Spring Cloud feign使用
Spring Cloud feign使用
- 前言
- 环境准备
- 应用模块
- 应用程序
- 应用启动
- feign特性
- 综上
1. 前言
我们在前一篇文章中讲了一些我使用过的一些http的框架
服务间通信之Http框架,其实最终还是准备讲述spring cloud fegin,使用spring cloud fegin完成更为优雅的http的调用方式,以及在服务之间的调用与远程调用的注意上,还有一些使用的问题。
2. 环境准备
这回搭建的一个完整的应用不再新建maven工程,改用gradle,spring boot工程推荐的还是使用gradle来构建,并且gradle相对于maven来说优势较多,应用的也越来越广,因此这回尝试一下,使用一回gradle构建spring cloud应用,具体采用的环境、工具等如下:
intellij 2016: 编写java程序。
jdk8 : 采用java8来编写应用,可以使用java8中一些特性编写更为优雅的代码和运行更为高效的程序。
gradle: 用于我们工程的构建、依赖管理、工程打包等等。
3. 应用模块
采用feign来进行服务之间的调用,一般都是需要一个注册中心,这回就采用eureka作为注册中心,以供于两个服务进行服务注册和服务发现,总体服务列别如下:
eureka-server: 服务注册中心,用于服务注册和服务发现。
service-a: a服务,服务消费者。
service-b: b服务,服务提供者。
4. 应用程序
gradle工程中的build.gradle等一些脚本不再展示出来,在这仅仅展示一下工程结构,如下:
.
├── build.gradle
├── eureka-server
│ ├── build.gradle
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── cn
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── enreka
│ │ └── EurekaServerApplication.java
│ └── resources
│ └── bootstrap.yml
├── gradlew
├── gradlew.bat
├── service-a
│ ├── build.gradle
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── cn
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── devh
│ │ ├── A1ServiceApplication.java
│ │ ├── controllers
│ │ │ └── AServiceController.java
│ │ └── fegin
│ │ └── ServiceBClient.java
│ └── resources
│ ├── application.yml
│ └── bootstrap.yml
├── service-b
│ ├── build.gradle
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── cn
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── devh
│ │ ├── B1ServiceApplication.java
│ │ └── controllers
│ │ └── ServiceB1Controller.java
│ └── resources
│ ├── application.yml
│ └── bootstrap.yml
├── settings.gradle
└── zuul
├── build.gradle
└── src
└── main
├── java
│ └── cn
│ └── com
│ └── zuul
│ └── ZuulApplication.java
└── resources工程结构大致和maven项目中差不多,zuul是api网关模块,这节暂时不讲,留在后期进行讲述。
4.1 eureka-server
eureka server采用的是无中心化的架构,无master/slave区分,每一个server都是对等的,既是Server又是Client,所以其集群方式可以自由发挥,可以各点互连,也可以接力互连采用eureka作为注册中心,在这里一个简单的应用中,我就采用了一个节点当做注册中心,eureka集群可以看看我先前写的这一篇文章Eureka的高可用以及服务提供者、服务消费者集群之间的调用方式,但是eureka作为注册中心也是存在着许多问题的,在随后的文章中进行讲述,同时也讲述zookeeper、etcd、consul和eureka之间的优劣势,话不多说,还是回到eureka server服务上来,单节点的eureka使用还是比较简单的,程序如下:
bootstrap.yml:
server:
port: 8761
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 30
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
server:
enable-self-preservation: falseEurekaServerApplication:
package cn.com.enreka;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
/**
* Created by xiaxuan on 17/8/27.
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
如此,一个简单的eureka就编写完成了,到时直接启动主程序,注册中心就可以正常启动起来。
4.2 服务提供者service-b
service-b是我们的服务提供者,应用比较简单,仅仅是提供一个一个接口以供消费者调用,具体应用程序如下:
配置文件bootstrap.yml:
server:
port: 8070
spring:
application:
name: service-b
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
registerWithEureka: true
fetchRegistry: true
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
配置文件application.yml:
msg: Hello配置文件bootstrap.yml和application.yml都可以用来配置参数,
bootstrap.yml可以理解成系统级别的一些参数配置,这些参数一般是不会变动的。
application.yml 可以用来定义应用级别的,如果搭配spring-cloud-config使用 application.yml里面定义的文件可以实现动态替换。spring-cloud-config在后期会进行一些讲述,到时再提一下另外一套配置中心,携程的apoll,挺不错。
B1ServiceApplication:
package cn.com.devh;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
/**
* Created by xiaxuan on 17/8/26.
