别以为真懂Openstack: 虚拟机创建的50个步骤和100个知识点(4)
六、Libvirt
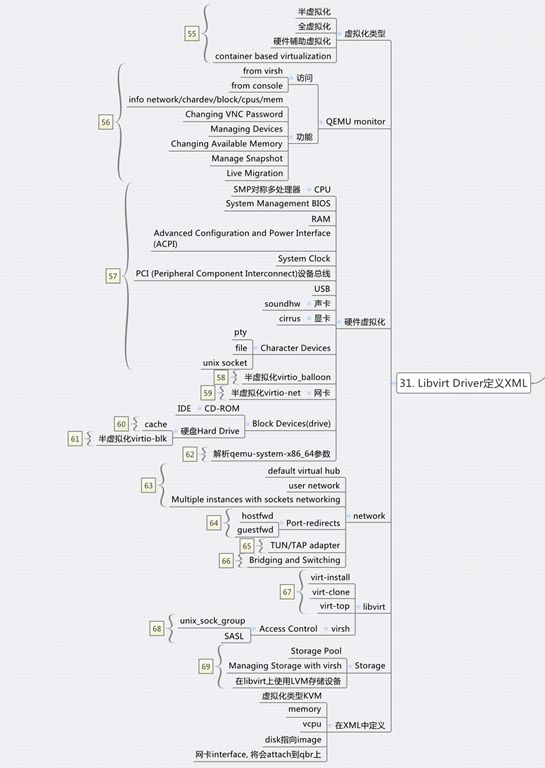
对于Libvirt,在启动虚拟机之前,首先需要define虚拟机,是一个XML格式的文件
列出所有的Instance
# virsh list
Id Name State
----------------------------------------------------
10 instance-00000006 running
# virsh dumpxml instance-00000006
我们发现里面定义了虚拟化类型kvm, vcpu, memory, disk, pty等,需要注意的是network,是一个tap device,attach到了qbr上。
虚拟化有很多种类型,参考下面的文章
虚拟化技术
[转]Virtualization Basics
当然虚拟机启动了之后,通过进程的查看,便能看到复杂无比的参数
# ps aux | grep instance-00000006
libvirt+ 22200 6.3 0.4 5464532 282888 ? Sl 09:51 0:09 qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -name instance-00000006 -S -machine pc-i440fx-trusty,accel=kvm,usb=off -cpu SandyBridge,+erms,+smep,+fsgsbase,+pdpe1gb,+rdrand,+f16c,+osxsave,+dca,+pcid,+pdcm,+xtpr,+tm2,+est,+smx,+vmx,+ds_cpl,+monitor,+dtes64,+pbe,+tm,+ht,+ss,+acpi,+ds,+vme -m 2048 -realtime mlock=off -smp 1,sockets=1,cores=1,threads=1 -uuid 73b896bb-7c7d-447e-ab6a-c4089532f003 -smbios type=1,manufacturer=OpenStack Foundation,product=OpenStack Nova,version=2014.1.1,serial=80590690-87d2-e311-b1b0-a0481cabdfb4,uuid=73b896bb-7c7d-447e-ab6a-c4089532f003 -no-user-config -nodefaults -chardev socket,id=charmonitor,path=/var/lib/libvirt/qemu/instance-00000006.monitor,server,nowait -mon chardev=charmonitor,id=monitor,mode=control -rtc base=utc,driftfix=slew -global kvm-pit.lost_tick_policy=discard -no-hpet -no-shutdown -boot strict=on -device piix3-usb-uhci,id=usb,bus=pci.0,addr=0x1.0x2 -drive file=/var/lib/nova/instances/73b896bb-7c7d-447e-ab6a-c4089532f003/disk,if=none,id=drive-virtio-disk0,format=qcow2,cache=none -device virtio-blk-pci,scsi=off,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4,drive=drive-virtio-disk0,id=virtio-disk0,bootindex=1 -netdev tap,fd=24,id=hostnet0,vhost=on,vhostfd=25 -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,id=net0,mac=fa:16:3e:ae:f4:17,bus=pci.0,addr=0x3 -chardev file,id=charserial0,path=/var/lib/nova/instances/73b896bb-7c7d-447e-ab6a-c4089532f003/console.log -device isa-serial,chardev=charserial0,id=serial0 -chardev pty,id=charserial1 -device isa-serial,chardev=charserial1,id=serial1 -device usb-tablet,id=input0 -vnc 0.0.0.0:0 -k en-us -device cirrus-vga,id=video0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x2 -device virtio-balloon-pci,id=balloon0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x5
然而谁能解释这些参数是干什么的?
