Linux设备驱动模型二 kobject
1 kobject
1.1 kobject数据结构
kobject是sysfs文件系统的基础数据结构,它定义在include/linux/kobjec.h中
struct kobject {
/*名称*/
const char *name;
/*与与所属的kset(list成员)组成链表*/
struct list_head entry;
/*父kobject;此成员未指定时,默认指向所属kset的kobject成员;在/sys文件系统中表示目录的上一层*/
struct kobject *parent;
/*指向所属的kset,可为NULL*/
struct kset *kset;
/*提供操作kobject属性特征(attribute)的接口*/
struct kobj_type *ktype;
/*sys文件信息*/
struct sysfs_dirent *sd;
/*kobject的引用计数*/
struct kref kref;
unsigned int state_initialized:1;
unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1;
unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int uevent_suppress:1;
}; kset的定义如下:
struct kset {
/*与子kobject的entry成员组成链表*/
struct list_head list;
/*自旋锁*/
spinlock_t list_lock;
/*kobject*/
struct kobject kobj;
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
}; kobj_type的定义如下:
struct kobj_type {
/*释放函数*/
void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj);
/*sys文件操作函数*/
const struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops;
/*文件属性*/
struct attribute **default_attrs;
const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *(*child_ns_type)(struct kobject *kobj);
const void *(*namespace)(struct kobject *kobj);
}; sysfs_direct被定义在fs/sysfs/sysfs.h,它的定义如下:
struct sysfs_dirent {
atomic_t s_count;
atomic_t s_active;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
struct lockdep_map dep_map;
#endif
/*上级目录*/
struct sysfs_dirent *s_parent;
struct sysfs_dirent *s_sibling;
/*名称*/
const char *s_name;
const void *s_ns; /* namespace tag */
union {
struct sysfs_elem_dir s_dir;
struct sysfs_elem_symlink s_symlink;
struct sysfs_elem_attr s_attr;
struct sysfs_elem_bin_attr s_bin_attr;
};
unsigned int s_flags;
unsigned short s_mode;
ino_t s_ino;
struct sysfs_inode_attrs *s_iattr;
}; 1.2 Kobject创建流程
我们看一下kobject的初始化过程。
初始化kobject有两种方式,分别是用kobject_init_and_add和kobject_create_and_add函数,他们的区别是:
1)kobject_init_and_add传入一个kobject指针和kobj_type指针,然后进行初始化
2)kobject_create_and_add创建一个kobject变量,并返回其指针,它不用传入kobj_type指针
1.2.1 kobject_init_and_add
下面看kobject_init_and_add函数的实现:
/**
* kobject_init_and_add - initialize a kobject structure and add it to the kobject hierarchy
* @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize
* @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject.
* @parent: pointer to the parent of this kobject.
* @fmt: the name of the kobject.
*
* This function combines the call to kobject_init() and
* kobject_add(). The same type of error handling after a call to
* kobject_add() and kobject lifetime rules are the same here.
*/
int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype,
struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list args;
int retval;
kobject_init(kobj, ktype);
va_start(args, fmt);
retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args);
va_end(args);
return retval;
} 它首先调用了kobject_init函数,再调用kobject_add_varg函数。先看kobject_init函数的实现:
/**
* kobject_init - initialize a kobject structure
* @kobj: pointer to the kobject to initialize
* @ktype: pointer to the ktype for this kobject.
*
* This function will properly initialize a kobject such that it can then
* be passed to the kobject_add() call.
*
* After this function is called, the kobject MUST be cleaned up by a call
* to kobject_put(), not by a call to kfree directly to ensure that all of
* the memory is cleaned up properly.
