mybatis学习笔记——第二天
mybatis框架执行过程:
1.配置SqlMapConfig.xml文件(名称不固定)
2.通过配置文件,加载mybatis运行环境,创建SqlSessionFactory会话工厂,SqlSessionFactory在实际使用时按单例模式
3.通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession,SqlSession是一个面向用户的接口(提供操作数据库的方法),但线程不安全,建议在方法体内使用
4.调用SqlSession方法操作数据,如果需要提交事务,执行SqlSession的commit()方法
5.释放资源,关闭SqlSession
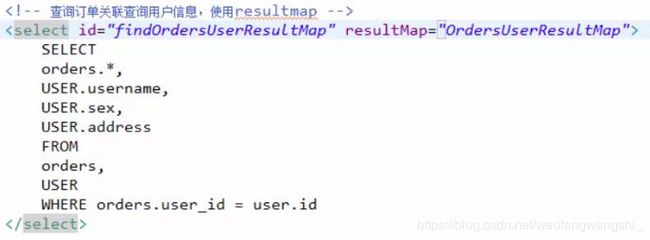
一、高级映射一对一查询,使用resultMap
查询订单关联查询用户信息
在订单类中定义一个user属性,把查询到订单关联的用户信息映射到这个user属性中
1.定义resultMap
2.编写statement
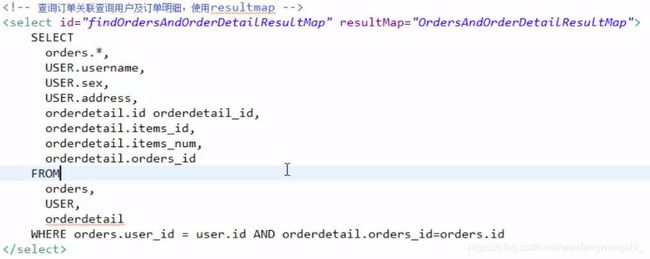
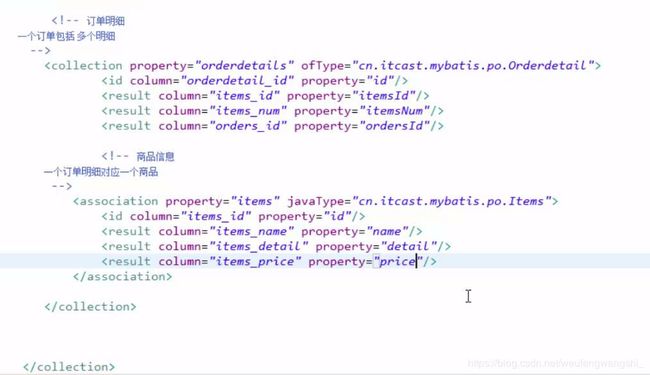
二、高级映射一对多查询
查询订单(关联用户)及订单明细
1.定义resultMap,在一对一的resultMap的基础上加上订单明细的映射信息,resultMap也可以使用继承extends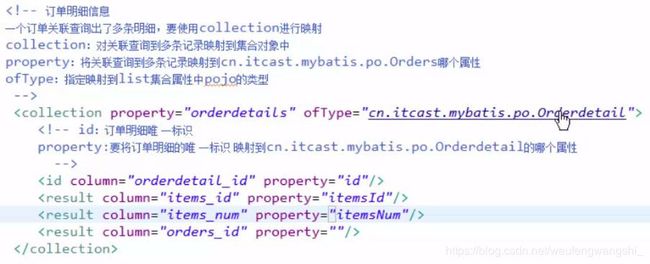
2.定义statement
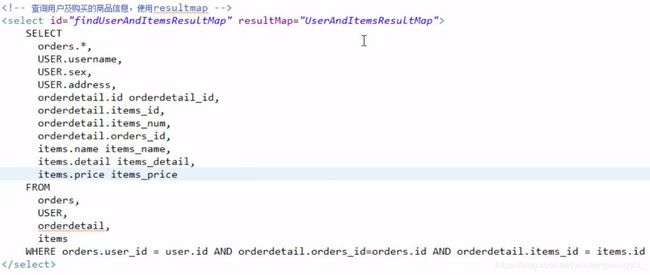
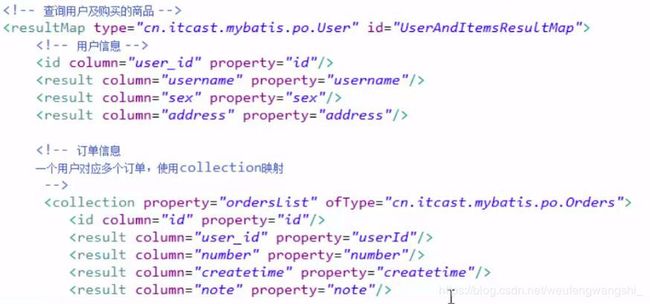
三、高级映射多对多查询
1.思路
2.定义statement
3.定义resultMap
四、延迟加载
resultMap可以实现高级映射,association、collection具有延迟加载功能
延迟加载:先从单表查询,需要时再去关联表进行关联查询
使用association实现延迟加载
1.定义resultMap
使用association中的select指定延迟加载去执行的statement的id
以上实例的全部mapper接口
本例使用最下面的接口
3.测试思路
4.延迟加载配置
mybatis默认没有开启延迟加载,要在sqlMapConfig.xml中的
五、缓存
1.一级缓存
一级缓存是sqlSession级别的缓存。在操作数据库时会构造sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个HashMap用于存储缓存数据
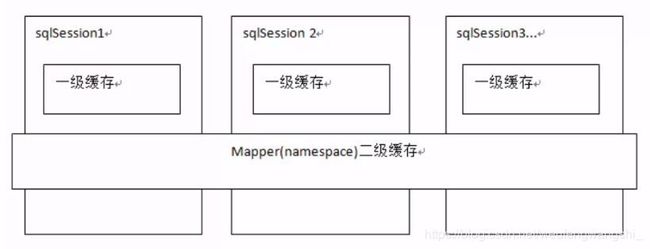
2.二级缓存
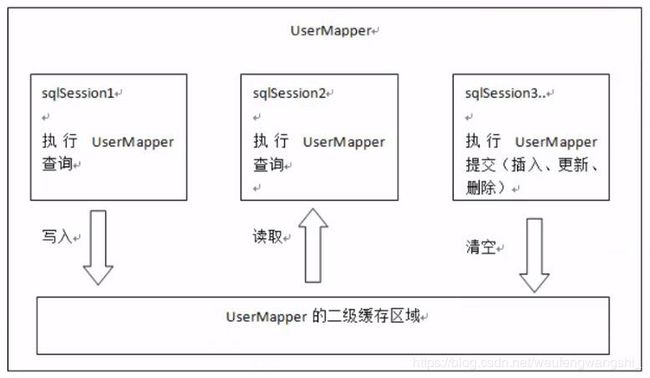