请仔细阅读下面两篇文章
QEMU KVM libvirt 手册(3) - Storage Media
QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(7): 硬件虚拟化
QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(8): 半虚拟化设备virtio
machine参数是总线Architecture,通过qemu-system-x86_64 --machine ?查看,default就是参数中的值。
accel=kvm说明虚拟化使用的是kvm
cpu表示处理器的参数以及处理器的一些flags,可以使用命令qemu-system-x86_64 --cpu ?查看
smp是对称多处理器,
-smp 1,sockets=1,cores=1,threads=1
qemu仿真了一个具有1个vcpu,一个socket,一个core,一个threads的处理器。
socket, core, threads是什么概念呢
(1)socket就是主板上插cpu的槽的数目,也即管理员说的”路“
(2)core就是我们平时说的”核“,即双核,4核等
(3)thread就是每个core的硬件线程数,即超线程
具体例子,某个服务器是:2路4核超线程(一般默认为2个线程),那么,通过cat /proc/cpuinfo看到的是2*4*2=16个processor,很多人也习惯成为16核了!
SMBIOS全称System Management BIOS,用于表示x86 architectures的硬件信息,包含BIOS,主板的信息,这里都是openstack,是假的了
-chardev socket,id=charmonitor,path=/var/lib/libvirt/qemu/instance-00000006.monitor,server,nowait
-mon chardev=charmonitor,id=monitor,mode=control
这是一对,用unix socket方式暴露monitor,从而可以通过virsh操作monitor
rtc是指system clock, -no-hpet是指不用更精准的时间。
-device piix3-usb-uhci,id=usb,bus=pci.0,addr=0x1.0x2 是USB,连接到PCI总线0上,是device 0, function 1
下面两个是一对
-drive file=/var/lib/nova/instances/73b896bb-7c7d-447e-ab6a-c4089532f003/disk,if=none,id=drive-virtio-disk0,format=qcow2,cache=none
-device virtio-blk-pci,scsi=off,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4,drive=drive-virtio-disk0,id=virtio-disk0,bootindex=1
表示硬盘,drive指向文件,device使用virtio,连到pci的总线0上,是device 4, funtion 0
下面两个是一对
-netdev tap,fd=24,id=hostnet0,vhost=on,vhostfd=25
-device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,id=net0,mac=fa:16:3e:ae:f4:17,bus=pci.0,addr=0x3
表示网卡,用tap device,device使用virtio,连接到pci的总线0上,是device 3,function 0
下面两个是一对
-chardev file,id=charserial0,path=/var/lib/nova/instances/73b896bb-7c7d-447e-ab6a-c4089532f003/console.log
-device isa-serial,chardev=charserial0,id=serial0
是chardev,将log重定向到console.log
下面两个是一对,是pty
-chardev pty,id=charserial1
-device isa-serial,chardev=charserial1,id=serial1
这是显卡
-device cirrus-vga,id=video0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x2
这是内存
-device virtio-balloon-pci,id=balloon0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x5
都连接到pci总线上,通过命令virsh # qemu-monitor-command instance-00000024 --hmp "info pci"可以查看pci总线上的所有设备。
这里面有很多半虚拟化的设备,从而可以提高性能
[转] KVM VirtIO paravirtualized drivers: why they matter
Virtio: An I/O virtualization framework for Linux
QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(8): 半虚拟化设备virtio
[转]Virtio balloon
除了硬件的虚拟化和半虚拟化,对于网络,qemu和kvm本身也有自己的机制
QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(9): network
QEMU Networking
Virtual Networking
同时对于存储,也有自己的机制
QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(11): Managing Storage
这一节最后要说的,就是libvirt对虚拟机的管理
有一个强大的工具叫monitor,可以进行多种操作,相当于机器的管理界面,也可以通过virsh进行操作,参考文章QEMU KVM libvirt手册(2)
最重要的命令行工具就是virsh了,参考QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(10):Managing Virtual Machines with libvirt
七、Neutron
这一步,就是讲instance连接到已经创建好的网络设备上
步骤33:创建qbr网桥
步骤34:创建veth pair,qvo和qvb
步骤35:将qvb添加到qbr上
步骤36:将qvo添加到br-int上
看起来复杂而清晰的连接过程,为什么要这样,需要理解neutron中的网络设备架构
其实很早就有人画出来了,如下面的图
在network Node上:
在Compute Node上:
当看到这里,很多人脑袋就大了,openstack为什么要创建这么多的虚拟网卡,他们之间什么关系,这些dl_vlan, mod_vlan_vid都是什么东东啊?
请参考文章neutron的基本原理
neutron的不同的private network之间是隔离的,租户隔离技术三种常用的VLAN, GRE,VXLAN,各有优缺点
VLAN原理
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of networking devices in the same broadcast domain.
有两种VLAN
Static VLAN/Port-based VLAN
- manually assign a port on a switch to a VLAN using an Interface Subconfiguration mode command.
Dynamic VLANs
- the switch automatically assigns the port to a VLAN using information from the user device, such as its MAC address, IP address, or even directory information (a user or group name, for instance).
- The switch then consults a policy server, called a VLAN membership policy server (VMPS), which contains a mapping of device information to VLANs.