*/
void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype)
{
char *err_str;
if (!kobj) {
err_str = "invalid kobject pointer!";
goto error;
}
/*ktype不能为NULL*/
if (!ktype) {
err_str = "must have a ktype to be initialized properly!\n";
goto error;
}
if (kobj->state_initialized) {
/* do not error out as sometimes we can recover */
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): tried to init an initialized "
"object, something is seriously wrong.\n", kobj);
dump_stack();
}
/*调用kobject_init_internal函数*/
kobject_init_internal(kobj);
/*设置ktype*/
kobj->ktype = ktype;
return;
error:
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject (%p): %s\n", kobj, err_str);
dump_stack();
} 从上面的代码可以看到,它调用了kobject_init_internal函数,并设置了kobject所指向的ktype,ktype必须不能为NULL。
再看kobject_init_internal函数的实现:
static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (!kobj)
return;
/*初始化引用计数器为1*/
kref_init(&kobj->kref);
/*初始化entry链表结点,用于与所属的kset的list成员组成链表*/
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry);
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0;
kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_initialized = 1;
} kobject_init_internal函数初始化引用计数器为1,并初始化entry链表结点。
- 我们再次回到kobject_init_and_add函数中,它接着调用了kobject_add_varg函数:
static int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent,
const char *fmt, va_list vargs)
{
int retval;
/*设置kobject的名称*/
retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs);
if (retval) {
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject: can not set name properly!\n");
return retval;
}
/*设置父kobject*/
kobj->parent = parent;
/*调用kobject_add_internal函数*/
return kobject_add_internal(kobj);
} kobject_add_varg函数主要做了以下3个工作:
1)动过kobject_set_name_vargs设置kobject的名称
2)设置kobject的parent成员,即所指向的父kobject,可以为NULL
3)调用kobject_add_internal函数
kobject_add_internal函数比较关键,接着看它的实现:
static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
int error = 0;
struct kobject *parent;
if (!kobj)
return -ENOENT;
if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) {
WARN(1, "kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty "
"name!\n", kobj);
return -EINVAL;
}
/*获取parent指向的kobject,这里调用了kobject_get,结束的时候必须用kobject_put*/
parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent);
/* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */
if (kobj->kset) {
/*如果parent没有设置,把parent指向所属ket的kobj成员*/
if (!parent)
parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj);
/*把kobject的entry成员添加到kset的list链表中*/
kobj_kset_join(kobj);
kobj->parent = parent;
}
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: parent: '%s', set: '%s'\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__,
parent ? kobject_name(parent) : "",
kobj->kset ? kobject_name(&kobj->kset->kobj) : "");
/*创建sys目录*/
error = create_dir(kobj);
if (error) {
kobj_kset_leave(kobj);
kobject_put(parent);
kobj->parent = NULL;
/* be noisy on error issues */
if (error == -EEXIST)
printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s with "
"-EEXIST, don't try to register things with "
"the same name in the same directory.\n",
__func__, kobject_name(kobj));
else
printk(KERN_ERR "%s failed for %s (%d)\n",
__func__, kobject_name(kobj), error);
dump_stack();
} else
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1;
return error;
} kobject_add_internal函数有几个关键点:
1)如果kobject的kset成员不为NULL,它会调用kobj_kset_join函数把kobject的entry成员添加到kset的list链表中
2)如果kobject的parent成员为NULL,则把它指向kset的kobject成员。
3)最后调用create_dir函数创建sys目录,关于create_dir,在上一章中有描述。
接着看kobj_kset_join函数的实现:
/* add the kobject to its kset's list */
static void kobj_kset_join(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (!kobj->kset)
