计蒜客2019蓝桥杯省赛B组模拟赛(一)题目及解析
蓝桥杯历年真题题目及题解目录汇总
A. 结果填空:钟表 题库链接
分值: 5
一天蒜头君 22:28:45 开始睡觉,06:24:26 醒来之后,蒜头君在想,今天我睡了多久?
请你告诉蒜头君睡了"h:m:s",如果 h,m,sh,m,s 不足两位时,前面补 00。
例如:蒜头君睡了 1010 小时 11 分钟 00 秒,那么请输出"10:01:00"(不包含引号)。
慢慢算,这种送分题要小心,考日期的话,要注意是否闰年
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("07:55:41");
}
}
B. 结果填空:青蛙爬井 题库链接
分值: 7
有一口深度为 high 米的水井,井底有一只青蛙,它每天白天能够沿井壁向上爬 up 米,夜里则顺井壁向下滑 down 米。
若青蛙从某个早晨开始向外爬,当 high = 60405,up = 105,dow = 35,计算青蛙多少天能够爬出井口?
注意:不能简单地认为每天上升的高度等于白天向上爬的距离减去夜间下滑的距离,因为若白天能爬出井口,则不必等到晚上。
模拟吧,虽然这里直接high/up的结果也对,但小心会有偏差,慢慢来,不差这几分钟,送分题要拿下
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 青蛙爬井 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
int up = in.nextInt();
int down = in.nextInt();
int s=0;
int ans = 0;
while(true) {
ans++;
s+=up;
System.out.println("h:"+s);
if(s>=n)
break;
s-=down;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("863");
}
}
C. 结果填空:倍数 题库链接
分值: 13
一天蒜头君在想,[l,r][l,r] 之间有多少个数字是 dd 的倍数呢?
但是区间 [l,r][l,r] 是 dd 的倍数的数字太多,于是聪明的蒜头君便找到了你。
当 l = 1032,r = 12302135942453,d = 234,d 的倍数有多少个呢?
看见数那么大,long也放不下,知道想考大数类,但大数类的暴力求余也超时,根本跑不出结果,这时就要换个思路了,用除法,r除d-l除d,因为计算机算出来的是整数,所以这就是答案,不过准确来说是r/d-(l-1)/d
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("52573230519");
}
}import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 倍数 {
//1032 12302135942453 234
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
BigInteger n = BigInteger.valueOf(1032);
BigInteger d = BigInteger.valueOf(234);
BigInteger t = new BigInteger("12302135942453");
BigInteger ans = BigInteger.ZERO;
// while(n.compareTo(t)<=0) {
// if(n.mod(d).equals(BigInteger.ZERO)) {
// ans=ans.add(BigInteger.ONE);
//// System.out.println(n+" "+d+" "+ans+" "+n.mod(d));
// }
// n=n.add(BigInteger.ONE);
// }
System.out.println(t.divide(d));
System.out.println(n.divide(d));
}
}
D. 结果填空:马的管辖 题库链接
分值: 17
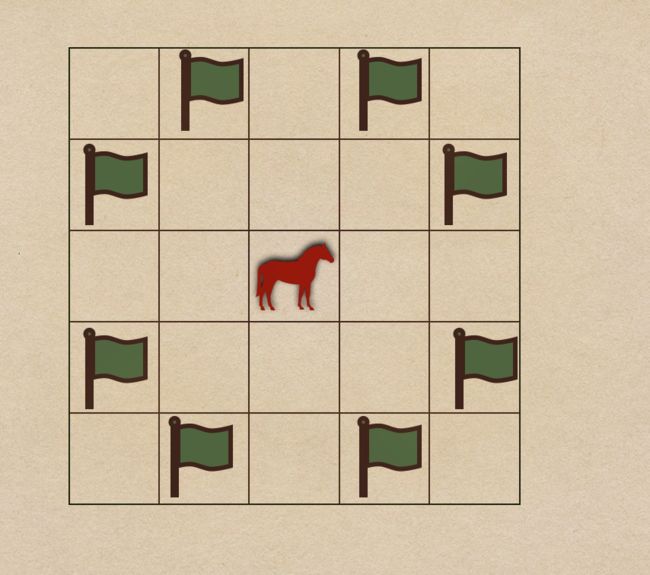
在中国象棋中,马是走日字的。一个马的管辖范围指的是当前位置以及一步之内能走到的位置,下图的绿色旗子表示马能走到的位置。
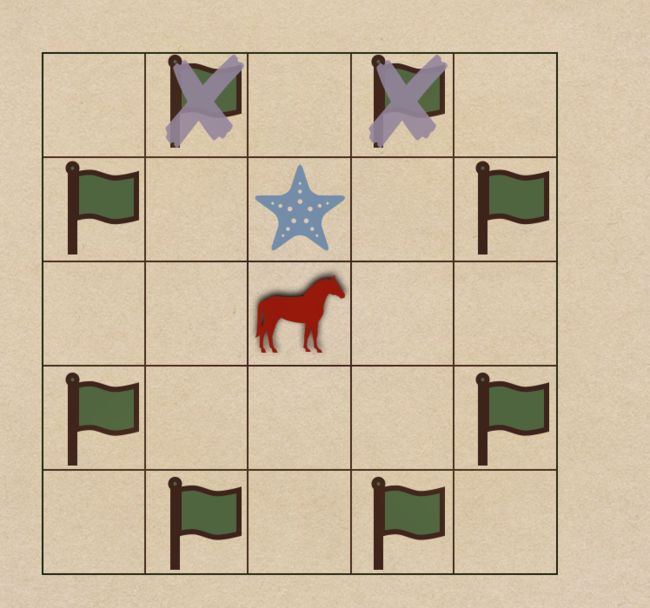
如果一匹马的某个方向被蹩马脚,它就不能往这个方向跳了,如下图所示,海星的位置存在旗子,马就不能往上跳到那两个位置了:
