Java数字处理类总结
文章目录
- 1. 数学运算
- 1.1 Math类
- 1.2 常用数学运算方法
- 1.2.1 三角函数方法
- 1.2.2 指数函数方法
- 1.2.3 取整函数方法
- 1.2.4 取最大值、最小值、绝对值函数方法
- 2. 随机数
- 2.1 Math.random()方法
- 2.2 Random类
- 3. 大数字运算
- 3.1 BigInteger
- 3.2 BigDecimal
- 4. 包装类
- 4.1 Integer
- 4.2 Boolean
- 4.3 Byte
- 4.4 Character
- 4.5 Double
1. 数学运算
1.1 Math类
在Math类中提供了众多数学函数方法,主要包括三角函数方法、指数函数方法、取整函数方法、取最大值、最小值以及平均值函数方法。这些方法都被定义为static形式。
可以使用如下形式调用:
Math.数学方法
在Math类中除了函数方法之外还存在一些常用数学常量,如PI、E等,可以用如下方式调用:
Math.PI
Math.E
1.2 常用数学运算方法
大致分为4大类别:三角函数方法、指数函数方法、取整函数方法以及取最大值、最小值和绝对值函数方法。
1.2.1 三角函数方法
在Math类中包含的三角函数方法如下:
public static double sin(double a):返回角的三角正弦
public static double cos(double a):返回角的三角余弦
public static double tan(double a):返回角的三角正切
public static double asin(double a):返回一个值的反正弦
public static double acos(double a):返回一个值的反余弦
public static double atan(double a):返回一个值的反正切
public static double toRadians(double angdeg):将角度转换为弧度
public static double toDegrees(double angdeg):将弧度转换为角度
角度与弧度的转换通常是不精确的。
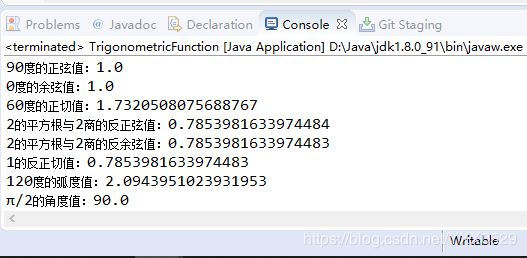
package Number;
//Math三角函数运算方法
public class TrigonometricFunction {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("90度的正弦值:"+Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println("0度的余弦值:"+Math.cos(0));
System.out.println("60度的正切值:"+Math.tan(Math.PI/3));
System.out.println("2的平方根与2商的反正弦值:"+Math.asin(Math.sqrt(2)/2));
System.out.println("2的平方根与2商的反余弦值:"+Math.acos(Math.sqrt(2)/2));
System.out.println("1的反正切值:"+Math.atan(1));
System.out.println("120度的弧度值:"+Math.toRadians(120.0));
System.out.println("π/2的角度值:"+Math.toDegrees(Math.PI/2));
}
}
1.2.2 指数函数方法
Math类中与指数相关的函数方法如下:
public static double exp(double a):用于获取e的a次方,即ea。
public static double log(double a):用于取自然对数,即lna。
public static double log10(double a):用于取底数为10的对数。
public static double sqrt(double a):用于取a的平方根,其中a的值不能为负值。
public static double cbrt(double a):用于取a的立方根。
public static double pow(double a,double b):用于取a的b次方,即ab。
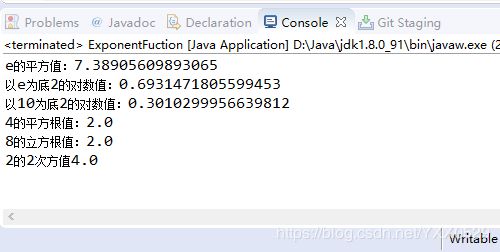
package Number;
//Math指数函数运算方法
public class ExponentFuction {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("e的平方值:"+Math.exp(2));
System.out.println("以e为底2的对数值:"+Math.log(2));
System.out.println("以10为底2的对数值:"+Math.log10(2));
System.out.println("4的平方根值:"+Math.sqrt(4));
System.out.println("8的立方根值:"+Math.cbrt(8));
System.out.println("2的2次方值"+Math.pow(2, 2));
}
}
1.2.3 取整函数方法
在Math类中主要包括以下几种取整方法。
public static double ceil(double a):返回大于等于参数的最小整数。
public static double floor(double a):返回小于等于参数的最大整数。
public static double rint(double a):返回与参数最接近的整数,如果两个同为整数且同样接近,则结果取偶数。
pubic static int round(float a):将参数加上0.5后返回与参数最近的整数。
public static long round(double a):将参数加上0.5后返回与参数最近的整数,然后强制转换为长整型。
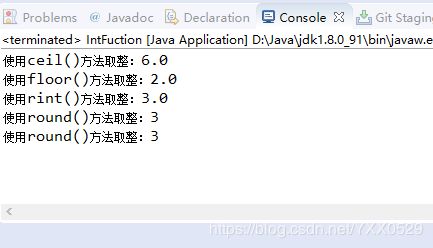
package Number;
//Math取整函数运算方法
public class IntFuction {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("使用ceil()方法取整:"+Math.ceil(5.2));