return;
kset_get(kobj->kset);
spin_lock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
list_add_tail(&kobj->entry, &kobj->kset->list);
spin_unlock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
} 很清楚地看到,此段代码把kobject的entry成员添加到以kset的list成员为头结点的链表中。
1.2.2 创建流程图
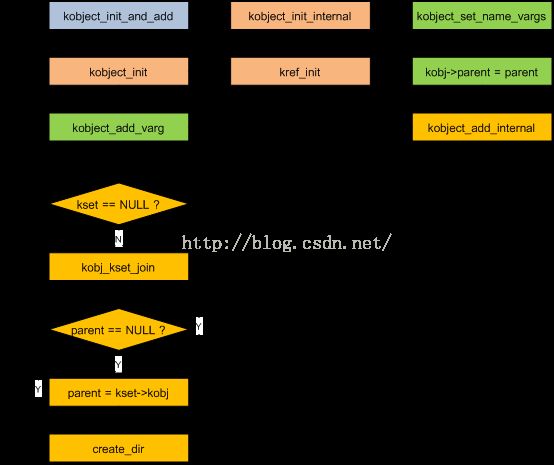
1.2.3 kobject_create_and_add
kobject_create_and_add的实现如下:
struct kobject *kobject_create_and_add(const char *name, struct kobject *parent)
{
struct kobject *kobj;
int retval;
kobj = kobject_create();
if (!kobj)
return NULL;
retval = kobject_add(kobj, parent, "%s", name);
if (retval) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "%s: kobject_add error: %d\n",
__func__, retval);
kobject_put(kobj);
kobj = NULL;
}
return kobj;
} 它调用了kobject_create和kobject_add函数。
Kobject_create的实现如下:
struct kobject *kobject_create(void)
{
struct kobject *kobj;
kobj = kzalloc(sizeof(*kobj), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!kobj)
return NULL;
kobject_init(kobj, &dynamic_kobj_ktype);
return kobj;可以看到,和之前的kobject_init_and_add函数一样,它也调用了kobject_init函数来初始化kobject,但此时传入的kobj_type指针是系统定义的kobj_type变量:
static struct kobj_type dynamic_kobj_ktype = {
.release = dynamic_kobj_release,
.sysfs_ops = &kobj_sysfs_ops,
}; 所以,我们应该明白:通过kobject_init_and_add初始化的kobject,其ktype成员是外部指定的,而通过kobject_create_and_add初始化的kobject,其ktype成员是系统定义的。
- 再看kobject_add的实现:
int kobject_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent,
const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list args;
int retval;
if (!kobj)
return -EINVAL;
if (!kobj->state_initialized) {
printk(KERN_ERR "kobject '%s' (%p): tried to add an "
"uninitialized object, something is seriously wrong.\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj);
dump_stack();
return -EINVAL;
}
va_start(args, fmt);
retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args);
va_end(args);
return retval;
} 可以看到,它调用了kobject_add_varg函数,此函数的实现在之前已描述过。
1.2.4 创建流程图
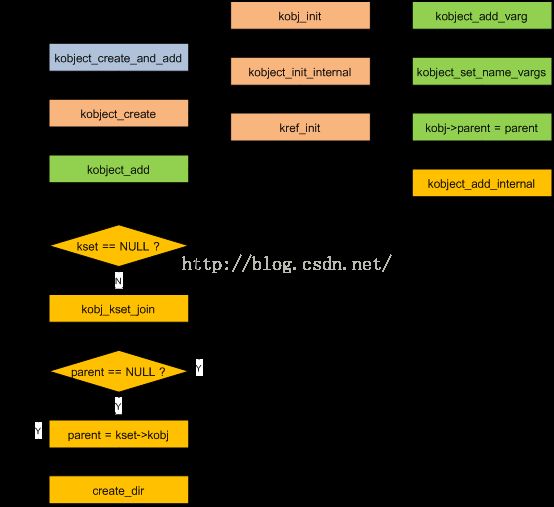
1.2.5 代码示例1
- 文件kobject_demo1.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*kobject变量*/
static struct kobject *mp_kobj;
/*
struct attribute {
const char *name;
mode_t mode;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
struct lock_class_key *key;
struct lock_class_key skey;
#endif
};
*/
/*struct attribute变量*/
static struct attribute m_attr = {
.name = "name",
.mode = S_IRWXUGO,
};
/*struct attribute数组*/
static struct attribute *m_attrs[] = {
&m_attr,
NULL,/*末尾必须为NULL*/
};
/**********************************************************/
//sysfs_ops
/*
struct sysfs_ops {
ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *,char *);
ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,const char *, size_t);
};
*/
/*sysfs_ops的show函数实现*/
static ssize_t kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
ssize_t count = 0;
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject_name(kobj) );
return count;
}
/*sysfs_ops的store函数实现*/
static ssize_t kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
/*struct sysfs_ops变量 */
static struct sysfs_ops m_sys_ops = {
.show = kobj_attr_show,
.store = kobj_attr_store,
};
/**********************************************************/
/*模块加载函数*/
static int __init kobj_init(void)
{
int error = 0;
/*struct kobject *kobject_create_and_add(const char *name, struct kobject *parent)
if use kobject_create_and_add, it will auto bind ktype to dynamic_kobj_ktype
so we can not set ktype member*/
mp_kobj = kobject_create_and_add("kobj_demo1_1", NULL);
if (!mp_kobj) {
goto out;
}
printk("%s success.\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
out:
printk("%s failed!\n", __FUNCTION__);
