Android自定义FlowLayout,可带固定按钮,可自定义样式、选择数量
各位old铁,我又回来了,一个多月没有写博客了,难免有些空虚。一直以来在Android面试中,很多面试中都会问你是否会自定义View,这是考验一个程序猿的标准,接下来就让我们进入今天的学习。
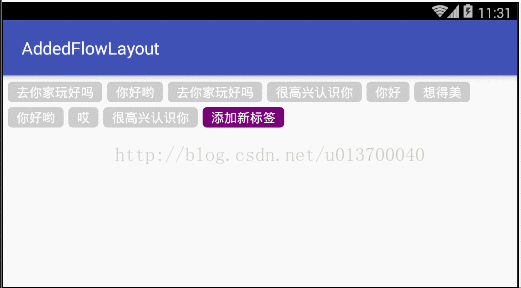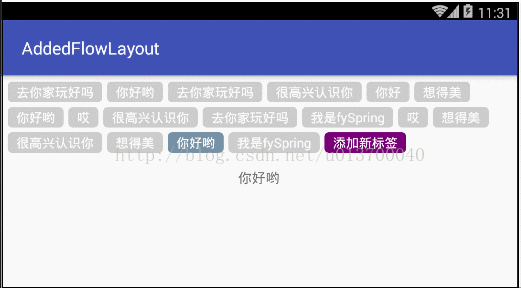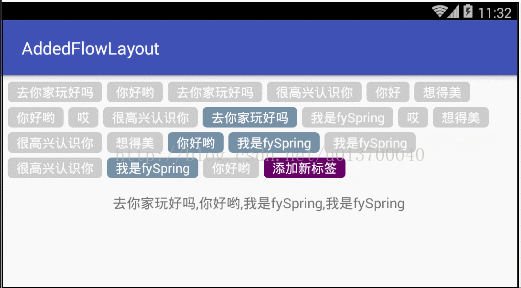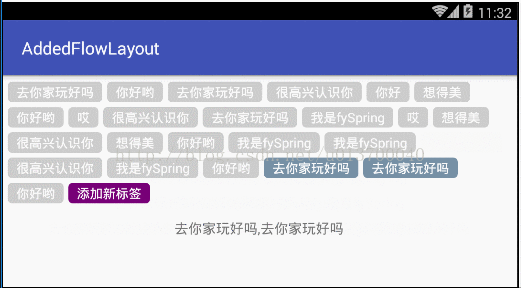
最近在项目中需要用到流布局FlowLayout,网上也有很多大神也早已实现自定义流布局,但是发现和我的需求有些不大一样,于是乎抱着学习的态度,自己写了这样的一个可添加固定按钮的流布局,可设置单选、多选或者不设置限制,这个固定按钮可以设置是否显示,我就先取名AddedFlowLayout 吧。大概是什么样式呢?先来看看我的效果吧。Demo依然在文章的最后,就是这么傲娇 ,、'`,、 (´∀`) ,、'`,、
在开始这篇文章之前,我们先来分析一下大致思路:
1、既然是流布局的话,我们在添加子View的时候首先得获得子View的宽度以及当前行剩余的可用宽度。如果子View的宽度大于剩余的可用宽度,则换行,反之继续添加在后面
2、再插入新的标签的时候,插入到倒数第二个的位置上,就可以保证最后一个一直是添加按钮。
我在这个布局中自定义了多个属性,以便可以通过一行代码达到一个效果,来看看我的代码吧,注:该样式需要写在values文件夹下的attrs文件中(该文件需要手动添加):
先来说一下每个参数的意思:
· addedText : 固定按钮的显示内容,默认为 添加
· isAdded : 是否显示固定按钮,默认为不显示
· maxNum : 设置选择标签的最大数量,不设置或者小于1都为不限制数量,为1的话是单选,大于1则为多选最大数量。
· textRes : 字体的样式,可以在此设置字体的大小,颜色,padding值
· textMargins : 每个Tag标签的外部margin值,默认为5
· tagBg : 标签按钮的背景样式,设置选中未选中状态
· addedBg : 添加按钮的背景样式,设置按下的样式
-
-
标签按钮的样式:
-
-
接下来是关键的自定义FlowLayout的代码了(注释都在代码里面,我就直接放完整的代码了):
/**
* Created by fySpring
* Date : 2017/7/13
* To do :自定义流布局
*/
public class AddedFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private static final String TAG = "AddedFlowLayout";
private Context mContext;
private List dataList = new ArrayList<>();
private List textViewList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 用来存储点的状态坐标
*/
private Map flagMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 存储所有的View,按行记录
*/
private List> mAllViews = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 记录每一行的最大高度
*/
private List mLineHeight = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 添加按钮的文本
*/
private String addedText;
/**
* 最大选择数,默认为0,小于0的情况不限制数量,为1的情况是单选,大于1的话为限制选择数量
*/
private int maxNum;
/**
* 当前显示类型是否为添加,默认不显示
*/
private boolean isAdded;
/**
* 添加标签的按钮Tv
*/
private TextView addedContentTv;
/**
* textView的基本样式
*/
private int textAppearance;
/**
* 选中的坐标,只针对单选的时候有效
*/
private int curSelPosition = -1;
/**
* layout的margins
*/
private int textMargins;
/**
* 标签按钮的背景样式
*/
private int tagBg;
/**
* 添加按钮的背景样式
*/
private int addedBg;
public AddedFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
this.mContext = context;
TypedArray ta = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.FlowLayoutView);
addedText = ta.getString(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_addedText) == null ?
