省略IP表示监听本机所有IP,并且 Listen 项可出现多次,用于监听本机的不同的IP地址
# Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 80DSO
DSO全称 Dynamic Shared Object:动态共享对象
配置指令实现模块加载,模块路径可使用相对路径,相对于ServerRoot(/etc/httpd),可知 modules 目录位置为 /etc/httpd/modules
# Example:
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so
LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so
# ...主服务配置部分
DocumentRoot
DocumentRoot 定义了主服务的文档页面路径
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"Directory
Directory 定义了基于文件系统路径指明对哪些资源进行访问控制
在指明DocumentRoot后,默认设置了主服务的文档根目录一组非常限制的功能,即根目录默认配置
<Directory />
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Directory>这里开始对DocumentRoot进行任何您想要的配置,需要注意的是相同项会覆盖默认配置,子目录会继承根目录配置。当然你也可以使用 Directory 单独对子目录进行 访问控制,这里我对子目录 manage 限制为 只允许 特定 IP段访问
"/var/www/html">
# Options 指令的可能值为 None, ALL, 或以下任意组合:
# Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
# Options 指令既复杂又重要,可以去以下链接了解更多信息
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/core.html#options
# Indexs:索引,即允许列目录
# FollowSymlinks:允许跟踪符号链接文件
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
# AllowOverride从字面上解释是允许覆盖的意思,即Apache允许另一配置文件(.htaccess)覆盖现有配置文件
# .htaccess是在一个特定的目录中放置一个包含指令的文件,其中的指令作用于此目录及其所有子目录。
AllowOverride None
# 访问控制即黑白名单
# deny 在 allow 之后,表示默认拒绝所有访问
# allow 在 deny 之后,表示默认允许所有访问
# Allow from all,允许所有访问
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
# 对 manage 目录访问控制
"/var/www/html/manage">
options FollowSymLinks
Order allow,deny
allow from 192.168.80.0/24
DirectoryIndex
DirectoryIndex 定义默认主页面
DirectoryIndex index.html index.html.var日志设定
错误日志
ErrorLog 定义了错误日志文件的存放路径
LogLevel 定义了错误日志记录等级
# 如果路径名不以 / 开头,则是一个相对于 ServerRoot 的相对路径
# 此处为相对路径,绝对路径为 /etc/httpd/logs/error_log
ErrorLog logs/error_log
# LogLevel 共有等级 debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, alert, emerg.
LogLevel warn访问日志
LogFormat 定义访问日志的记录格式
CustomLog 定义了访问日志文件的存放路径及使用的格式
# 详情http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_log_config.html#formats
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
LogFormat "%{Referer}i -> %U" referer
LogFormat "%{User-agent}i" agent
# 此处为相对路径,
# 访问日志路径 /etc/httpd/logs/access_log
# 使用 combined 日志格式
CustomLog logs/access_log combinedAlias
Alias 定义路径别名即虚拟目录
# 定义别名 icons 对应 /var/www/icons/ 目录
# 即访问 URL/icons/ 时,访问 /var/www/icons/ 目录
Alias /icons/ "/var/www/icons/"
# 对 /var/www/icons/ 目录访问控制
AddDefaultCharset
AddDefaultCharset 设定默认字符集
# UTF-8, GBK, GB2312, GB18030
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8server-status
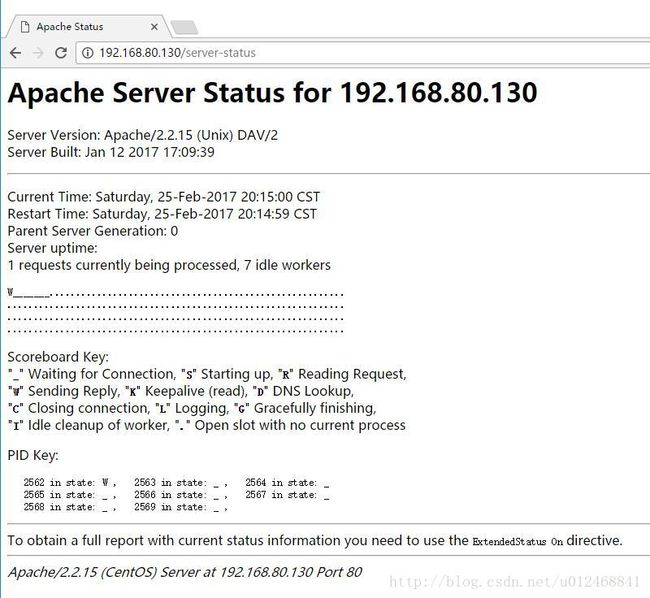
内置 server-status 页面,允许由mod_status生成的服务器状态报告,访问地址:URL/server-status
虚拟主机部分
虚拟主机部分模板
# 大部分 Directive 中的指令都适用于 VirtualHost
#
#实现虚拟主机的方案
- 基于IP