System.out.println("使用floor()方法取整:"+Math.floor(2.5));
System.out.println("使用rint()方法取整:"+Math.rint(2.7));
System.out.println("使用round()方法取整:"+Math.round(3.4f));
System.out.println("使用round()方法取整:"+Math.round(2.5));
}
}
1.2.4 取最大值、最小值、绝对值函数方法
public static double max(double a,double b):取a与b之间的最大值。
public static int min(int a,int b):取a与b之间的最小值。
public static int abs(int a):取参数的绝对值。
(int/long/float/double):整型、长整型、浮点型、双精度型。
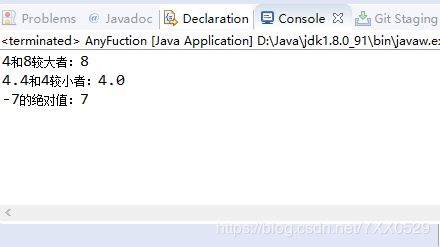
package Number;
//Math取整函数运算方法
public class AnyFuction {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("4和8较大者:"+Math.max(4, 8));
System.out.println("4.4和4较小者:"+Math.min(4.4, 4));
System.out.println("-7的绝对值:"+Math.abs(-7));
}
}
2. 随机数
Java中提供了两种产生随机数的方式,分别为调用Math类的random()方法生成随机数和调用Random类生成各种数据类型的随机数。
2.1 Math.random()方法
运行结果: 语法如下: 在Java中提供了大数字的操作类。BigInteger类是针对大整数的处理类,BigDecimal是针对大小数的处理类。 语法如下: 常用方法: 常用方法: 常用方法: 常用方法: 常用方法: 常用方法:Math.random():0<=(*)<1。
(int)(Math.Random()n):0<=(}m+(int)(Math.Random()n):m<=()package Number;
/**
* 定义偶数的方法
* @param num1 起始范围参数
* @param num2 终止范围参数
* @return 随机的范围内偶数
*/
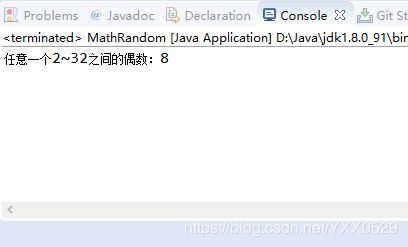
public class MathRandom {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//调用产生随机数方法
System.out.println("任意一个2~32之间的偶数:"+GetEvenNum(2, 32));
}
public static int GetEvenNum(double num1,double num2) {
//产生num1~num2之间的随机数
int s = (int)num1+(int)(Math.random()*(num2-num1));
if (s % 2 == 0) { //判断随机数是否为偶数
return s; //返回
}else {
return s+1;
}
}
}
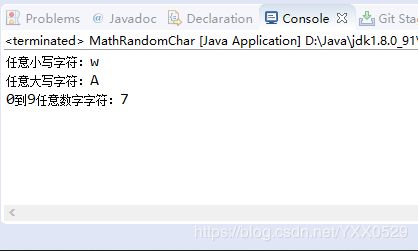
使用Math类的random()方法也可以随机生成字符。
(char)(cha1+Math.random()*(cha2-cha1+1);package Number;
//定义获取任意字符之间的随机字符
public class MathRandomChar {
public static char GetRandomChar(char cha1,char cha2) {
return (char)(cha1+Math.random()*(cha2-cha1+1));
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("任意小写字符:"+GetRandomChar('a', 'z'));
System.out.println("任意大写字符:"+GetRandomChar('A', 'Z'));
System.out.println("0到9任意数字字符:"+GetRandomChar('0', '9'));
}
}
2.2 Random类
Random r = new Random();
常用方法:
public int nexInt():返回一个随机整数。
public int nextInt(int n):返回大于等于0且小于n的随机整数。
public long nextLong():返回一个随机长整型值。
public boolean nextBoolean():返回一个随机布尔型值。
public float nextFloat():返回一个随机浮点型。
public double nextDouble():返回一个随机双精度型值。
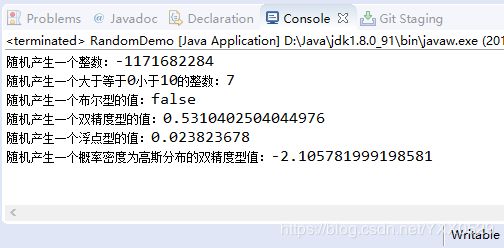
public double nextGaussian():返回一个概率密度为高斯分布的双精度值。package Number;
import java.util.Random;
//Random类生成随机数
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Random r = new Random(); //实例化一个Random类
System.out.println("随机产生一个整数:"+r.nextInt());
System.out.println("随机产生一个大于等于0小于10的整数:"+r.nextInt(10));
System.out.println("随机产生一个布尔型的值:"+r.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("随机产生一个双精度型的值:"+r.nextDouble());
System.out.println("随机产生一个浮点型的值:"+r.nextFloat());
System.out.println("随机产生一个概率密度为高斯分布的双精度型值:"+r.nextGaussian());