"添加" : ta.getString(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_addedText);
maxNum = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_maxNum, 0);
isAdded = ta.getBoolean(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_isAdded, false);
textAppearance = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_textRes, R.style.default_text_flag_style);
textMargins = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_textMargins, 5);
tagBg = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_tagBg,R.drawable.default_text_flag_style);
addedBg = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_addedBg,R.drawable.default_text_add_tag_style);
/**
* 如果状态为添加的话则初始化添加按钮
*/
if (isAdded) {
addedContentTv = new TextView(mContext);
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams
(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp.setMargins(textMargins, textMargins, textMargins, textMargins);
addedContentTv.setLayoutParams(lp);
addedContentTv.setText(addedText);
addedContentTv.setTextAppearance(mContext, textAppearance);
addedContentTv.setBackgroundResource(addedBg);
addView(addedContentTv);
addedContentTv.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (onAddedTagClickListener != null)
onAddedTagClickListener.onAddTagClick();
}
});
}
ta.recycle();
}
/**
* 因为我们只需要支持margin,所以使用系统的MarginLayoutParams
*/
@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
/**
* 设置默认的MarginLayoutParams
*/
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
}
/**
* 设置数据
*
* @param list 需要展示的数据
*/
public void setDataList(List list) {
dataList.clear();
textViewList.clear();
dataList.addAll(list);
for (int i = 0; i < dataList.size(); i++) {
//初始化所有的点都为未选中
flagMap.put(i, false);
String data = dataList.get(i);
TextView tv = initNewTextView(data, i);
addView(tv,i);
textViewList.add(tv);
}
invalidate();
}
/**
* 添加新的数据后从最后一条插入进去
*/
public void addNewData(String newData) {
final int position = textViewList.size();
dataList.add(newData);
flagMap.put(position, false);
TextView tv = initNewTextView(newData, position);
addView(tv, position);
textViewList.add(tv);
invalidate();
}
/**
* 提取公用的初始化TextView方法
*
* @param dataStr 数据
* @param position 位置
* @return TextView
*/
private TextView initNewTextView(String dataStr, final int position) {
final TextView tv = new TextView(mContext);
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams
(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
lp.setMargins(textMargins, textMargins, textMargins, textMargins);
tv.setLayoutParams(lp);
tv.setText(dataStr);
tv.setTextAppearance(mContext, textAppearance);
tv.setBackgroundResource(tagBg);
tv.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//无限制的选择
if (maxNum < 1) {
if (flagMap.get(position)) {
tv.setSelected(false);
flagMap.put(position, false);
} else {
tv.setSelected(true);
flagMap.put(position, true);
}
} else if (maxNum == 1) {
//单选状态
if (flagMap.get(position)) {
//已选中的话就取消
curSelPosition = -1;
tv.setSelected(false);
flagMap.put(position, false);
} else {
//未选中的话就先清空上一个选项,再设当前项为选中
if (curSelPosition != -1) cancelCurSel(curSelPosition);
curSelPosition = position;
tv.setSelected(true);
flagMap.put(position, true);
}
} else {
//有限制的选择
if (flagMap.get(position)) {
tv.setSelected(false);
flagMap.put(position, false);
} else {
if (getSelNum() < maxNum) {
tv.setSelected(true);
flagMap.put(position, true);
} else {
Toast.makeText(mContext, "最多选择" + maxNum + "项哦!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
if (onSelChangedListener != null)
onSelChangedListener.onSelChanged();
}
});
return tv;
}
/**
* 清空全部选中状态
*/
private void cancelAllSel() {
for (int i = 0; i < flagMap.size(); i++) {
flagMap.put(i, false);
textViewList.get(i).setSelected(false);
}
}
/**
* 取消指定项的选中
*/
private void cancelCurSel(int position) {
flagMap.put(position, false);
textViewList.get(position).setSelected(false);
}
/**
* 获取当前选中的子项个数
*
* @return 子项个数
*/
private int getSelNum() {
int num = 0;
for (Map.Entry entry : flagMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue())
num++;
}
return num;
}
/**
* 获取选中的数据list
*
* @return 选中的数据list
*/
private List getSelDataList() {
List selDataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry entry : flagMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue())
selDataList.add(dataList.get(entry.getKey()));
}
return selDataList;
}
/**
* 负责设置子控件的测量模式和大小 根据所有子控件设置自己的宽和高
*
*
* 首先得到其父容器传入的测量模式和宽高的计算值,然后遍历所有的childView,
* 使用measureChild方法对所有的childView进行测量。
* 然后根据所有childView的测量得出的宽和高得到该ViewGroup如果设置为wrap_content时的宽和高。
* 最后根据模式,如果是MeasureSpec.EXACTLY则直接使用父ViewGroup传入的宽和高,否则设置为自己计算的宽和高。
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 获得它的父容器为它设置的测量模式和大小
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
/**
* 如果是warp_content情况下,记录宽和高
*/
