搜索回溯问题_滑动窗口
前言
参考链接,有八皇后问题
- 搜索与回溯是计算机解题中常用的算法,很多问题无法根据某种确定的计算法则来求解,可以利用搜索与回溯的技术求解。回溯是搜索算法中的一种控制策略。它的基本思想是:为了求得问题的解,先选择某一种可能情况向前探索,在探索过程中,一旦发现原来的选择是错误的,就退回一步重新选择,继续向前探索,如此反复进行,直至得到解或证明无解。
- 如迷宫问题:进入迷宫后,先随意选择一个前进方向,一步步向前试探前进,如果碰到死胡同,说明前进方向已无路可走,这时,首先看其它方向是否还有路可走,如果有路可走,则沿该方向再向前试探;如果已无路可走,则返回一步,再看其它方向是否还有路可走;如果有路可走,则沿该方向再向前试探。按此原则不断搜索回溯再搜索,直到找到新的出路或从原路返回入口处无解为止
搜索框架
搜索伪代码/公式
基本上所有的搜索与回溯都是这个公式的变种
void Search(int k)
{
if(到达目的地)
输出;
for(int i = 1; i <= 算符种数;i++)//开始搜索
{
}
//别人写的
void Search(int k)
{
for (i=1;i<=算符种数;i++)//
if (满足条件)
{
保存结果
if (到目的地) 输出解;
else Search(k+1);
恢复:保存结果之前的状态{回溯一步}
}
}
八皇后问题
八皇后
注:八皇后没有标记问题,是因为每个节点只能被访问一次

题目
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
题解题解
int FindNextItem(int row, int column, int string_index)//从row, column搜string_index开始的字符
{
if(string_index == word.size() - 1)
{
if(board[row][column] == word[word.size() - 1])
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
if(board[row][column] == word[string_index])//满足条件才标记,否则返回0
{
map[row][column] = 1;//标记
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int new_row = row + direction[k][0];
int new_column = column + direction[k][1];
if(new_row >= 0 && new_row < board.size() && new_column >=0 && new_column < board[0].size())//在范围内寻找下一个
{
if(map[new_row][new_column])//不能已经访问
continue;
if(FindNextItem(new_row,new_column, string_index+1))
return true;
}
//map[new_row][new_column] = 0;
}
map[row][column] = 0;
}
return 0;
}
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<bool >> map;
vector<vector<int>> direction{{0,1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1,0}};
int rows, cols;
public:
bool hasPath(char* matrix, int rows, int cols, char* str)
{
//标志位,初始化为false
vector<bool> flag (strlen(matrix), 0);
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){
//循环遍历二维数组,找到起点等于str第一个元素的值,再递归判断四周是否有符合条件的----回溯法
if(judge(matrix,i,j,rows,cols,flag,str,0)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//judge(初始矩阵,索引行坐标i,索引纵坐标j,矩阵行数,矩阵列数,待判断的字符串,字符串索引初始为0即先判断字符串的第一位)
bool judge(char* matrix,int i,int j,int rows,int cols,vector<bool> &flag,char *str,int k){
//先根据i和j计算匹配的第一个元素转为一维数组的位置
int index = i*cols+j;
//递归终止条件
if(i<0 || j<0 || i>=rows || j>=cols || matrix[index] != str[k] || flag[index] == true)
return false;
//若k已经到达str末尾了,说明之前的都已经匹配成功了,直接返回true即可
if(k == strlen(str)-1)
return true;
//要走的第一个位置置为true,表示已经走过了
flag[index] = true;
//回溯,递归寻找,每次找到了就给k加一,找不到,还原
if(judge(matrix,i-1,j,rows,cols,flag,str,k+1) ||
judge(matrix,i+1,j,rows,cols,flag,str,k+1) ||
judge(matrix,i,j-1,rows,cols,flag,str,k+1) ||
judge(matrix,i,j+1,rows,cols,flag,str,k+1) )
{
return true;
}
//走到这,说明这一条路不通,还原,再试其他的路径
flag[index] = false;
return false;
}
};
二叉树路径总和题目
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
返回:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
思路:递归求解,当前层处理将当前值加入到temp的vector里面,如果左子树非空,左子树递归,如果右子树非空,右子树递归,如果节点为叶子节点,判断是否left_sum == node->val 从而加入结果中。
**注意本题用到回溯,**原因是如果不用回溯,则将不断拷贝vector,时间消耗很大,如果采用引用方式,则不用拷贝,但是当前值判断结束后要pop_back
void CalculateAddNode(vector<int> &path,TreeNode *node, int left_sum)
{
path.push_back(node->val);
if(node -> left != NULL)
{
CalculateAddNode(path, node->left, left_sum - node->val);
}
if(node -> right != NULL)
{
CalculateAddNode(path, node->right, left_sum - node->val);
}
if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
if(node->val == left_sum)
{
res.push_back(path);
}
}
path.pop_back();
}
求没有重复数字的全排列
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