}
}
3. 大数字运算
3.1 BigInteger
public BigInteger(String val)
常用方法:
public BigInteger add(BigInteger val):加
public BigInteger subtract():减
public BigInteger multiply():乘
public BigInteger divide():除
public BigInteger remainder():取余
public BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder():商 余数
public BigInteger pow(int exponent):次方
public BigInteger negate():相反数
public BigInteger shiftLeft(int n):左移n位(n为整数)
public BigInteger shiftRight(int n):右移n位(n为整数)
public BigInteger and():与
public BigInteger or():或
public int compareTo():比较
public boolean equals():数值相等,返回true。
public BigInteger min():较小数
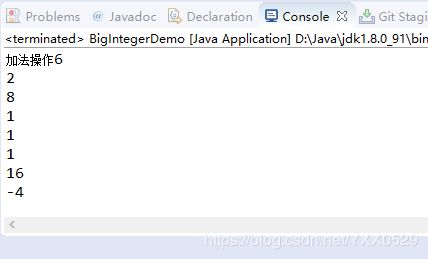
public BigInteger max():较大数package Number;
import java.math.BigInteger;
//BigInteger类处理数
public class BigIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
BigInteger bigInstance = new BigInteger("4");
System.out.println("加法操作"+bigInstance.add(new BigInteger("2"))); //将十进制2转换为BigInteger形式
System.out.println(bigInstance.subtract(new BigInteger("2")));
System.out.println(bigInstance.multiply(new BigInteger("2")));
System.out.println(bigInstance.divide(new BigInteger("3")));
//商
System.out.println(bigInstance.divideAndRemainder(new BigInteger("3"))[0]);
//余数
System.out.println(bigInstance.divideAndRemainder(new BigInteger("3"))[1]);
System.out.println(bigInstance.pow(2));
System.out.println(bigInstance.negate());
}
}
3.2 BigDecimal
public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend):加
public BigDecimal subtract():减
public BigDecimal multiply():乘
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor,int scale,int roundingMode):除,除数,商小数点后的位数,近似处理模式。package Number;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigDecimalDemo {
static final int location = 10;
/**
* 定义加法方法,参数为加数与被加数
*
* @param value1
* 相加的第一个数
* @param value2
* 相加的第二个数
* @return 两数之和
*/
public BigDecimal add(double value1,double value2) {
//实例化Decimal对象
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value2));
return b1.add(b2);
}
/**
* 定义减法方法,参数为减数与被减数
*
* @param value1 被减数
* @param value2 减数
* @return 运算结果
*/
public BigDecimal sub(double value1,double value2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value2));
return b1.subtract(b2);
}
/**
* 定义乘法方法,参数为乘数与被乘数
*
* @param value1 第一个乘数
* @param value2 第二个乘数
* @return
*/
public BigDecimal mul(double value1,double value2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value2));
return b1.multiply(b2);
}
/**
* 定义除法方法,参数为除数与被除数
* @param value1 被除数
* @param value2 除数
* @return
*/
public BigDecimal div(double value1,double value2) {
return div(value1, value2,location);
}
//定义除法方法,参数分别为除数与被除数以及商小数点后的位数
public BigDecimal div(double value1,double value2,int b) {
if (b < 0) {
System.out.println("b值必须大于等于0");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(value2));