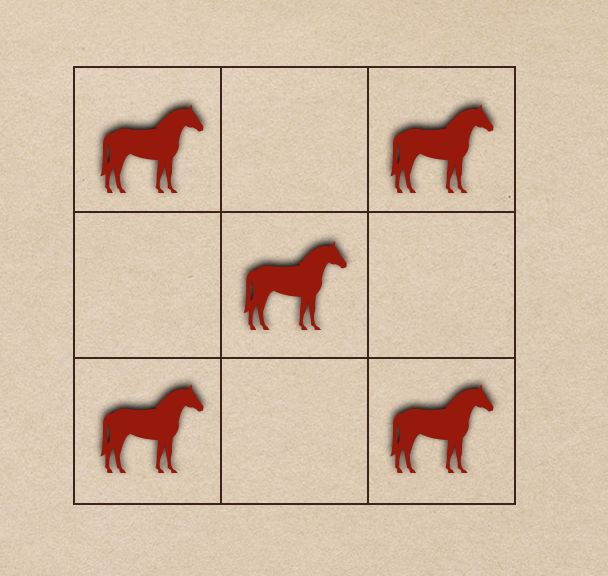
那么问题来了,在一个 n×m 的棋盘内,如何用最少的马管辖住所有 n×m 个格子。比如 n=m=3 时,最少要用 5 只马才能管辖所有棋盘,一种可能的方案如下:
当 n=m=5 时,请你求出用最少马管辖的 方案个数。
官方搜索代码,二进制枚举
运行结果:至少9匹马,90种方案,这个是暴搜,c++运行也挺久的,注意题目问的是方案个数
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int px[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int py[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int dx[4][2] = {-1, 1, -1, 1, 2, 2, -2, -2};
int dy[4][2] = {2, 2, -2, -2, -1, 1, -1, 1};
int vis[5][5], g[5][5];
int n = 5, m = 5;
bool in(int x, int y) { return x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m; }
int main() {
int r = n * m;
int minx = r + r, ans = 0;
for (int s = 0; s < 1 << r; s++) {
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
if (s >> i & 1) {
g[i / m][i % m] = 1;
cnt++;
} else {
g[i / m][i % m] = 0;
}
}
if (cnt > minx) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (g[i][j] == 0) continue;
vis[i][j] = 1;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + px[k], y = j + py[k];
if (in(x, y) && g[x][y] == 0) {
for (int u = 0; u < 2; u++) {
int tx = i + dx[k][u];
int ty = j + dy[k][u];
if (in(tx, ty)) {
vis[tx][ty] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (vis[i][j] == 0) {
ok = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if (ok) {
if (cnt < minx) {
minx = cnt;
ans = 1;
} else if (cnt == minx) {
ans++;
}
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", minx, ans);
return 0;
}
E. 代码填空:LIS 题库链接
分值: 9
参考:leetcode 300. 最长上升子序列(Longest Increasing Subsequence) 单调队列+dp
答案:int k = find(0, len, a[i]);
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static final int N = (int)1e5 + 9;
public static int n = 0;
public static int[] f = new int[N];
public static int[] a = new int[N];
public static int find(int l, int r, int x) {
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (f[mid] < x) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
return l;
}
public static int lis() {
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
/*在这里填写必要的代码*/
int k = find(0, len, a[i]);