题目
思路:搜索回溯。递归参数是已经有的列表,以及当前列表的长度。本层递归做的事情是探索没有被遍历的节点,并标记为已经遍历,然后进行下一层遍历,做完以后要回溯。
void dfs(vector<int> &nums, int index, vector<int> &cur)
{
if(index == nums.size())
{
res.push_back(cur);
return ;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if(!flags[i])
{
flags[i] = 1;
cur.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, index + 1, cur);
cur.pop_back();
flags[i] = 0;
}
}
}
括号组合
给出 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。
思路:递归参数是剩余的左括号数和剩余的右括号数,两个都为0加入,右括号大于左括号剪枝。
void dfs(int left, int right, string cur)
{
if(left == 0 && right == 0)
{
res.push_back(cur);
return ;
}
if(right < left)
return ;
if(left > 0)
dfs(left - 1, right, cur + "(");
if(right > 0)
dfs(left, right - 1, cur + ")");
}
孤岛数量,深搜,广搜
题目链接
class Solution {
private:
int row, col;
bool isValid(int i, int j)
{
if(i >= 0 && i < row && j >= 0 && j < col)
return 1;
return 0;
}
vector< vector<int>> direction={{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
if(grid.empty())
return 0;
row = grid.size();
col = grid[0].size();
int num = 0;
vector<vector<int>> map(row,vector<int>(col,0));
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if(!map[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1')
{
num++;
bfs(i,j,map,grid);
}
}
return num;
}
void dfs(int row_i, int col_j, vector<vector<int>> &map, vector<vector<char>> &grid)
{
map[row_i][col_j] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int new_row = row_i + direction[i][0], new_col = col_j + direction[i][1];
if(isValid(new_row,new_col) && !map[new_row][new_col] && grid[new_row][new_col] == '1')
dfs(new_row,new_col, map,grid);
}
}
void bfs(int row_i, int col_j, vector<vector<int>> &map, vector<vector<char>> &grid)
{
queue<pair<int ,int>> queue_bfs;
queue_bfs.push({row_i,col_j});
map[row_i][col_j] = 1;
while(!queue_bfs.empty())
{
int top_row = queue_bfs.front().first, top_col = queue_bfs.front().second;
queue_bfs.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int new_row = top_row + direction[i][0], new_col = top_col + direction[i][1];
if(isValid(new_row,new_col) && !map[new_row][new_col] && grid[new_row][new_col] == '1')
{
queue_bfs.push({new_row,new_col});
map[new_row][new_col] = 1;
}
}
}
}
};
滑动窗口
leetcode链接
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < s.size()) {`
// 增大窗口
window.add(s[right]);
right++;
while (window needs shrink) {
// 缩小窗口
window.remove(s[left]);
left++;
}
}
/* 滑动窗口算法框架 */
void slidingWindow(string s, string t) {
unordered_map<char, int> need, window;
for (char c : t) need[c]++;
int left = 0, right = 0;
int valid = 0;
while (right < s.size()) {
// c 是将移入窗口的字符
char c = s[right];
// 右移窗口
right++;
// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
...
/*** debug 输出的位置 ***/
printf("window: [%d, %d)\n", left, right);
/********************/
// 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩
while (window needs shrink) {
// d 是将移出窗口的字符
char d = s[left];
// 左移窗口
left++;
// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
...
}
}
这样的好处是如果right遍历到最后一个元素时,while可以不断优化.
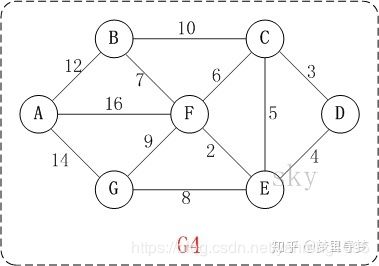
最短路径算法
迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
基本思想
- 通过Dijkstra计算图G中的最短路径时,需要指定起点s(即从顶点s开始计算)。
- 此外,引进两个集合S和U。S的作用是记录已求出最短路径的顶点(以及相应的最短路径长度),而U则是记录还未求出最短路径的顶点(以及该顶点到起点s的距离)。
- 初始时,S中只有起点s;U中是除s之外的顶点,并且U中顶点的路径是”起点s到该顶点的路径”。然后,从U中找出路径最短的顶点,并将其加入到S中;接着**,更新U中的顶点和顶点对应的路径(S不需要更新)**。 然后,再从U中找出路径最短的顶点,并将其加入到S中;接着,更新U中的顶点和顶点对应的路径。 … 重复该操作,直到遍历完所有顶点。