- 为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个地址
- 基于PORT
- 为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个专用PORT
- 基于ServerName
- 为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个专用ServerName
注意
一般虚拟主机莫与中心主机混用,所以,要使用虚拟主机,先禁用中心主机;
禁用中心主机:注释DocumentRoot
示例-基于ServerName实现
# 创建 web1 和 web2 目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /var/www/html/vhosts/web1
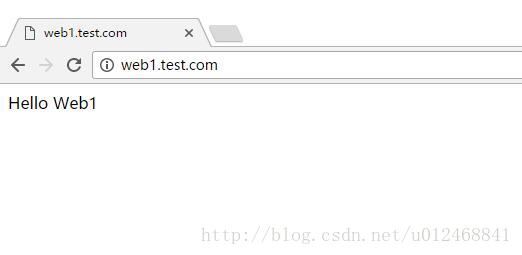
[root@localhost ~]# echo "Hello Web1" > /var/www/html/vhosts/web1/index.html
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /var/www/html/vhosts/web2
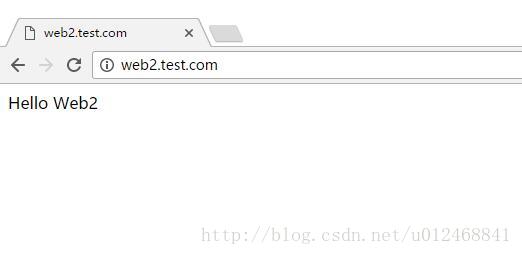
[root@localhost ~]# echo "Hello Web2" > /var/www/html/vhosts/web2/index.html
# 编辑 httpd 配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# 注释 DocumentRoot
# DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
# 启用 NameVirtualHost
NameVirtualHost 192.168.80.130:80
# 添加编辑 VirtualHost
192.168.80.130:80>
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/vhosts/web1"
ServerName web1.test.com
CustomLog logs/web1-access_log combined
192.168.80.130:80>
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html/vhosts/web2"
ServerName web2.test.com
CustomLog logs/web2-access_log combined
# 重启 httpd 服务
[root@localhost vhosts]# service httpd restart访问时
Windows:
修改本机 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\host 文件添加
192.168.80.130 web1.test.com
192.168.80.130 web2.test.com
基于用户的访问控制
基本认证流程
基于BASIC认证
(1) 定义安全域
模板
示例
<Directory "/var/www/html/manage">
options None
AllowOverride None
AuthType Basic
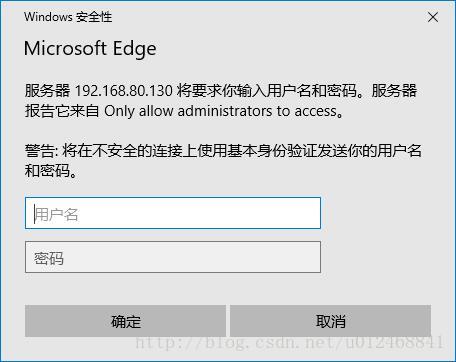
AuthName "Only allow administrators to access"
AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswd"
Require valid-user
Directory>(2)提供账号和密码存储(文本文件)
- 使用 htpasswd 命令进行管理
- htpasswd [options] passwordfile username
- -c:自动创建passwordfile,因此,仅应该在添加第一个用户时使用;
- -m:md5加密用户密码
- -s:sha1加密用户密码
- -D:删除指定用户
- htpasswd [options] passwordfile username
htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswd admin(3)实现基于组进行认证
模板
<Directory "">
Options None
AllowOverride None
AuthType Basic
AuthName "STRING"
AuthUserFile "/PATH/TO/HTTPD_USER_PASSWD_FILE"
# 定义组文件路径
AuthGroupFile "/PATH/TO/HTTPD_GROUP_FILE"
# 允许指定组登录访问
Require group GROUP1 GROUP2 …
Directory>组文件模板
GRP_NAME: user1 user2 user3 …示例
# 添加组文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/.htgroup
webadmin: admin administrator
<Directory "/www/htdocs/admin">
Options None
AllowOverride None
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Administator private"
AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswd"
AuthGroupFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/.htgroup"
Require group webadmin
Directory>