在Android Studio中实现AIDL远程服务调用
最近在看《Android开发艺术探索》这本书,看到IPC这部分的时候,对照者书上所说,对有疑问的地方做了一些实验,因为IDE最近更新为了Android Studio,Android更新为了7.1,发现很多地方和以前不一样了,网上找到的参考代码很多还是老的,所以这里整理一下,记在下面。
结构
我要实现的是一个典型的C/S结构。客户端APP要实现一个加法的功能,通过AIDL调用远端服务APP,然后返回结果。交互过程如下:
实现DemoServer
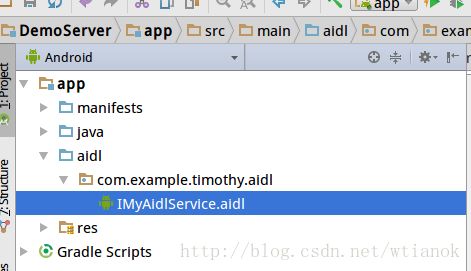
新建aidl
首先新建工程DemoServer,在app下新建文件夹aidl,在aidl文件夹下面新建包com.example.timothy.aidl,在这个包下新建aidl文件IMyAidlService.aidl。aidl文件的内容如下:
package com.example.timothy.aidl;
interface IMyAidlService {
int plus(int a, int b);
}实现服务
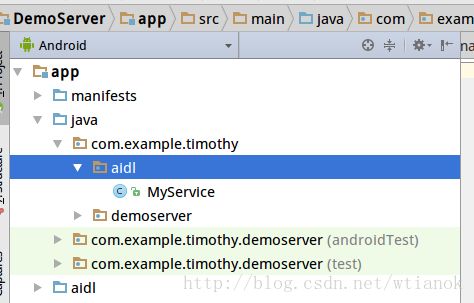
在java文件夹下新建一个包com.example.timothy.aidl,在包中新建MyService。
首先,在MyService中新建一个成员类MyBinder,实现IMyAidlService中定义的接口。
private class MyBinder extends IMyAidlService.Stub {
@Override
public int plus(int a, int b) throws RemoteException {
Log.d(TAG, "plus() is called, a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
return a + b;
}
}然后定义一个MyBinder类型的成员变量,并在onBind函数中返回:
private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}最后在AndroidManifest.xml中将MyService配置为远程服务即可。
<service
android:name="com.example.timothy.aidl.MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":remote">
service>实现DemoClient
客户端程序要调用服务端的接口,首先要有一个IMyAidlService的成员变量,然后再调用bindService函数进行绑定。bindService函数的参数有三个:Intent、ServiceConnection和Flag。FLAG没啥好说的,下面分别就另外三个组件进行说明。
IMyAidlService成员变量
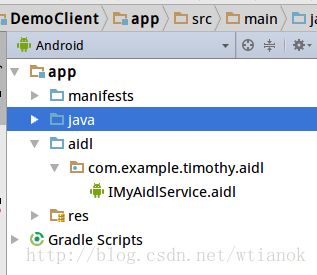
新建项目DemoClient。在app下新建aidl文件夹,在该文件夹下新建com.example.timothy.aidl包,把DemoServer中的IMyAidlService.aidl文件复制到这个包中。
在MainActivity中增加成员变量mService:
private IMyAidlService mService;ServiceConnection
在MainActivity中增加成员变量con,实现ServiceConnection的两个接口:
private ServiceConnection con = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mService = IMyAidlService.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mService = null;
}
};onServiceConnected这个方法将在bindService方法成功绑定之后被调用,在这个方法里,将IBinder类型的参数转化成IMyAidlService类型之后,赋值给上面的变量mService。
需要注意的时,onServiceDisconnected函数并不会在调用unbindService之后被调用。根据谷歌的解释,这个函数是在服务器端出现异常导致绑定断开的时候被调用的。
Intent
一般而言,调用bindService来绑定服务有两种方法:显示和隐式。显示需要应用服务的类型。在远程服务中,远程服务的类型是引用不到的,所以这里只能使用隐式调用。在Android4.x时代,隐式调用的方法如下:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent();
Intent.setAction("xxx.xxx.xxx");
bindService(bindIntent, con, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);然而,到了Android5.0时代,谷歌对绑定服务做了安全性要求,这种方法就不能用了。新的方法如下:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent();
bindIntent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.example.timothy.demoserver",
"com.example.timothy.aidl.MyService"));
bindService(bindIntent, con, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);ComponentName这个对象的构造函数有两个参数,第一个是包名,第二个是类名。注意了,这里就有个坑了。这个包名不是Service的包名,而是APP的包名。在这个例子里面,MyService的包名是com.example.timothy.aidl,APP的包名即MainActivity的包名是:com.example.timothy.demoserver,如果你用了前者,恭喜你,系统会告诉你:
Unable to start service Intent { cmp=com.example.timothy.aidl/.MyService } U=0: not found这个坑,我找了一个多小时才填上。
如果你非要用action来绑定服务,也是可以实现的。首先要在服务端配置service的intent-filter:
<service
android:name="com.example.timothy.aidl.MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":remote">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.timothy.aidl.myservice" />
intent-filter>
service>然后在客户端调用bindService,不过依然要指定APP的包名:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent();
bindIntent.setAction("com.example.timothy.aidl.myservice");
bindIntent.setPackage("com.example.timothy.demoserver");
bindService(bindIntent, con, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);现在,就能通过mService来调用服务端的plus方法了。