有两种connection
Access-Link Connections
- a device that has a standardized Ethernet NIC that understands only standardized Ethernet frames
- Access-link connections can only be associated with a single VLAN.
Trunk Connections
- trunk connections are capable of carrying traffic for multiple VLANs.
IEEE’s 802.1Q
优点
Increased performance
- reducing collisions
- limiting broadcast traffic
- Less need to be routed
Improved manageability
- Manage logical groups
Increased security options
- packets only to other members of the VLAN.
缺点
limited number of VLANs 4000 -> 1000
number of MAC addresses supported in switches
GRE的原理
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol that can encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over an Internet Protocol internetwork.
Header
优点
Resolve the VLAN and MAC limitations by encapsulating communications within p2p 'tunnels' which hid the guest MAC information exposing only the MAC addresses of host systems.
L2 to L3, after leaving the encapsulated L2 virtual network, the traffic is forwarded to a gateway which can de-encapsulate traffic and route it out onto the leveraged unencapsulated network.
缺点
Point to point tunnel
Pool extensibility
Few switches can understand GRE Header, so load distribution and ACL (both depends on IPs and ports) can not be applied
VXLAN原理
Allow for virtual machines to live in two disparate networks yet still operate as if they were attached to the same L2.
Components:
- Multicast support, IGMP and PIM
- VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI): 24-bit segment ID
- VXLAN Gateway
- VXLAN Tunnel End Point (VTEP)
- VXLAN Segment/VXLAN Overlay Network
- When VM1 wants to send a packet to VM2, it needs the MAC address of VM2 this is the process that is followed:
- VM1 sends a ARP packet requesting the MAC address associated with 192.168.0.101
- This ARP is encapsulated by VTEP1 into a multicast packet to the multicast group associated with VNI 864
- All VTEPs see the multicast packet and add the association of VTEP1 and VM1 to its VXLAN tables
- VTEP2 receives the multicast packet decapsulates it, and sends the original broadcast on portgroups associated with VNI 864
- VM2 sees the ARP packet and responds with its MAC address
- VTEP2 encapsulates the response as a unicast IP packet and sends it back to VTEP1 using IP routing
- VTEP1 decapsulates the packet and passes it on to VM1
- At this point VM1 knows the MAC address of VM2 and can send directed packets to it as shown in in Figure 2: VM to VM communication:
- VM1 sends the IP packet to VM2 from IP address 192.168.0.100 to 192.168.0.101
- VTEP1 takes the packet and encapsulates it by adding the following headers:
- VXLAN header with VNI=864
- Standard UDP header and sets the UDP checksum to 0×0000, and the destination port being the VXLAN IANA designated port. Cisco N1KV is currently using port ID 8472.
- Standard IP header with the Destination being VTEP2’s IP address and Protocol 0×011 for the UDP packet used for delivery
- Standard MAC header with the MAC address of the next hop. In this case it is the router Interface with MAC address 00:10:11:FE:D8:D2 which will use IP routing to send it to the destination
- VTEP2 receives the packet as it has it’s MAC address as the destination. The packet is decapsulated and found to be a VXLAN packet due to the UDP destination port. At this point the VTEP will look up the associated portgroups for VNI 864 found in the VXLAN header. It will then verify that the target, VM2 in this case, is allowed to receive frames for VNI 864 due to it’s portgroup membership and pass the packet on if the verification passes.
- VM2 receives the packet and deals with it like any other IP packet.
优点
Address 4K VLAN Limitation
Solves mac address scaling issues
Better scalability and failover
缺点
VXLAN expects multicast to be enabled on physical networks, and it does MAC flooding to learn end points.
But IP multicast is usually disabled
Need MAC preprovisioning via a SDN Controller
Software VTEPs may have performance issue
在Openstack中,neutron的很多网络功能都是由openvswitch实现的,因而本人专门研究了一下openvswitch,参考下面的文章
OpenFlow学习笔记
Openvswitch手册(1)
Openvswitch手册(2)
Openvswitch手册(3)
Openvswitch手册(4)
[转]Comparing sFlow and NetFlow in a vSwitch
[转]Rapidly detecting large flows, sFlow vs. NetFlow/IPFIX
Openvswitch手册(5)
Openvswitch手册(6)
Openvswitch手册(7)
Openvswitch手册(8)
Openvswitch手册(9)
Openvswtich 学习笔记
对于网络的管理,有很多好的工具可以使用
[转] iptables
HTB Linux queuing discipline manual - user guide笔记
iproute2学习笔记
tcpdump
[转]Linux操作系统tcpdump抓包分析详解
[转] IPTables for KVM Host
[转] Firewall and network filtering in libvirt
[转] XEN, KVM, Libvirt and IPTables
http://tldp.org/HOWTO/Traffic-Control-HOWTO/
http://rlworkman.net/howtos/iptables/iptables-tutorial.html