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class B1ServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(B1ServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
和普通的spring boot启动程序没有太多的不同,仅仅只是加了一个@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,便于服务注册和服务发现,同时还可以使用的是另外一个注解,为@EnableEurekaClient,两个的用法基本相同,下次有空讲讲另外一个注解的用途。
提供服务的controller,ServiceB1Controller:
package cn.com.devh.controllers;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by xiaxuan on 17/8/28.
*/
@RestController
public class ServiceB1Controller {
@Autowired
DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@Value("${msg:unknown}")
private String msg;
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String printServiceB() {
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = discoveryClient.getLocalServiceInstance();
return serviceInstance.getServiceId() + " (" + serviceInstance.getHost() + ":" + serviceInstance.getPort() + ")" + "===>Say " + msg;
}
}
提供的接口也比较简单,就是返回当前的serviceId、host、port和一条hello语句。
4.3 服务消费者service-a
service-a是服务消费者,大致和service-b相同,但是还包括feign来调用server-b提供的服务,配置文件不再展示出来,最后会有整体的代码的下载路径,其他具体代码如下:
A1ServiceApplication:
package cn.com.devh;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
/**
* Created by xiaxuan on 17/8/25.
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class A1ServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(A1ServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
启动程序与与service-b没有区别,都是加上了一个注解@EnableDiscoveryClient用于服务注册和服务发现使用,然后还单独加上了一个注解@EnableFeignClients,这个注解就是确保feign可以正常使用。
ServiceBClient:
package cn.com.devh.fegin;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* Created by xiaxuan on 17/8/26.
*/
@FeignClient(name = "service-b")
public interface ServiceBClient {
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
String printServiceB();
}
对service-b编写的feignClient,到时用来直接调用service-b提供的服务,而之所以能够正常调用到service-b的服务,就是通过feign中的name字段,会通过注册中心找到对应的服务。
controller,AServiceController:
package cn.com.devh.controllers;
import cn.com.devh.fegin.ServiceBClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by xiaxuan on 17/8/26.
*/
@RestController
public class AServiceController {
@Value("${name:unknown}")
private String name;
@Autowired
private ServiceBClient serviceBClient;
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String printServiceA() {
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = discoveryClient.getLocalServiceInstance();
return serviceInstance.getServiceId() + " (" + serviceInstance.getHost() + ":" + serviceInstance.getPort() + ")" + "===>name:" + name + "
" + serviceBClient.printServiceB();
}
}
提供的服务也是比较简单,输出当前服务在注册中心中的serviceId、host、port和使用feign调用service-b的服务。
以上就是我们整个应用中的三个服务,注册中心eureka-server,服务提供者service-b,服务消费者service-a.
5. 应用启动
分别启动三个服务,注册中心eureka-server,服务提供者service-b,服务消费者service-a,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8761,观察服务状况,如下图:
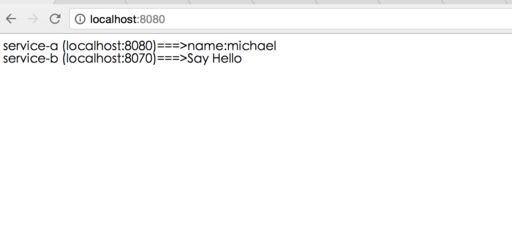
两个服务都正常启动,现在直接在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/,调用service-a提供的接口,结果如下图:
成功输出当前服务在注册中心的信息并且成功调用service-b提供的服务。
6. feign特性
在这个简单的应用中,service-a通过feign调用service-b的服务,并输出service-a和service-b在注册中心中的信息,整个应用编写的还是比较简单,而且feign还有许多其他有意思的特性。
feign不仅有一个name属性,还有一个url属性,如果指定name属性的话,会直接调用在注册中心中注册的本地服务,如果是还指定了url属性的话,就可以直接调用远程的非注册中心的服务,这样在调用其他服务的时候就非常方便,只要url相同,方法签名中的参数相同,就可以成功的调用对方的服务。
同时feign还可以设置断路由,如果服务调用失败的话,可以调用本地写的failback方法,返回一些默认信息或者抛错之类,给了非常灵活的自由度。
另外feign还有重试次数、超时设置、更换底层使用的httpClient框架等等,都非常有意思,有兴趣的可以google看看。
7. 综上
代码地址在:microservices
一个简单的应用,提供一个注册中心、服务提供者、服务消费者,服务消费者通过feign调用服务提供者者service-b提供的服务。
如果feign配合ribbon还有路由等等配合一起使用,就比较有意思了,就基本相当于实现了服务之间的高可用,这个在后期进行讲述。
下一篇文章讲述在docker中将这几个应用运行起来并进行服务之间的调用。