return error;
}
/*模块退出函数*/
static void __exit kobj_exit(void)
{
//删除kobject
kobject_del(mp_kobj);
//使引用计数减1并调用kobj_type的release函数
kobject_put(mp_kobj);
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
module_init(kobj_init);
module_exit(kobj_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("tonny");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("kobject demo");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- 文件Makefile
FILE=kobject_demo1
obj-m:=$(FILE).o
KERNELBUILD :=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
default:
make -C $(KERNELBUILD) M=$(shell pwd) modules
echo insmod/rmmod ./$(FILE).ko to load or uninstall
clean:
rm -rf *.o *.ko *.mod.c .*.cmd *.markers *.order *.symvers .tmp_versions - 编译及运行:
$ make #编译模块
$ sudo dmesg -c #清除内核日志
$ sudo insmod ./kobject_demo1.ko #加载内核模块
$ sudo dmesg #察看内核日志
[ 1954.839828] kobj_init success.
$ cd /sys/kobj_demo1/ #进入/sys目录
$ pwd
/sys/kobj_demo1
$ ls
name
$ cat name #察看kobject属性
kobj_demo1
$ sudo rmmod ./kobject_demo1.ko #卸载内核模块
$ sudo dmesg
[ 3609.041498] kobj_release
[ 3609.041501] kobj_exit - kobject_demo1.c的关键地方:
1)通过kobject_init_and_add函数初始化kobject,同时传入了ktype变量。
2)因为没有设置父kobject或kset,所以kobject_demo1出现在/sys顶层目录下
3)在删除kobject的时候,必须调用kobject_put函数,以便清除kobject所有相关的内存,kobject_put函数的实现如下:
/**
* kobject_put - decrement refcount for object.
* @kobj: object.
*
* Decrement the refcount, and if 0, call kobject_cleanup().
*/
void kobject_put(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (kobj) {
if (!kobj->state_initialized)
WARN(1, KERN_WARNING "kobject: '%s' (%p): is not "
"initialized, yet kobject_put() is being "
"called.\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj);
kref_put(&kobj->kref, kobject_release);
}
} 1.2.6 代码示例2
通过kobject_create_and_add函数创建kobject
- 文件kobject_demo1_1.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*kobject变量*/
static struct kobject *mp_kobj;
/*
struct attribute {
const char *name;
mode_t mode;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
struct lock_class_key *key;
struct lock_class_key skey;
#endif
};
*/
/*struct attribute变量*/
static struct attribute m_attr = {
.name = "name",
.mode = S_IRWXUGO,
};
/*struct attribute数组*/
static struct attribute *m_attrs[] = {
&m_attr,
NULL,/*末尾必须为NULL*/
};
/**********************************************************/
//sysfs_ops
/*
struct sysfs_ops {
ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *,char *);
ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,const char *, size_t);
};
*/
/*sysfs_ops的show函数实现*/
static ssize_t kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
ssize_t count = 0;
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject_name(kobj) );
return count;
}
/*sysfs_ops的store函数实现*/
static ssize_t kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
/*struct sysfs_ops变量 */
static struct sysfs_ops m_sys_ops = {
.show = kobj_attr_show,
.store = kobj_attr_store,
};
/**********************************************************/
/*模块加载函数*/
static int __init kobj_init(void)
{
int error = 0;
/*struct kobject *kobject_create_and_add(const char *name, struct kobject *parent)
if use kobject_create_and_add, it will auto bind ktype to dynamic_kobj_ktype
so we can not set ktype member*/
mp_kobj = kobject_create_and_add("kobj_demo1_1", NULL);
if (!mp_kobj) {
goto out;
}
printk("%s success.\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
out:
printk("%s failed!\n", __FUNCTION__);
return error;
}
/*模块退出函数*/
static void __exit kobj_exit(void)
{
//删除kobject
kobject_del(mp_kobj);
//使引用计数减1并调用kobj_type的release函数
kobject_put(mp_kobj);
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
module_init(kobj_init);