与一级缓存相比,二级缓存范围更大,多个sqlSession可以共享同一个Mapper下的二级缓存区域
UserMapper有一个二级缓存区域,其他的Mapper也有自己的二级缓存区域,按namespace分。如果两个mapper的namespace相同,那么这两个mapper执行sql查询到的数据将存在相同的二级缓存区域中
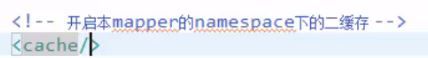
(1)使用前需要先开启二级缓存,先在sqlMapConfig.xml的
然后在具体的mapper.xml中开启二级缓存,标签中具体属性按需使用
(2)将实体类实现序列化接口
针对每次查询都需要最新数据的sql,可以在statement中设置useCache=false,禁用二级缓存
六、mybatis整合ehcache
1.导入jar包
2.配置mapper中cache的type值为ehcache对cache接口的实现类型
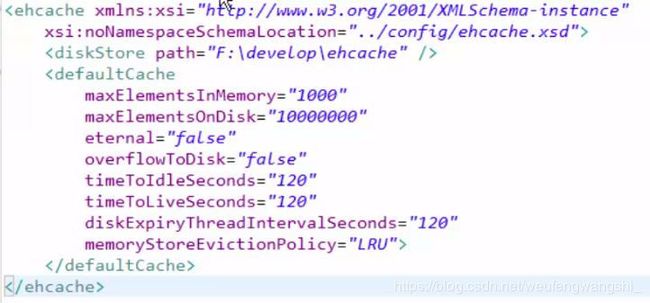
3.创建ehcache.xml配置文件
整合mybatis和其他缓存框架,主要是接口?
七、spring整合mybatis
1.导入jar包
spring的jar包
mybatis的jar包
spring和mybatis整合jar包
其中,c3p0用的0.9.5.2,mchange-commons-java用的0.2.11
2.
3.applicationContext.xml
3.sqlMapConfig.xml
4.userMapper.xml
5.userMapper.java接口
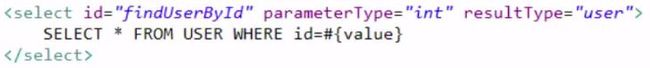
public interface UserMapper {
public User findUserById(int id);
}6.测试代码
public class UserMapperTest {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception{
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml");
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() {
UserMapper userMapper = (UserMapper) applicationContext.getBean("userMapper");
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}八、逆向工程
mybatis-generator-core
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39056805/article/details/80585941 这位大佬整理的非常好,需要时去看