f[k] = a[i];
if (k == len) {
len++;
}
}
return len;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
n = cin.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = cin.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(lis());
}
}F. 程序设计:找质数 题库链接
分值: 11
一天蒜头君猜想,是不是所有的偶数(除了 2),都可以用两个质数相加得到呢?于是聪明的蒜头君就找你来验证了。
输入格式
第一行输入一个整数 t 表示测试组数。
接下来 t 行,每行一个整数 n。
输出格式
输出两个整数,因为答案可能有多个,所有要求输出的这两个整数是所有答案中字典序最小的。
数据范围
对于 30% 的数据 1≤t≤10^3。
对于 60% 的数据 1≤t≤10^5。
对于 100% 的数据 1≤t≤10^6,4≤n≤10^6,n 为偶数。
样例输入复制
3
4
8
20样例输出复制
2 2
3 5
3 17
这代码超时,只有3分?用倍筛没错,3分的原因是因为2个for循环还可以优化 is[a] && is[x-a] 简单的数学关系优化,下面贴2份代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = in.nextInt();
boolean[] is = new boolean[1000000+5];
is[1] = true;
for(int i=2;i<=1000000;i++)
if(!is[i])
for(int j=2*i;j<=1000000;j+=i)
is[j] = true;
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=2;i<=1000000;i++)
if(!is[i])
list.add(i);
int n = list.size();
// System.out.println(n);
while(t-->0) {
int x = in.nextInt();
for(int i=0;ix)
break;
}
if(flag)
break;
}
}
}
} #include
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 100005;
bool p[1000005];
int main() {
int _;
scanf("%d", &_);
for (int i = 2; i <= 1000000; i++) {
p[i] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i * i <= 1000000; i++) {
if (p[i]) {
for (int j = i * i; j <= 1000000; j += i) {
p[j] = false;
}
}
}
while (_--) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 2;; i++) {
if (p[i] && p[n - i]) {
printf("%d %d\n", i, n - i);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
G. 程序设计:后缀字符串 题库链接
分值: 19
一天蒜头君得到 n 个字符串 si,每个字符串的长度都不超过 10。
蒜头君在想,在这 n 个字符串中,以 si 为后缀的字符串有多少个呢?
输入格式
第一行输入一个整数 n。
接下来 n 行,每行输入一个字符串 si。
输出格式
输出 n 个整数,第 ii 个整数表示以 si 为后缀的字符串的个数。
数据范围
对于 50% 的数据,1≤n≤10^3。
对于 100% 的数据,1≤n≤10^5。
所有的字符串仅由小写字母组成。
样例输入复制
3
ba
a
aba样例输出复制
2
3
1下面代码2个for O(n^2)复杂度,10^5的数据会超时,拿60%分
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
String[] s = new String[n];
for(int i=0;i官方解,放进map里面,把时间复杂度降低到了O(s.length*n),这里的字符串长度不超过10,是常数,所以最终的时间复杂度为O(n),所以解题的时候要注意数据范围!!!