module_exit(kobj_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("tonny");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("kobject demo");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 与kobject_demo1.c不同的是,kobject_demo1_1.c并没有创建kobj_type变量
1.2.7 代码示例3
前面两个示例并没有指定父kobject即parent成员,下面指定其parent成员
- kobject_demo2.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define ATTR_NAME "name"
#define ATTR_VALUE "value"
struct my_object {
struct kobject kobj;
int value;
};
static struct my_object *m_obj1;
static struct my_object *m_obj2;
/**********************************************************/
//attrubute
static struct attribute m_attr_name = {
.name = ATTR_NAME,
.mode = S_IRWXUGO,
};
static struct attribute m_attr_value = {
.name = ATTR_VALUE,
.mode = S_IRWXUGO,
};
static struct attribute *m_attrs[] = {
&m_attr_name,
&m_attr_value,
NULL,
};
/**********************************************************/
//sysfs_ops
static ssize_t kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
ssize_t count = 0;
struct my_object *mobj;
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
if (!strcmp(attr->name, ATTR_NAME)) {
count = sprintf(buf, "%s\n", kobject_name(kobj) );
} else if (!strcmp(attr->name, ATTR_VALUE)) {
mobj = container_of(kobj, struct my_object, kobj);
count = sprintf(buf, "%d\n", mobj->value);
}
return count;
}
static ssize_t kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
struct my_object *mobj;
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
if (!strcmp(attr->name, ATTR_VALUE)) {
mobj = container_of(kobj, struct my_object, kobj);
sscanf(buf, "%d", &mobj->value);
}
return count;
}
static struct sysfs_ops m_sys_ops = {
.show = kobj_attr_show,
.store = kobj_attr_store,
};
/**********************************************************/
//kobj_type
void kobj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
struct my_object *mobj = container_of(kobj, struct my_object, kobj);
if (mobj) {
//释放my_object内存
kfree(mobj);
}
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
static struct kobj_type m_ktype = {
.release = kobj_release,
.sysfs_ops = &m_sys_ops,
.default_attrs = m_attrs,
};
/**********************************************************/
static int __init kobj_init(void)
{
int error = 0;
//申请m_obj1内存
m_obj1 = (struct my_object *)kzalloc(sizeof(struct my_object), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!m_obj1) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
//申请m_obj2内存
m_obj2 = (struct my_object *)kzalloc(sizeof(struct my_object), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!m_obj2) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto out1;
}
//初始化m_obj1的kobject
error = kobject_init_and_add(&m_obj1->kobj, &m_ktype, NULL, "kobj_demo1");
if (error) {
goto out2;
}
////初始化m_obj2的kobject,并指定其parent为m_obj1->kobj
error = kobject_init_and_add(&m_obj2->kobj, &m_ktype, &m_obj1->kobj, "kobj_demo2");
if (error) {
goto out2;
}
//初始化value值
m_obj1->value = 1;
m_obj2->value = 2;
printk("%s success.\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
out2:
kfree(m_obj2);
out1:
kfree(m_obj1);
out:
printk("%s failed!\n", __FUNCTION__);
return error;
}
static void __exit kobj_exit(void)
{
//删除kobject
kobject_del(&m_obj2->kobj);
//使引用计数减1并调用kobj_type的release函数
kobject_put(&m_obj2->kobj);
kobject_del(&m_obj1->kobj);
kobject_put(&m_obj1->kobj);
printk("%s\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
module_init(kobj_init);
module_exit(kobj_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("tonny");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("kobject demo");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");