//调用除法方法,商小数点后保留b位,并将结果进行四舍五入操作
return b1.divide(b2,b,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
}
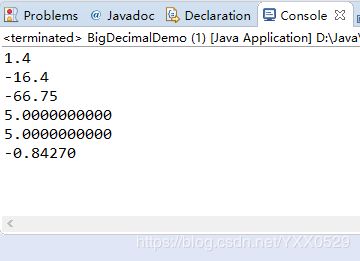
public static void main(String args[]) {
BigDecimalDemo b = new BigDecimalDemo();
//加法
System.out.println(b.add(-7.5, 8.9));
//减法
System.out.println(b.sub(-7.5, 8.9));
//乘法
System.out.println(b.mul(-7.5, 8.9));
//除法,小数点后保留10位
System.out.println(b.div(10, 2));
//除法,小数点后保留10位
System.out.println(b.div(10, 2, 10));
//除法,小数点后保留5位
System.out.println(b.div(-7.5, 8.9, 5));
}
}
4. 包装类
4.1 Integer
byteValue() [byte]
compareTo() [int]
equals() [boolean]
intValue() [int]
shortValue() [short]
toString() [String]
valueOf() [Integer]
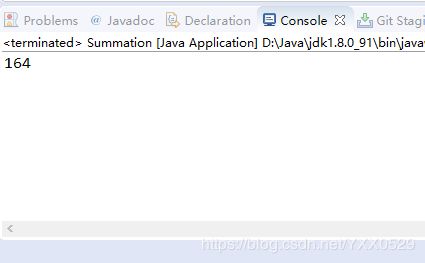
parseInt() [int]等价整数值package Number;
//数组元素相加
public class Summation {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str[]= {"89","12","10","18","35"};
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
int myint = Integer.parseInt(str[i]);
sum = sum + myint;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
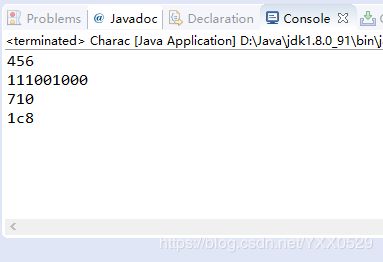
package Number;
//X进制之间的转换
public class Charac {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//十进制
String str1 = Integer.toString(456);
//二进制
String str2 = Integer.toBinaryString(456);
//八进制
String str3 = Integer.toOctalString(456);
//八进制
String str4 = Integer.toHexString(456);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str4);
}
}
4.2 Boolean
booleanValue() [boolean]
equals() [boolean]
parseBoolean [boolean]
toString() [String]
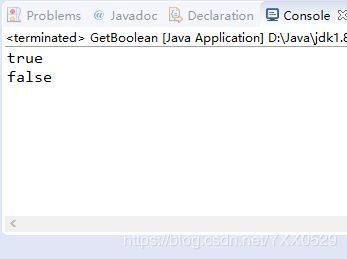
valueOf() [boolean]package Number;
//booleanValue()方法输出数据
public class GetBoolean {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Boolean boolean1 = new Boolean(true);
Boolean boolean2 = new Boolean("ok");
System.out.println(boolean1.booleanValue());
System.out.println(boolean2.booleanValue());
}
}
4.3 Byte
byteValue() [byte]
compareTo() [int]
doubleValue() [double]
intValue() [int]
parseByte() [byte]
toString() [String]
valueOf() [byte]
equals() [boolean]4.4 Character
charValue() [char]
compareTo() [int]
equals() [Boolean]
toUpperCase() [char]
toLowerCase() [char]
toString() [String]
isUpperCase() [boolean]
isLowerCase() [boolean]package Number;
//判断字符大小写状态
public class UpperOrLower {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Character myCharacter1 = new Character('A');
Character myCharacter2 = new Character('a');
System.out.println(myCharacter1+"是大写字母吗?"+Character.isUpperCase(myCharacter1));
System.out.println(myCharacter2+"是小写字母吗?"+Character.isLowerCase(myCharacter2));
}
}
4.5 Double
byteValue() [byte]
compareTo() [int]
equals() [boolean]
intValue() [int]
isNaN() [boolea]NaN:非数字,返回true,否则返回false。
toString() [String]
valueOf() [double]
doubleValue() [double]
longValue() [long]