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 100005;
string a[N];
int main() {
map mp;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].size(); j++) {
mp[a[i].substr(j)]++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << mp[a[i]] << endl;
}
return 0;
} H. 程序设计:轻重搭配 题库链接
分值: 21
hhha,来个反面教材,应该从n/2开始匹配,因为他们最多可以匹配n/2对,所以不要从n/2之前就配对了,这样浪费了,也不要最轻和最重匹配,这样也会造成浪费
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i=2*a[l]) {
l++;
r--;
ans++;
}
else {
l++;
ans++;
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
} c++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int a[500005];
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sort(a, a + n);
int ans = n, pos = n / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
while (pos < n && a[pos] < a[i] * 2) pos++;
if (pos == n) break;
ans--;
pos++;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
} java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i=2*a[l]) {
l++;
r++;
ans++;
} else
r++;
}
System.out.println(n-ans);
}
} I. 程序设计:抠图 题库链接
分值: 23
蒜头君在做图像处理的项目时,遇到了一个问题。他需要摘取出图片中,某个黑色线框内的图片,现在请你来帮助他完成这一步,把黑色线框外的区域全部变为黑色,即只保留黑色线框内的颜色。
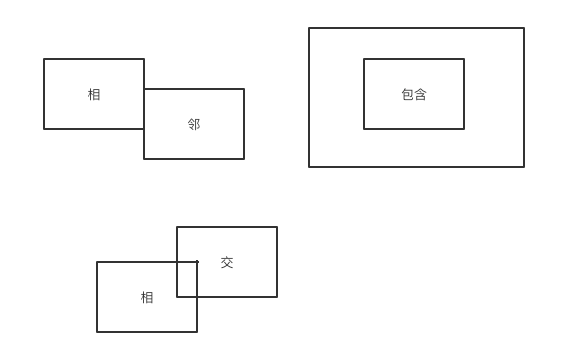
蒜头君可能同时摘取多个线框,这些线框不会出现相邻,相交,包含关系,因为选择线框太多,所以蒜头君可能把其中一部分的线框少画一条边,所以这种线框是无效的。
已知图中除了黑线上的点外,图像中没有纯黑色(即像素为 00 的点)。
矩形关系说明:
其中下面的数据也属于相邻。
也就是说 0 的周围(八个方向),不会有另外一个矩形的 0。
输入格式
第一行输入测试数据的组数 N(0 每组测试数据的第一行是两个整数 H,W 分别表示图片的高度和宽度 (3 \le H,W \le 500)(3≤H,W≤500)。 随后的 H 行,每行有 W 个正整数,表示该点的像素值。(像素值都在 0 到 255 之间,0 表示黑色,255 表示白色),每行整数之间使用 以矩阵形式输出,先把黑色框之外的区域变黑,然后输出图像中各点的像素值。 对于 30% 的数据,线框是宽度为 11 的矩形,并且线框都是完整的。 对于 60% 的数据,线框是宽度不固定的的矩形,并且线框都是完整的。 对于100% 的数据,线框可能有多个(题目保证线框不会出现相邻,相交,包含关系),线框是宽度不固定,有部分线框可能缺失其中的一条边(可以认为这种线框为无效线框)。 对于第一组数据: 这是一个完整的矩形,所以会保留线框内的颜色,保留下 (3,2),(3,3)(3,2),(3,3) 的像素值。 对于第二组数据: 只有一个矩形,这个矩形不是完成整的矩形,所有是无效线框,所以没有像素值被保留。 对于第三组数据: 有多个矩形,且矩形都满足不相邻,相交,包含的关系。 样例输入复制 样例输出复制 一模一样的java代码会超时呵呵,还有就是末尾空格会爆0 分值: 25 在蒜厂年会上有一个抽奖,在一个环形的桌子上,有 n 个纸团,每个纸团上写一个数字,表示你可以获得多少蒜币。但是这个游戏比较坑,里面竟然有负数,表示你要支付多少蒜币。因为这些数字都是可见的,所以大家都是不会出现的赔的情况。 游戏规则:每人只能抓一次,只能抓取一段连续的纸团,所有纸团上的数字和就是你可以获得的蒜币。 蒜头君作为蒜厂的一员在想,我怎么可以获得最多的蒜币呢?最多能获取多少蒜币呢? 因为年会是发奖,那么一定有大于 0 的纸团。 第一行输入一个整数 n,表示有 n 个纸团。 第二行输入输入 n 个整数 ai,表示每个纸团上面写的数字(这些纸团的输入顺序就是环形桌上纸团的摆放顺序)。 输出一个整数,表示蒜头君最多能获取多少蒜币。 10个样例过8个样例的代码,把它看成最大字段和,然后稍微优化一下,这里出现了环,我们通常的做法是,构造2*n的数组把环拆了 官方解,单调队列 '\t'隔开。输出格式
数据约定
样例解释
3
4 5
1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 1
1 0 1 0 1
1 0 0 0 1
5 6
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
10 10
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 00 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0#include J. 程序设计:蒜厂年会 题库链接
输入格式
输出格式
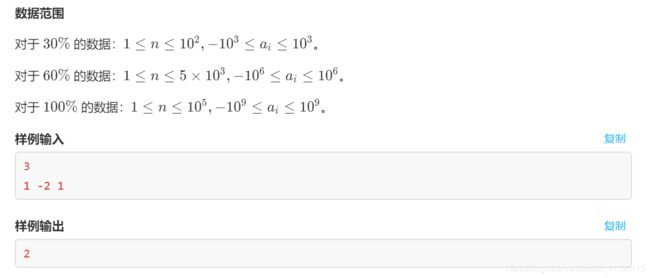
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[2*n+5];
for(int i=0;i#include