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
/**
* 记录每一行的宽度,width不断取最大宽度
*/
int lineWidth = 0;
/**
* 每一行的高度,累加至height
*/
int lineHeight = 0;
int cCount = getChildCount();
// 遍历每个子元素
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量每一个child的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到child的lp
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 当前子控件实际占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
// 当前子控件实际占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
/**
* 如果加入当前childWidth后超出最大宽度,则的到目前最大宽度给width,累加height,然后跳转下一行
*/
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);// 取最大的
lineWidth = childWidth; // 重新开启新行,开始记录
// 叠加当前高度,
height += lineHeight;
// 开启记录下一行的高度
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
// 否则累加值lineWidth,lineHeight取最大高度
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
// 如果是最后一个,则将当前记录的最大宽度和当前lineWidth做比较
if (i == cCount - 1) {
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth
: width, (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight
: height);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 存储每一行所有的childView
List lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
int cCount = getChildCount();
// 遍历所有的childView
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
//获取每个childView的宽高
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
/**
* 如果已经需要换行
*/
if (childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + lineWidth > width) {
// 记录这一行所有的View以及最大高度
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 将当前行的childView保存,然后开启新的ArrayList保存下一行的childView
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
lineWidth = 0;// 重置行宽
lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* 如果不需要换行,则累加
*/
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}
// 记录最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
// 得到总行数
int lineNums = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNums; i++) {
// 每一行的所有的views
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
// 当前行的最大高度
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
Log.e(TAG, "第" + i + "行 :" + lineViews.size() + " , " + lineViews);
Log.e(TAG, "第" + i + "行, :" + lineHeight);
// 遍历当前行所有的View
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View child = lineViews.get(j);
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
//计算childView的left,top,right,bottom
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
Log.e(TAG, child + " , l = " + lc + " , t = " + t + " , r ="
+ rc + " , b = " + bc);
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.rightMargin
+ lp.leftMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
}
/**
* 添加按钮点击事件接口,手动添加新的标签
*/
private OnAddedTagClickListener onAddedTagClickListener;
public interface OnAddedTagClickListener {
void onAddTagClick();
}
public void setOnAddedTagClickListener(OnAddedTagClickListener onAddedTagClickListener) {
this.onAddedTagClickListener = onAddedTagClickListener;
}
/**
* 选中后展示的接口,刷新请求数据等等
*/
private OnSelChangedListener onSelChangedListener;
public interface OnSelChangedListener {
void onSelChanged();
}
public void setOnSelChangedListener(OnSelChangedListener onSelChangedListener) {
this.onSelChangedListener = onSelChangedListener;
}
/**
* 获取选中的String,以逗号分割
* @return
*/
public String getSelString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String data : getSelDataList()) {
sb.append(data).append(",");
}
if (sb.length() > 0)
return sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1);
return sb.toString();
}
} 当你还意犹未尽的时候,我们的自定义FlowLayout已经完成啦,来看看怎么使用。
在界面中可以这样写,当然也可以按照自定义的标签去写,目前我就用了三个标签:
flowLayout = (AddedFlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.added_flow_layout);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
position = random.nextInt(tags.length);
dataList.add(tags[position]);
}
/**
* 没有数据的情况可以不用调用该方法,我这里是设置测试数据
*/
flowLayout.setDataList(dataList);
/**
* 添加按钮的点击事件
*/
flowLayout.setOnAddedTagClickListener(new AddedFlowLayout.OnAddedTagClickListener() {
@Override
public void onAddTagClick() {
position = random.nextInt(tags.length);
flowLayout.addNewData(tags[position]);
}
});
/**
* 标签按钮的点击事件
*/
flowLayout.setOnSelChangedListener(new AddedFlowLayout.OnSelChangedListener() {
@Override
public void onSelChanged() {
contentTv.setText(flowLayout.getSelString());
}
});2017/7/17 更新 今天使用的过程中发现了一个严重的问题,当要获取自定义的属性时
textAppearance = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.FlowLayoutView_textRes, R.style.default_text_flag_style);
其中会出现问题 java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: Can't convert to integer: type=0x1
要将 ta.getInteger 换成 ta.getResourceId ,前面的方法是将资源文件转了int,后面的是直接拿到资源文件。
如果自定义的属性不是获取资源文件的话,则需使用ta.getInteger 。
源码点我点我
以上就是自定义AddedFlowLayout的全部代码了,各位old铁觉得可以的话顺手点个赞或者关注咯?欢迎深入探讨哟~