《机器学习实战》Python3实现代码(第三章节)
本文是针对《机器学习实战》(第三章)内所需要的程序代码进行修改(书中使用的是py2),现已py3呈现。
程序清单3-1:
from math import log
def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[1,1,'maybe'],
[1,1,'yes'],
[1,0,'no'],
[0,1,'no'],
[0,1,'no']
]
labels = ['no surfacing','flippers']
return dataSet,labels
def clacShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2)
return shannonEnt
if __name__== '__main__':
dataSet,label = createDataSet()
print(clacShannonEnt(dataSet))
运行结果:1.3709505944546687
程序清单3-2:
def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
#create a new list,ban from change the data of testData
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataSet:
#function:
#find the data in the dataSet and accord with the value which need to return
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet
运行结果:[[1, 'maybe'], [1, 'yes'], [0, 'no']]
程序清单3-3:
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1
baseEntropy = clacShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0
bestFeature = -1
for i in range (numFeatures):
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * clacShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
if(infoGain > bestFeature):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature
程序清单3-4:
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
if len(dataSet[0])==1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(label[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniquevVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniquevVals:
subLabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet,bestFeat,value),subLabels)
return myTree
def majorityCnt(classList):
#存储classList中每个标签出现的频率
classCount = {}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount [vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse = True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
运行结果:{'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: {'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}}
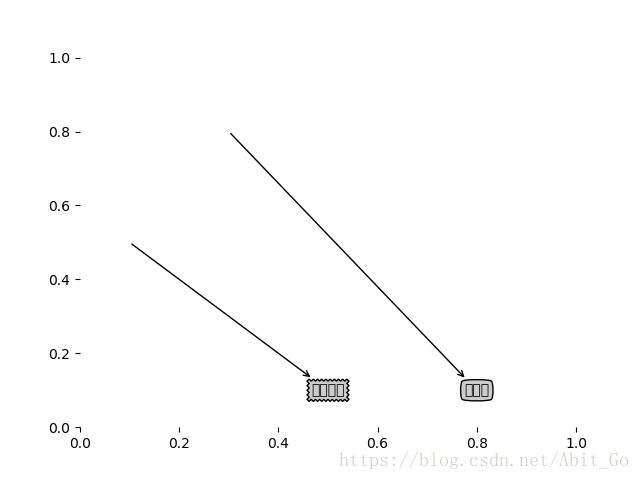
程序清单3-5:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#定义文本框呵箭头格式
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle='sawtooth',fc='0.8')
leafNode = dict(boxstyle='round4',fc='0.8')
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle='<-')
def plotNode(nodeTxt,centerPt,parentPt,nodeType):
#绘制箭头的注解
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt,xy=parentPt,xycoords='axes fraction',\
xytext=centerPt,textcoords='axes fraction',va='center',ha='center',\
bbox=nodeType,arrowprops=arrow_args)
def createPlot():
fig = plt.figure(1,facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111,frameon = False)
plotNode('决策节点',(0.5,0.1),(0.1,0.5),decisionNode)
plotNode('叶节点',(0.8,0.1),(0.3,0.8),leafNode)
plt.show()
createPlot()后面的代码不做描述,原因为不是核心机器学习代码。